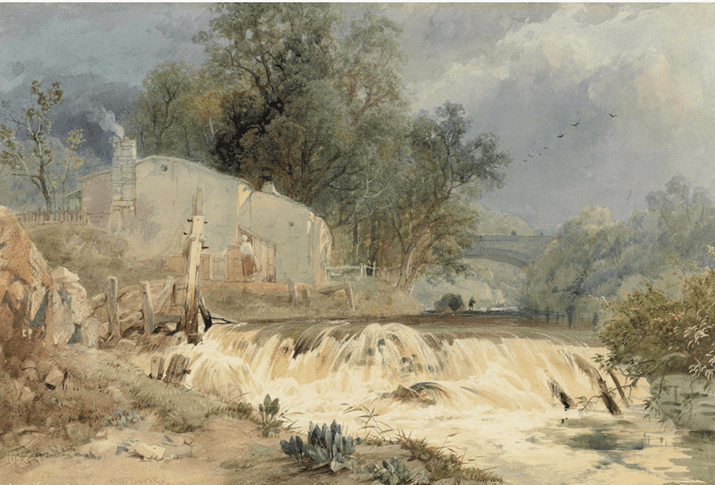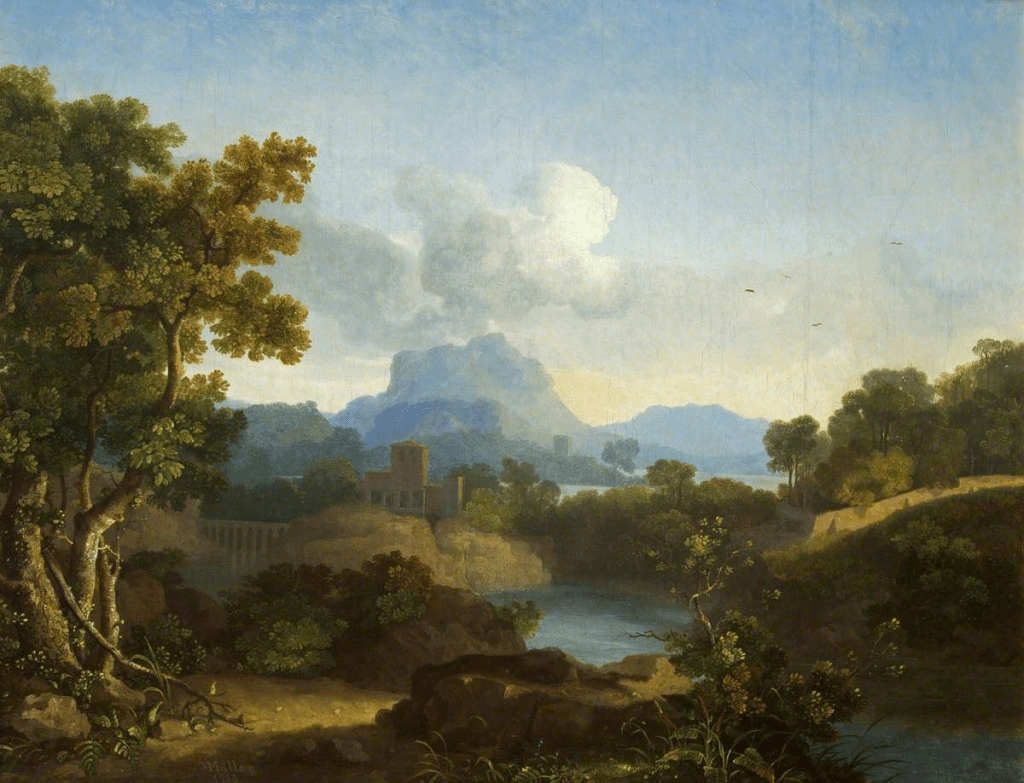The Later years

The Gaol Burning and St Paul’s Bedminster by William Muller (c.1831)
William Muller’s home in the city of Bristol was rocked by civil unrest in 1831. The Reform Riots, as they became known, took place between the 29th and 31st of October and were part of the 1831 riots in England. The riots came about because of the second Reform Bill which was voted down in the House of Lords, and consequently shelved efforts at electoral reform. The Bristol Riots were a reaction to the statement in Parliament of a senior judge, Sir Charles Wetherell, that the people of Bristol were not in favour of reform, despite 17,000 signatures on a petition supporting the reforms.
