Title Page for the series Famous Places in the Sixty-odd Provinces of Japan by Hiroshige
Hiroshige was born in Edo (now Tokyo) in 1797 and grew up in a minor samurai family. His father was part of the firefighting force assigned to Edo Castle. It was here that Hiroshige was given his first exposure to art. In 1811, young Hiroshige entered an apprenticeship with the celebrated Toyohiro Utagawa. After only a year, he was bestowed with the artist’s name Utagawa. He soon gave up in his role in the fire department to focus entirely on painting and print design. Hiroshige’s artistic genius went largely unnoticed until 1832. In Hiroshige Utagawa’s groundbreaking series of Japanese woodblock prints. The 53 Stations of the Tokaido which he produced between 1832 and 1833, he captured the journey along the Tokaido road, the highway connecting Edo to Kyoto, the imperial capital. With the Tokugawa Shogunate relaxing centuries of age-old restrictions on travel, urban populations embraced travel art and Hiroshige Utagawa became one of the most prominent and successful ukiyo-e artists.
Chikugo Province, The Currents Around the Weir by Hiroshige. Print from Hiroshige’s Famous Views of the Sixty-odd Provinces series.

Chikugo River
The Chikugo Province can be found in southern Japan in Fukuoka Prefecture. In this print by Hiroshige, the Chikugo River can be seen flowing through the foreground, as it separates Chikugo Province on the left from Chikuzen Province to the seen in the bottom right. The village of Haki appears within the trees of the far bank, as the mountains rise above the pink clouds of sunset. The river is a much-loved spot for fishing and the choice of fish is the Ayu. The Ayu often referred to as the is one of Japan’s best summer foods, known for its delicate flavour is found in Japan’s rivers. It is a small, slender fish that thrives in spotless and clear water. This characteristic has earned it the elegant nickname “the queen of clear rivers” in Japan.
Satsuma Province, Bo Bay, The Two-sword Rocks by Hiroshige Print from Hiroshige’s Famous Views of the Sixty-odd Provinces series
In the print entitled Satsuma Province, Bo Bay, The Two-sword Rocks we are treated to a remarkable view of the “Two-sword Rocks” in Bo Bay, which are two rock pillars extend skywards from the water, as viewed from Mount Use. Two boats are depicted in the print, one a ferry which transports a couple of passengers across the river passing close to the strange rock formations. Many other smaller rocks forming small islands can be seen in the distance as well as white-sail boats on the rosy coloured horizon. This was another example of Hiroshige using a vertical print.
Bitchu Province, Gokei by Hiroshige Print from Hiroshige’s Famous Views of the Sixty-odd Provinces series
The small waterfalls in the Makadani River
The Bitchū Province was a province of Japan situated on the Inland Sea side of western Honshū, in what is today western Okayama Prefecture. This is another of Hiroshige’s beautiful landscape prints which depicts the Gokei Valley with the Makidani River rushing through, crashing over many waterfalls on its relentless journey. Like the previous print we see the rock formations reaching vertically towards the sky. On the left of the river, we see tiny citizens walking along the riverbank. Hiroshige forgoes the fiery shades of fall but concentrates on emphasizing the monumentality of the landscape through the scale of the travellers and trees. The minute size of the pedestrians, who walk along the riverbank, gives us a sense of how big the valley sides are and how it emphasizes the enormous granite peaks along the valley.
Izumo Province, Taisha, Depiction of Hotohoto by Hiroshige Print from Hiroshige’s Famous Views of the Sixty-odd Provinces series

Izumo Taisha Shrine (Izumo Grand Shrine)
Beneath a canopy of cedar, three women pass through the grounds of the Izumo Grand Shrine. The great Shrine of Izumo Taisha is one of the most important ancient shrine in Japan. It was said to be the oldest, known to have existed at least the 7th Century, according to Japan’s oldest chronicles. The main building was built on 1744 and apparently has undergone 25 reconstructions. It was dedicated to the kami Okuninushi, the deity of earth and the harmony of nature, agriculture, and medicine. He was also believed to bring happiness and harmony to human relationships, that is why it magnetizes lots of young women who wish to be married. In the print we see that fog has reduced most of the scene to silhouette, the women carry trays laden with auspicious symbols of the New Year. Hotohoto is a New Year’s celebration local to the region. The festival takes its name from the onomatopoeia of knocking on a door. There are different traditions associated with this festival, including leaving rice cakes (mochi) on the doorstep for a god’s messenger to replace with a straw craft, or children going door-to-door to receive mochi and small gifts. Today, the former Izumo Province belongs to modern Shimane Prefecture.
