Love at first sight.
“…The very first moment I beheld him, my heart was irrevocably gone…”
– Jane Austen
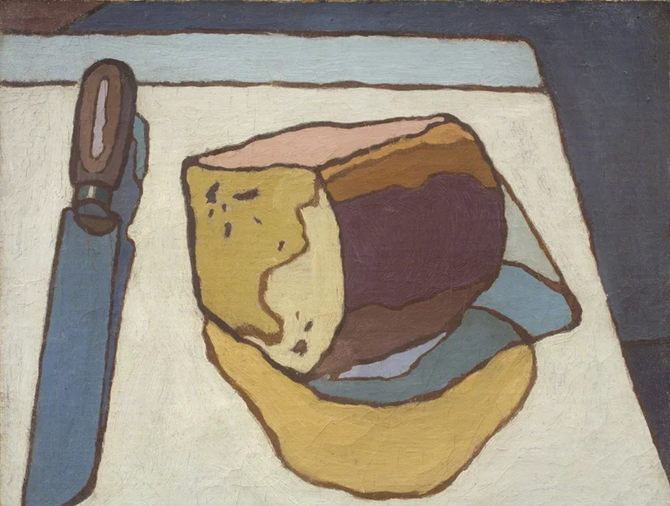

Bread and Knife by Cyril Mann (c.1955)
Still Life of Bottle and Jug by Cyril Mann (c.1955)
In the mid-1950s Cyril Mann’s painting style changed and he entered what was known as his solid shadow period. This was a complete change of style for him in comparison to his earlier works which had concentrated on the effects of direct sunlight and yet light came into play with these “shadow” works. They concentrated on shadows that were seen below objects when viewed under an overhead light source. In 2018 the Piano Nobile Gallery in London put on an exhibition of Cyril Mann’s work entitled The Solid Shadow Paintings. The gallery wrote about the works on display:
“…Undertaken between 1951 and 1957, Mann’s solid shadow paintings were a dazzling interjection in the subdued art world of fifties Britain. This was his most original period and it stands as his lasting contribution to the history of twentieth-century painting. It is an explosive programme of work, representing ordinary objects with boldly outlined shadows and bright, sometimes luminous colour. A dazzling interjection in the subdued art world of fifties Britain, these works have never been displayed together and the exhibition offers an exciting insight into the artist’s radiant formal language…”
After Mary walked out on Cyril in the middle of the night with her their daughter Sylvia, he had to fend for himself. Fortunately for Cyril, his daughter maintained contact with him and visited him regularly. Sylvia, who was a year younger than Renske, won a scholarship to the City of London School for Girls . After successfully completed her schooling she left London, aged eighteen, and went to Keele University to read English Literature and French. Whilst there, Sylvia also took on some temping work to supplement her student grant. Cyril was very proud of his daughter and what she had achieved although he had to admit they had, at times, a tempestuous relationship and he found her quite difficult at times. On occasions, it would appear that Sylvia also found her relationship with her father equally problematic. Renske got to know Sylvia and often said that she was everything she should have loved to have been herself: tall, a head taller than Cyril and Renske, blonde and beautiful. She also had Cyril’s violet-blue eyes and sensitive mouth and in some ways, Renske often felt pangs of jealousy.
Self portrait by Cyril Mann (1956)
Cyril struggled to survive financially as the sale of his paintings were not going well although this could have been more down to his obstinacy and the cantankerous ways he treated dealers and galleries, rather than the quality of his paintings.