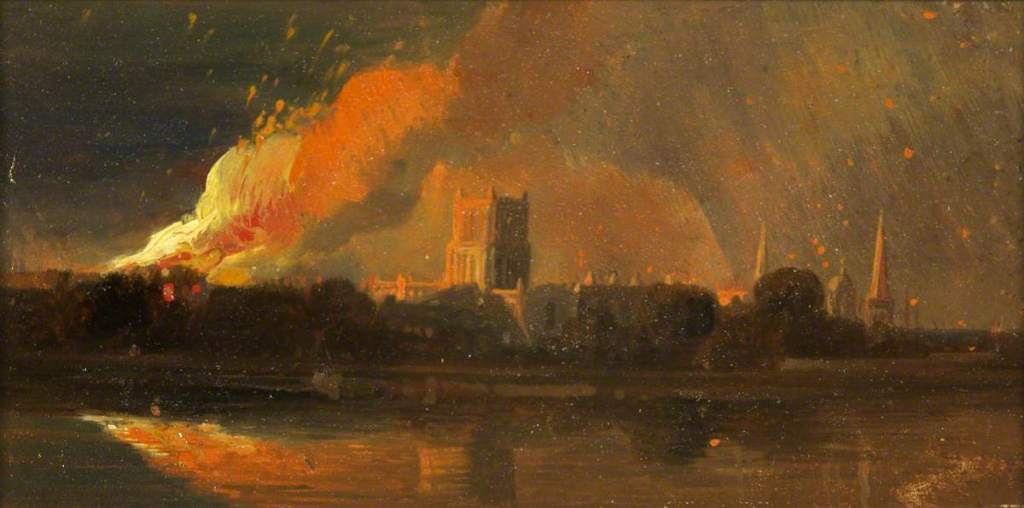
The Burning of the Bishop’s Palace by William Muller (c.1831)
It was at a time when only five per cent of the population, (and they had to be men!) had the right to vote which was based on their wealth. Wetherell came to Bristol on his annual visit to Bristol, public meetings were organised in Queen Square on 10th, 11th and 12th October to decide on how to carry the fight forward. Demonstrators met Wetherell on his arrival in Bristol on October 29th, and soon, full scale rioting broke out, with angry crowds of protesters taking control of the city for two days.
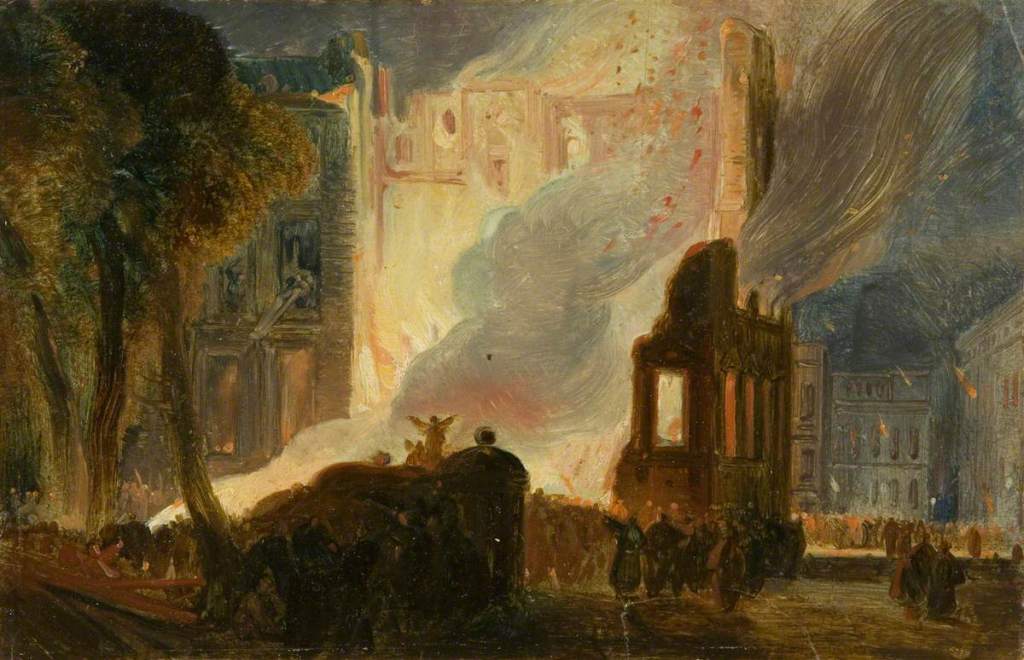

The Burning of the Mansion House, Queens Square by William Muller (1831)
Troops were brought in to end the riots and Wetherell escaped dressed as a woman while the crowds stayed, looting the wine cellar of the Mansion House and becoming drunk and reckless. Over the next two days rioters broke into Bridewell Jail and Lawford’s Gate Prison and set prisoners free. The Tollhouses, the Bishop’s Palace and, in Queen Square, the Mansion House and the Custom House, were all attacked.