Tanba Province, Kanegasaka by Hiroshige. Print from Hiroshige’s Famous Views of the Sixty-odd Provinces series
Tanba Province was one of the old provinces of Japan, located in San’indo. It covered the middle part of the present Kyoto prefecture, At the bottom of Hiroshige’s print we can see a narrow path which rises sharply along the mountainside before it disappears beyond the horizon. The area is located on a connecting road to northern Kyoto. As one can see, it is a difficult and dangerous upward climb which was ultimately thought too steep for travel.

Meiji-period tunnel
To solve the problem the Meiji-period tunnel built in its place still stands today. In the top right of the print one can see that Hiroshige has depicted the arch between two rock formations as a stone beam. It is thought that he came to know about this structure through travel guides (meishoki) or other paintings of Kanegasaka. Today, the former Tanba Province belongs to central Kyoto Prefecture and east-central Hyogo Prefecture.
Sado Province, The Goldmines by Hiroshige Print from Hiroshige’s Famous Views of the Sixty-odd Provinces series.
In Hiroshige’s print of the Sado goldmines we see a lush green forest which gives way to the rocky entrance to the mine. Miners dot the foreground as the mountainside opens into three mining shafts, each internally reinforced with wood. While the island had been known for its gold since the 12th century, the gold from Sado became an important source of wealth for the Tokugawa shogunate during the Edo period. Though the local economy prospered from the mines in the 17th century, by Hiroshige’s time the veins were running dry and the working conditions had significantly declined. The mines finally closed in 1989. Today, the former Sado Province corresponds to Sado Island in Niigata Prefecture

Doyu no Warito goldmine on Sado Island
Doyu no Warito is a relic of opencast mining from the Edo Period (1603-1867), which is said to be a pit in the early stages of the development of Sado’s gold and silver mines. As the digging went deeper and deeper to extract more gold ore, the mountaintop was split into a V-shape. The crack on the summit reaches approximately thirty metres in width and seventy-four metres in depth. The mountain with the crack holds a mother lode of gold, stretching about ten metres wide, called the Doyu Vein, and after the Meiji Period (1868-1912), large-scale development was carried out under the Warito. Today, the former mining area is a tourist attraction and has been nominated as a World Heritage Site.
I will conclude this blog with a quote from Charles Holmes’:
“…Hiroshige can be of service to us in another way. He is perhaps the artist through whom the great Japanese masters may best be approached by Europeans. The originality and force of his design, the brilliancy of his colour, his fairly successful realism, and more than all, his evident seriousness, his open sympathy with what has seemed admirable to our romantic tastes, render him attractive at once. His great predecessors are more reticent, more abstract, more remote from us. It is hardly surprising, then, that the painter who, in our own times, has assimilated most perfectly the spirit of Japan should have received this inspiration in the main from Hiroshige. To have a share with Velasquez in the making of Mr. Whistler’s style is no slight honour, and among the artists of modern Japan – the Japan of the last fifty years – there is no other who deserves it so well...”
Apart from various Wikipedia sites the information for this blog came from:
ISSUU – Hiroshige: Famous Places in the 60-odd Provinces -Ronin Gallery
The Woodblock Prints of Utagawa Hiroshige – Appreciation by Charles Holmes
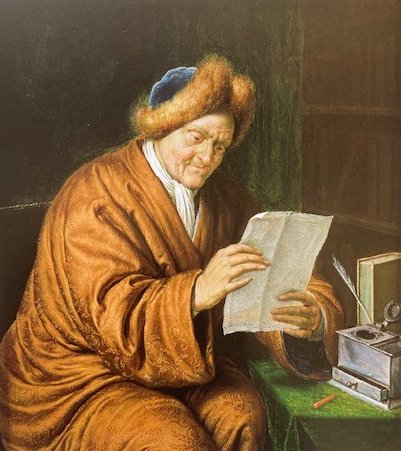
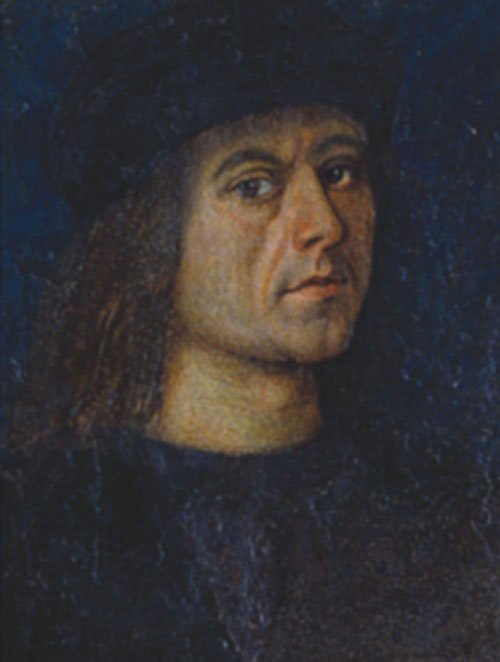
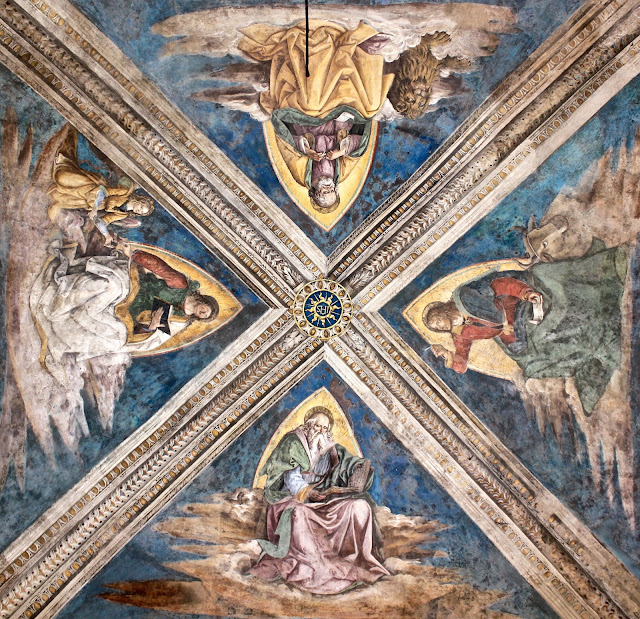
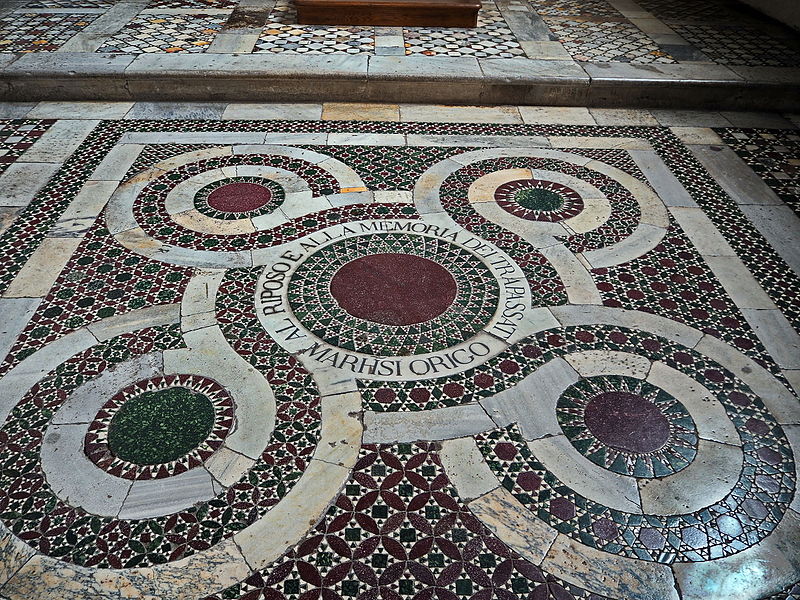




















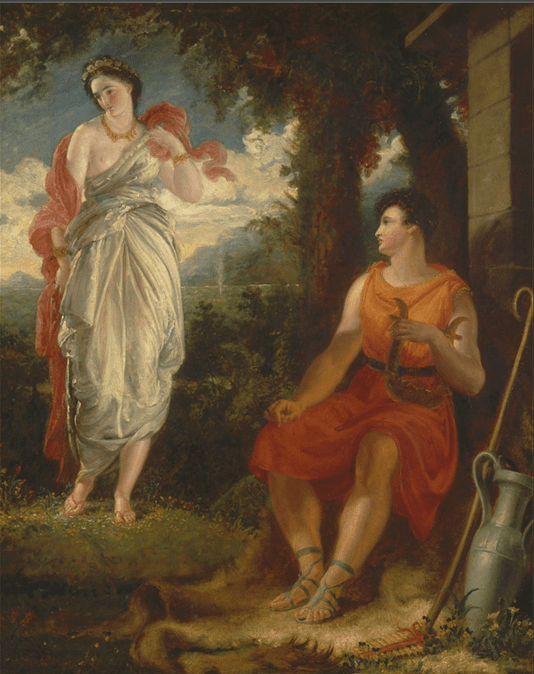
















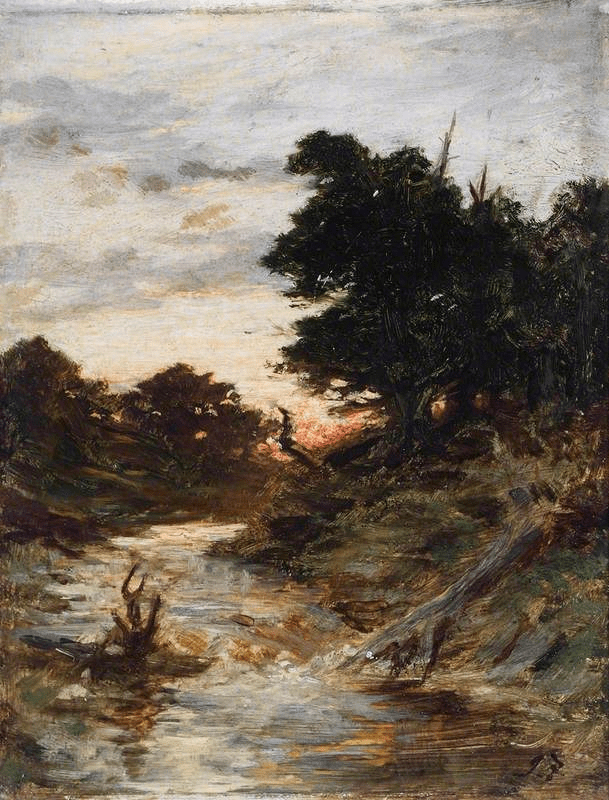
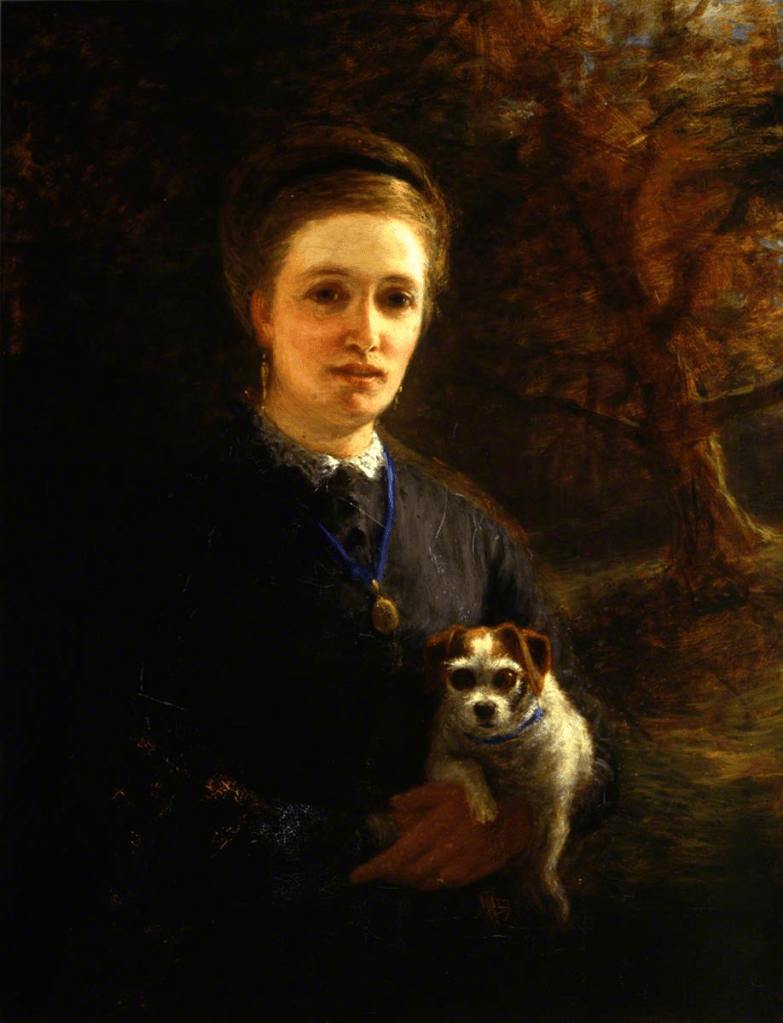
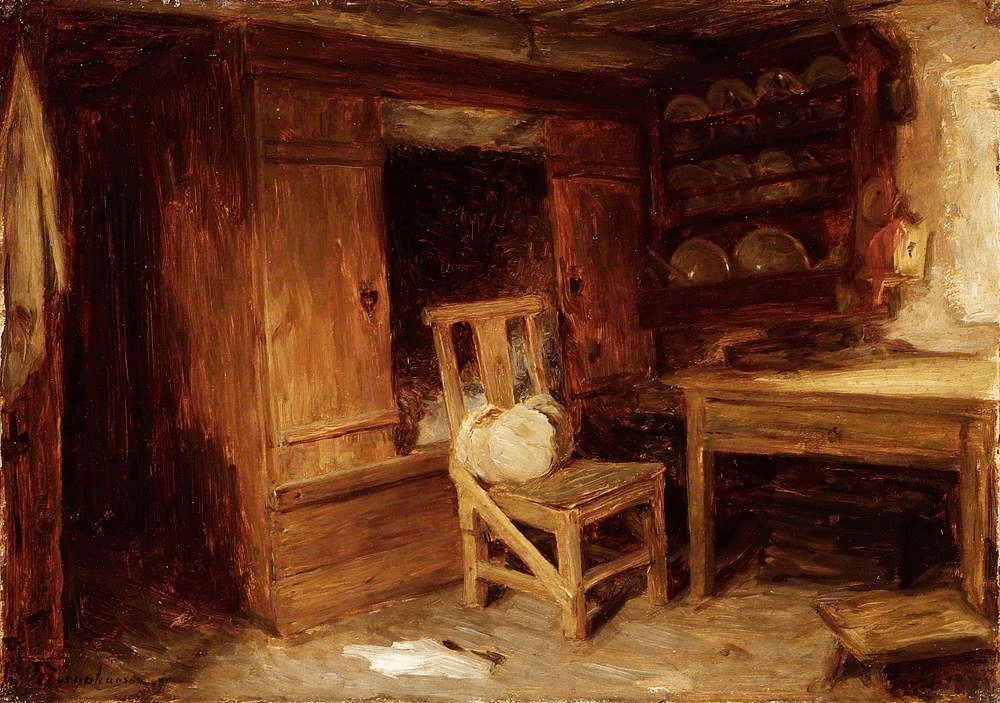




































