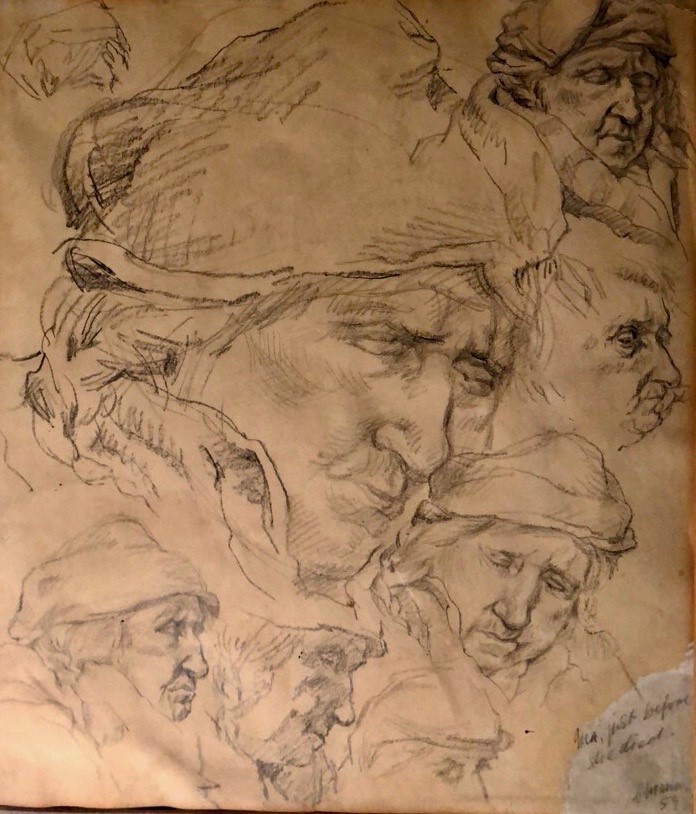

Ma, Just before she died by Cyril Mann
The years 1958 and 1959 proved to be a distressing time for Cyril Mann. He had been suffering a great deal of pain and was seriously ill with stomach ulcers. The discomfort had made him stop painting and teaching and the final straw to this misery was the death of his mother whom he had visited whilst she was in a Nottingham nursing home. He had made a number of facial sketches of his mother in 1959 during her last days. She had outlived her husband, her daughter and two of her three sons.
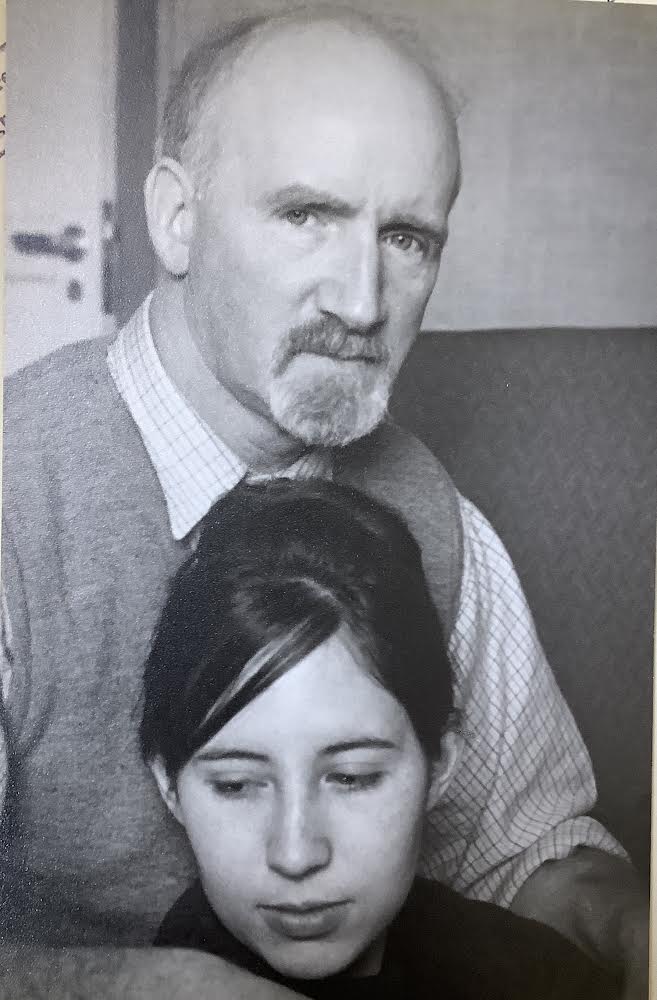
Cyril and Renske
Things changed for Cyril at the end of 1959 when on the evening of December 18th Renske van Slooten came into his life. Renske first met Cyril Mann at the Kingsway Day College in Holborn, London, where he was teaching students. Her “boyfriend” and dancing partner at the time, who knew she was interested in art, took her to meet his former art teacher. Renske remembers the moment well and, in her book, The Girl in the Green Jumper, she recalls that first sight of the artist:
“…As I stood on tiptoe peering through the window, I could see Cyril with his back to me, slumped at his desk in front of his students with their easels and drawing boards. His hair, what there was of it was long and unkempt. He wore a crumpled tweed jacket with leather elbow patches. He wasn’t tall a bit over five foot at most. To me, barely out of my teens and recently arrived from Holland, he looked old, at least fifty. Yet before I’d even seen his face, I felt drawn to him…”
She also distinctly remembered the park warden’s prediction of meeting and marrying an “old” artist. At that first sighting of Cyril in his art class she was totally captivated by him. Renske says of her first impression of Cyril:
“…A strange feeling came over me. This was it! I remembered the park warden’s prediction. I was mesmerised. I saw his hair was too long, his tweed jacket with leather elbow patches was tatty, he looked worn out, depressed. Didn’t take any notice of me. I couldn’t care less what he looked like and how scruffy he was. I was attracted to him, not because he was older, but because I’m always attracted to people who are unusually gifted. And I sensed that he was…”

Cyril Mann painting in a small room in Bevin Court