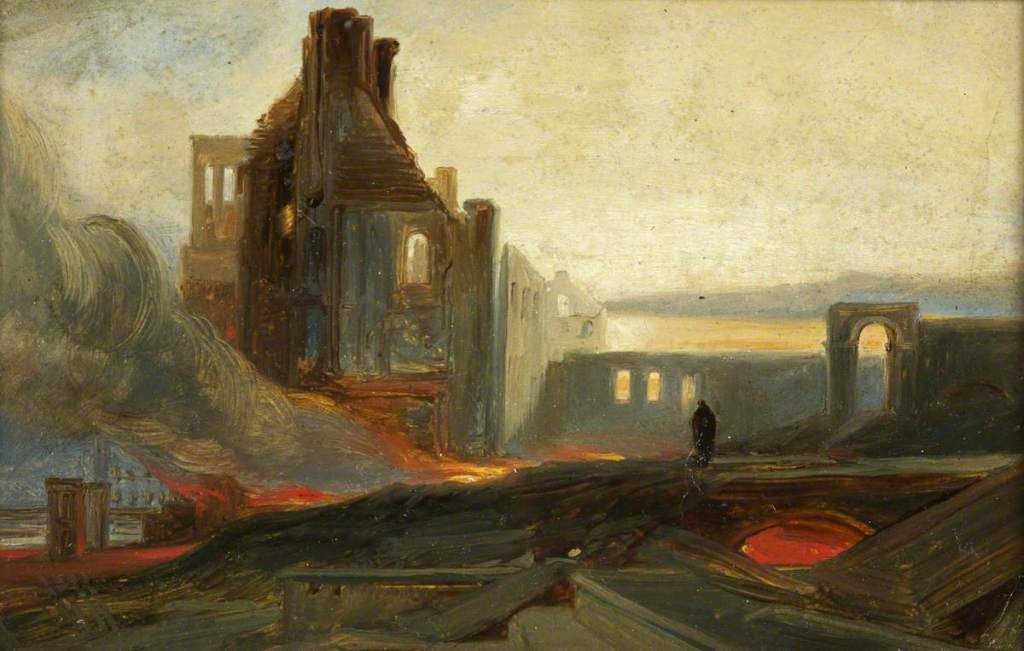

Ruins of Warehouses in Prince Street by William Muller (c.1831)
Nineteen-year-old William Muller and his younger brother, Edmund, witnessed the riots first hand. William made several sketches of the buildings in flames and the ruins of what remained. Later he turned the sketches into a number of paintings such as Rioting in Queen’s Square, The Remains of the Mansion House, Ruins of the Custom House, with only the bare and broken columns standing. He also completed a work entitled Removing the Prisoners at night to the Gaol, with the glare of burning buildings all around.