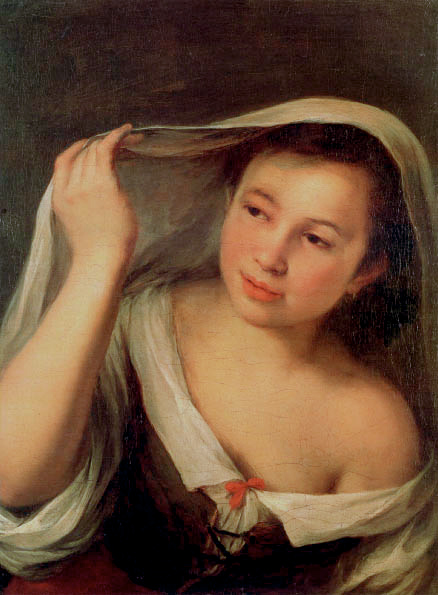
 The Seville exhibition was a collection of fifty-five paintings by Murillo from museum collections around the world. The exhibition was divided into nine sections each providing a glimpse of the world through Murillo’s eyes. The sections were designated as Holy Childhood, A family of Nazareth, Glory on Earth, The Immaculate Conception, Compassion, Penitence, Storyteller, Genre painting and Portraiture. It was a journey through his religious works to the social realism of 17th century Seville, which has been described as a city of paupers and saints, of rascals and wealthy noblemen and merchants who, through their wealth, were able to have Murillo paint their portraits.
The Seville exhibition was a collection of fifty-five paintings by Murillo from museum collections around the world. The exhibition was divided into nine sections each providing a glimpse of the world through Murillo’s eyes. The sections were designated as Holy Childhood, A family of Nazareth, Glory on Earth, The Immaculate Conception, Compassion, Penitence, Storyteller, Genre painting and Portraiture. It was a journey through his religious works to the social realism of 17th century Seville, which has been described as a city of paupers and saints, of rascals and wealthy noblemen and merchants who, through their wealth, were able to have Murillo paint their portraits.