After that first meeting, Cyril and Renske set up a date for the following evening. She was buoyed by the thought of being in the company of a professional artist. Cyril was almost half an hour late at the rendezvous admitting he had fallen asleep whilst reading a book. Fortunately for him Renske had waited patiently for him. Cyril invited her back to his flat to look at some of his artwork. At this time, he was renting a top-floor flat in a council housing block at Bevin Court in Islington. Totally captivated by both Cyril and his painting, Renske admits she paid little attention to the flat itself, which was overflowing with his paintings, books and sculptures. Renske remembers the artwork as being quite small, dark and gloomy and yet she says that they were among the most beautiful she had ever seen. She told him that some reminded her of works by Turner. He was delighted at that assertion as he looked upon the English artists as one of his great heroes.

St Paul’s from Bankside by Cyril Mann (c.1952)
One of the paintings which she really liked was his work entitled St Paul’s from Bankside. It depicted the dome of St Paul’s looming above the rooftops from across the River Thames. Nowadays at this point on the Thames, the Millenium Bridge spans the river besides the Tate Modern. Renske said that at first glance at the work, she thought it was a monochrome depiction but on closer inspection she could see that the greys were shot through with blue, yellow and warm pink. Cyril told her that the city should be viewed on a grey day. He went on to assert:
“…One day people will recognise my qualities as an artist purely on the strength of my ability to perceive greys in their infinite variety…”
It was this assertion that one day he would be acclaimed a great artist that would haunt him all his life as he never felt recognised as a truly great painter.

St Paul’s by Cyril Mann (1948)
It is interesting to compare the 1952 painting with the one he completed in 1948. The latter was painted in his favoured style at the time that of facing the sun and concentrating on the effect of direct sunlight. The view is from Moor Lane which dominates the foreground in which we see four people walking along the pavement, to the side of which is a low wall. A fifth figure crosses the road. Over the other side of the wall is a vast empty space, the result of heavy wartime bombings. In the midground we see multi storey buildings, churches and to the right, the familiar outline of St Paul’s Cathedral.

St Paul’s from Bevin Court by Cyril Mann (1961)
Another of Cyril Mann’s cityscapes featuring St Paul’s cathedral was his painting entitled St Paul’s from Bevin Court.