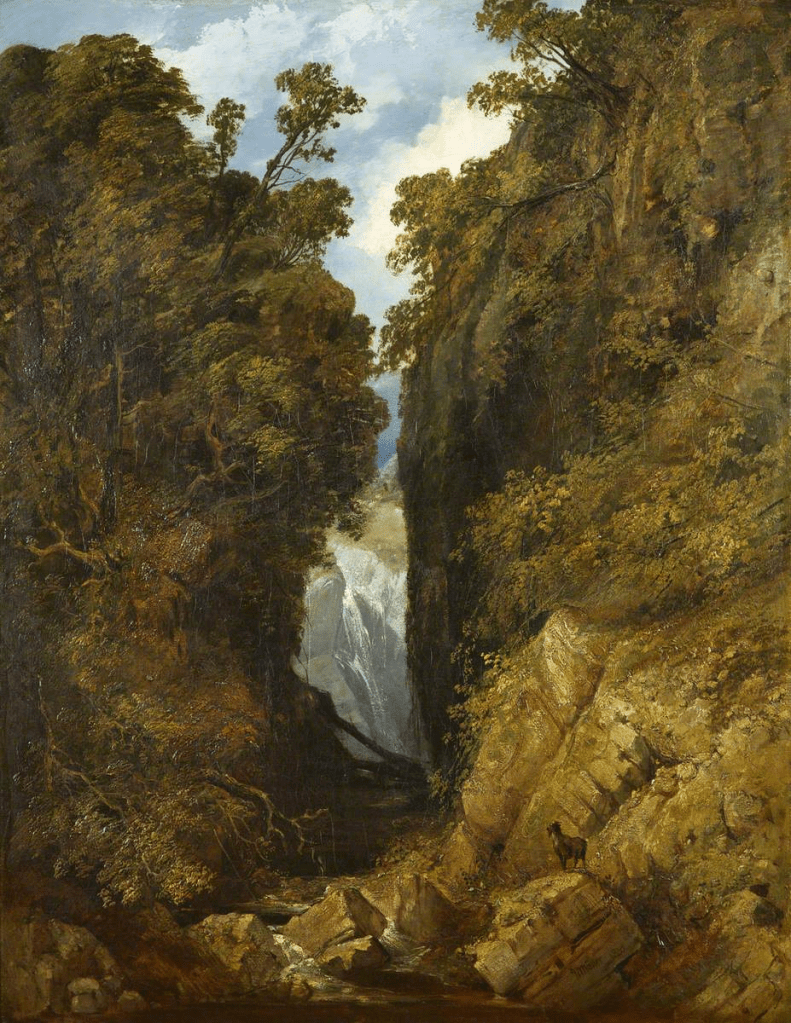
Of all Muller’s painting trips he undertook, North Wales was one of his favourite destinations. In a letter to a friend he called the area, Our English Switzerland. His first foray to the region was in June 1833 when he along with fellow artists, John Skinner Prout and Samuel Jackson left Bristol, crossed the River Severn and traversed the Brecon Beacons, finally arriving at the foothills of Cader Idris.
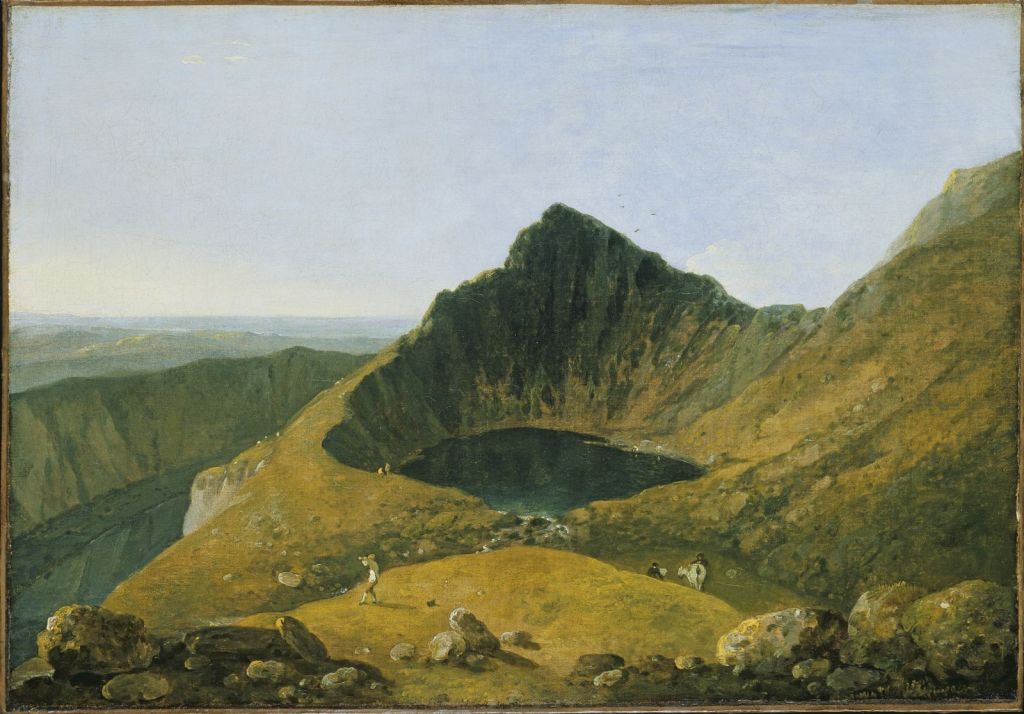

Llyn y Cau by Richard Wilson (1765)
The three men climbed part of the way up the mountain to gain a view of Llyn-y-Cau, a lake Muller referred to as Wilson’s Lake after Richard Wilson’s magnificent depiction of the lake in his 1765 painting.