A month had passed since their first meeting and Renske and Cyril were happy about how things were progressing. Renske, however, was not happy with her communal living at the YWCA and told Cyril she needed another place to live. He made a few suggestions, including sharing a flat with his ex-girlfriend, but Renske came straight out and asked if she could live with Cyril in his flat ! The problem was that Cyril’s home was a one-bed flat and he slept on a single bed in a room that was full of paintings, easels and other artistic paraphernalia. Renske was not put off by this and said that as they were both small, they could both sleep in the bed. For Renske, it was nothing to be ashamed of, although her work colleagues at the Dutch-owned company, when they were told, were scandalised, Scandalised that she was living with a man, scandalised that she was living with a married man twenty-eight years older than her and that his daughter, Sylvia, was only a year younger than her, and scandalised that she was living in a poor and rough council estate.
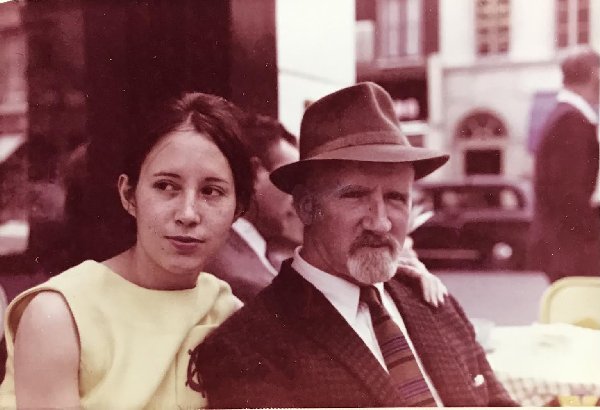

Renske and Cyril Mann in the mid 1960s
However, Renske was passionately in love with “her” artist and was not going to listen to subtle and not-so-subtle warnings about what she had done. News of Renske’s situation of living with a married man got back to her boss who contacted the Dutch embassy in London and asked that her parents be informed about their daughter’s living and romantic situation. Her father and mother were horrified and she was summoned home. She was still not twenty-one and therefore, by Dutch law, she remained under their control. Despite their protestations Renske declared that she would marry Cyril with or without their permission. One can just imagine the thoughts that were going through the parents’ heads having been told that she intended to marry a man who was a year older than Renske’s own mother. What her parents failed to realise that it was not the older man who was grooming their young daughter, it was their young daughter who was the prime mover in forging this relationship. Renske returned to London and moved in with Cyril. She wanted to marry him but could not as he was still married to his first wife, Mary !
Having lived apart for ten years, the marriage between Cyril and his first wife Mary ended in divorce on August 24th 1960 and eight days later, on September 1st, one week after Renske’s twenty-first birthday, Cyril and Renske were married.
Mixed Flowers by Cyril Mann (1961)
Cyril had suffered stomach ulcers for years and had had to endure constant stomach pains after every meal which had weakened him and caused bouts of ill temper. One day in April 1960, whilst out walking alone, he collapsed in the street and was rushed to the Royal Free Hospital where he underwent an emergency operation for a perforated stomach ulcer. Following the operation and probably due to the pressures of having to earn a living from his teaching and the need to sell his artwork, both of which he was unable to do due to his physical illness, he suffered a serious mental breakdown. Renske was upset by Cyril’s physical and mental decline and set about remedying the situation by putting Cyril’s life back on an even keel. She believed that Cyril was not able to cope with having to teach, which he hated, and paint and so she maintained her job and became the breadwinner. For Cyril this financial support from Renske liberated him from the drudgery of having to teach and the necessity of providing money to put food on the table. After release from hospital Cyril went to convalesce at the Artists’ Rest Home in Rickmansworth, a town in south-west Hertfordshire, where he was allocated a comfortable room, painting facilities and three good meals a day.