Swallow Falls, Betwys y Coed by William Muller (1837)
Muller and Prout parted company with Jackson and explored the Conwy Valley from Betwys-y-Coed, all the way down to the sea. Muller was so taken with what he saw that he returned to the area on several occasions. During the winter of 1841 he and his brother travelled to North Wales and stayed at an inn in “Roe” now the small village of Rowen which was up-river from the coastal town of Conwy. He returned the following summer to paint en plein air in oils. In a letter to a fellow artist he wrote:
“…I paint in oil on the spot, and rather large, indeed. I am more than ever convinced in the actual necessity of looking at nature with a much more observant eye than the mass of young artists do, and in particular at skies. These are generally neglected…”
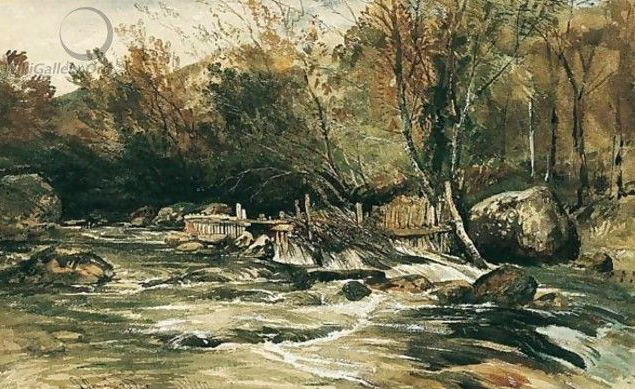
Salmon Trap on the River Lledr by William Muller (1842)

Interior with Goats, Betwys y Coed by William Muller (c.1833)
In July 1834, twenty-two year old Muller set off for Europe on a seven-month journey of discovery along with his good friend and fellow artist, the watercolourist, George Arthur Fripp. They left Bristol docks on a schooner and sailed to Antwerp. Having disembarked they went to Brussels and then moved across the German border, arriving in Cologne. They then followed the river south, eventually arriving at Heidelberg where they rested for several days.