Studio Corner by Cyril Mann (1961)
His operation had left Cyril pain-free and he went back to his painting with a noted added gusto, but all was not well. Renske remembers one horrendous evening when a hyped-up Cyril had decided he was going to design, what he termed, “the greatest mural the world had ever seen”. She had been sleeping badly and was desperate to go to bed but Cyril refused to let her sleep and demanded that she helped him plan this great mural, an extensive paper plan of which had been tacked to the carpeted floor of their bedroom/living room. He flew into a rage when Renske just wanted to lay down and sleep and demanded she helped him. It finally got too much for her and she, determined to have an uninterrupted sleep, took some tranquilizers and sleeping pills and collapsed on the bed. The next thing she remembered was waking up in hospital. When she had collapsed, Cyril couldn’t shake her awake, and so he called an ambulance.
Cyril with black eye
The ambulance arrived along with some police. Cyril demanded that he should accompany her to the hospital in the ambulance but they refused him. He was furious and lost control, attacking both the ambulance staff and the police and for his troubles received a black eye but worse still another ambulance was summoned and after consultation with a psychiatric nurse, he ordered him to be sectioned, taken to a mental unit, placed in a straitjacket, and then taken to a padded cell. His passport photograph taken days after the incident shows Cyril with a black eye after his altercation with the ambulance men.
Interior with Red Chair by Cyril Mann (c.1961)
After a fortnight’s detention at the psychiatric hospital, Cyril was allowed home, heavily sedated, and having had to promise to take his medication every day. Cyril was unhappy with the terms of his release as he believed the medication would threaten his libido. Besides doing that, he asserted that the pills would also affect his creative artistic thoughts and to counteract this he unilaterally began to reduce the amount of medication he had been prescribed. As often is the case, to raise spirits Renske decided to perform a deep-clean of the flat and buy some new furniture, including a garishly bright red upholstered chairs which Cyril loved and said that the new additions inspired him.
………..to be continued.
It would not have been possible for me to put together this and following blogs about the artist, Cyril Mann, without information gleaned from a number of sources:
The comprehensive biography of Cyril Mann, The Sun is God by John Russell Taylor
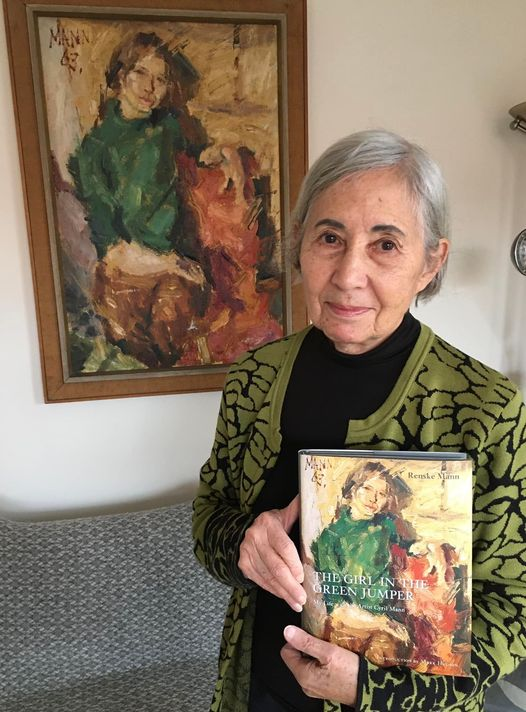
Renske Mann with her book The Girl in the Green Jumper, My life with the artist Cyril Mann
The intimate autobiography of Cyril Mann’s life by his second wife Renske, entitled The Girl in the Green Jumper.
This autobiography has now been turned into a play which receives its World Premiere on Wednesday March 13th at the Playground Theatre, London, 8 Latimer Rd, London W10 6RQ.
Finally, and most importantly I owe many thanks to Renske Mann herself who provided me with information and photographs appertaining to her late husband Cyril.
Piano Nobile Gallery London for information and pictures.


