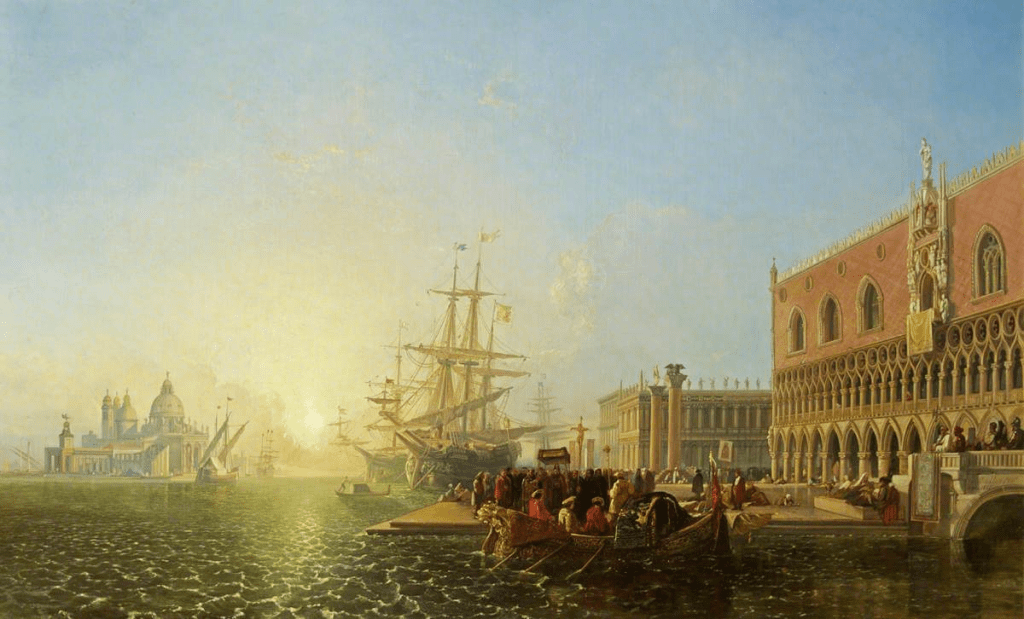
The Doge’s Palace, Venice by William Muller (1834)
The pair crossed the Alps and arrived in Northern Italy, visited the area around Lake Maggiore and staying in the lakeside town of Baverno. Finally they arrived in Venice where they stayed for almost two months.
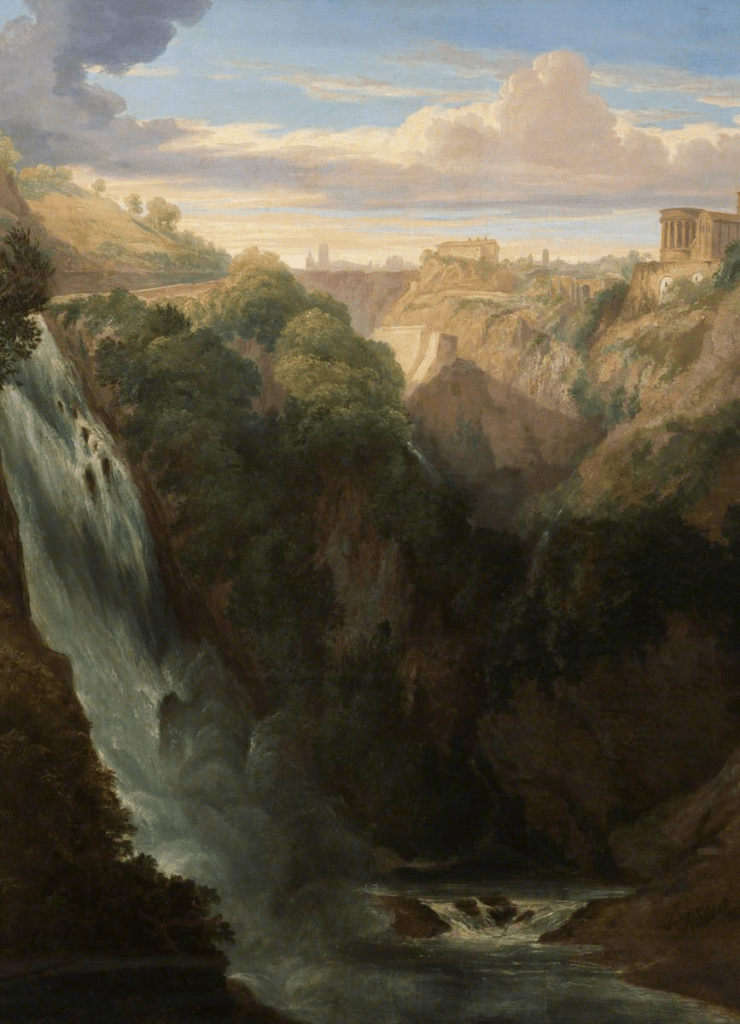

The Falls of Tivoli by William Muller (1837)
At the end of November 1834 they moved to Florence on their way to Rome where they spent that Christmas. The one place Muller was determined to visit was Tivoli a town 30 kilometres north-east of Rome, where many British watercolourists had visited and stayed to capture the spectacular views. Muller made many sketches and in 1837 completed his painting The Falls of Tivoli.
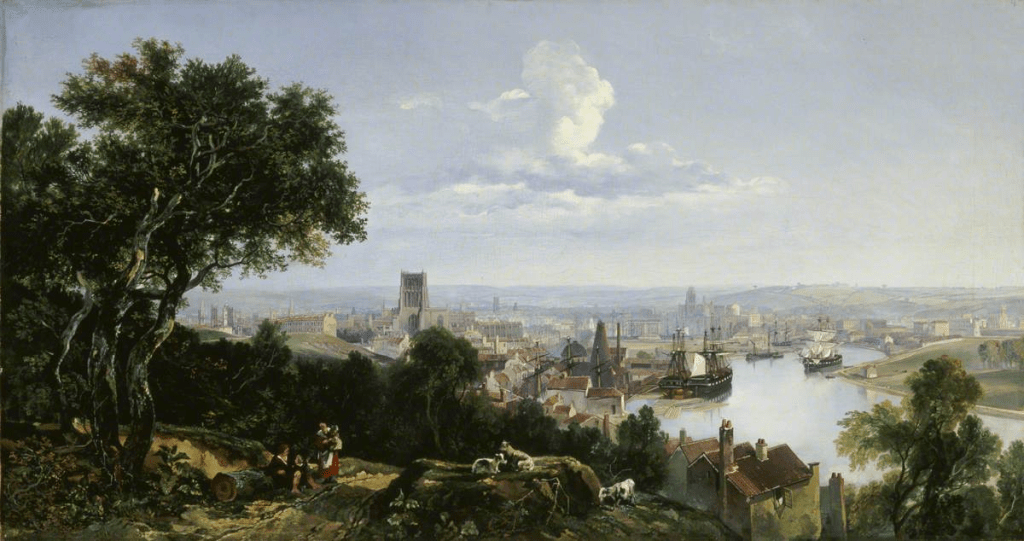
View of Bristol from Clifton Wood by William Muller (1837)
Muller returned to Bristol from his European tour in February 1835 and he set about converting his European and North Wales sketches into finished oil paintings. In 1838 he once again left the shores of England and this time his ultimate destination was Egypt. He went via Paris where he managed to visit the Louvre and was impressed by the landscape works of the Dutch painter, Jacob van Ruisdael and the Swiss painter, Francisco Mola. Muller travelled overland to Marseille and then embarked on a sea passage to Malta and Constantinople. From there he took a boat to the Greek island of Siros and then journeyed to Piraeus and Athens where he stayed for six weeks.

Temple of Theseus by William Muller (1839)
Whilst in the Greek capital Muller completed more than forty watercolours, many of which were of the Acropolis or views from this elevated monument. Athens had been a popular destination for artists and this love of the area could be put down to James Stuart and Nicholas Revett’s 1762 book, Antiquities of Athens. It was the first of four volumes and was the first accurate survey of ancient Greek architecture ever completed. Their detailed drawings done at the sites of the ancient ruins between 1751 and 1754 transformed our understanding of Greek architecture.
In November 1838 Muller left Greece and set sail on a French steamer for Egypt. He disembarked at Alexandria. Although earlier artists, such as Turner, and the marine painter Clarkson Stanfield, had produced drawing of Egyptian sites using sketches made by amateur artists, none had actually visited the country and it is thought that William Muller was one of the first established European artists to set foot in Egypt.

Prayers in the Desert by William Muller (Exhibited at the RA in 1943)
Muller was impressed with Alexandria, likening it to a kaleidoscope of humanity but the Egyptian town was, in his view, bettered by what he saw when he visited Cairo with its long delicate minarets and Asyut but it was the mass of people of these cities that astonished him the most. His most exciting time was when he mingled with the people at the slave market and he liked to immerse himself amongst the crowds dressed in their highly coloured clothes.

The Ramesseum at Thebes, Sunset by William Muller (1840)
In December 1838, Muller left Cairo and journeyed down the River Nile and on December 10th got his first sight of the pyramids at Giza. In his book, An Artist’s Tour of Egypt he recounted life on the small river boat:
“…it is tedious, to an extent one can form little conception of, to be shut up in a small boat, with not enough room to stand upright – 9 feet long and in its widest 6 – with little to do but shoot from its windows at crocodiles, pelicans and other birds, in particular vultures; of these being particularly fond of objects of Natural History, I made a tolerably numerous collection…..Shooting, sketching and smoking, at the expiration of twenty days I found I had arrived at Dundara…”
The Entrance to a Small Temple at Medinet Habu, Luxor, by William Muller (1840)
On January 1st 1839, at the end of his four hundred mile journey up the Nile, Muller arrived at Thebes. Here on the eastern banks were temples at Luxor and Karnak and on the western side the Ramesseum, the ruined mortuary temple of Ramesses II at Qurnah, the Valley of the Kings, the Valley of the Queens and many more monuments.

The Pyramids by William Muller (1843)
Despite the sometimes treacherous conditions, his expedition resulted in some of the finest travel records of any artist of the 1840s. Muller eventually returned home to Bristol via Malta, Naples, Rome and London in March 1839. Once home he set about completing paintings from sketches he made during is long journey.
In late Autumn 1839 William decided that he needed metropolitan success with his work and left Bristol and moved to London and he and fellow artist, Edward Dighton moved into a residence on Rupert Street, Haymarket and later 22 Charlotte Street, Bloomsbury. Muller and Dighton joined the Clipstone Street Academy at which figurative painting was taught using models and life classes and this was important to Muller who had been weak when it came to drawing figures.
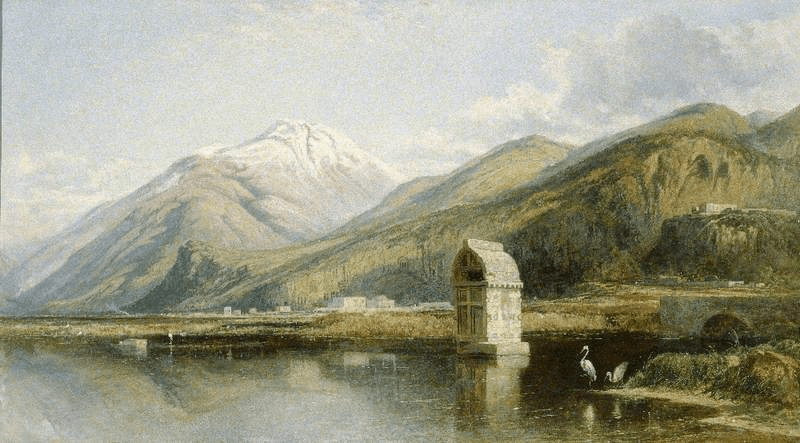

Tomb in the Water, Telmessos, Lycia by William Muller (1845)
Muller, along with fellow artist, Harry Johnson, visited the eastern Mediterranean for the second time when the pair travelled to Lycia, a remote part of south west Turkey, in September 1843. There, he had camped for months and encountered ferocious storms, torrential rain, and endured living close to malarial swamps. Muller eventually made his way home in April 1844 after being away for eight months. He left his numerous sketches in London to be framed and headed to Bristol to stay with his brother. He contacted his patron, William Wethered, and and on May 7th 1884, wrote to him about the Lycia expedition:
“…I am home at last – after a most fatiguing travel…….I will look forward to showing you what I have done in sketches – they are satisfactory I believe, & contain some splendid subjects – but I almost question if I had foreseen what I have had to go through to obtain them if I should ever have visited the country…”

Flower Piece by William Muller (1845)
In early 1845 William Muller became ill, probably exhausted due to overworking. He had at that time numerous commissions to complete and he believed they would lead to him becoming a very successful painter. He was disappointed and annoyed with how is paintings were exhibited at that year’s Royal Academy exhibition but nevertheless carried on painting despite his rapidly deteriorating health. His fingers became swollen and he was finding it difficult to hold a paint brush. On September 8th 1845 whilst his brother was setting his palette for him to work on a still-life painting, William Muller fell back and died aged just 33.
Wooded Landscape with Children by William Muller (1845)
Muller is buried in the Unitarian burial ground, Brunswick Cemetery, off Brunswick Square, Bristol. His grave is marked by a simple polished black stone slab inscribed Sacred to the memory of William James Muller who died Sep 8th 1845. A bust of the painter is located at the entrance to the cloister in Bristol Cathedral.