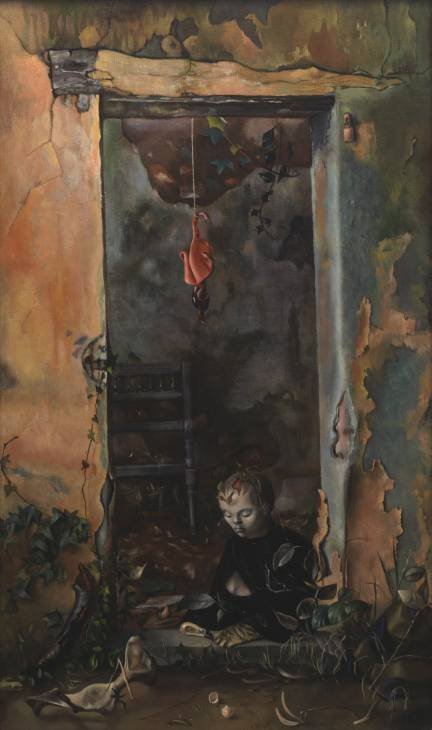
In a couple of recent blogs I looked at the life and works of two female artists who were possibly best known because of their partners. I featured Frida Kahlo whose fame partly derived from her marriage to the Mexican muralist Diego Rivera and I showcased the life and works of Gabriele Münter whose one-time partner was Wassily Kandinsky. Today I want to introduce you to an artist who on her own merits would become the most celebrated female painter of her time. Her name is Leonor Fini.
I would like to tell you that I have always been a lover of her work but sadly I have to admit that until last Monday I had never even heard of her. It was purely by chance that I came across a painting of hers, which I am featuring today. It was one of those paintings, which once viewed, was hard to forget. I found it fascinating. I was mesmerised by it and I had to return to stand in front of it a number of times. It is housed in the Tate Modern in London and I was there primarily to see the Edvard Munch exhibition but thought that I would take the opportunity to look at some of the paintings in the permanent collection of the museum. I think I have said before that I am not a lover of modern art and find a lot of it very hard to understand but I am constantly being told that I should “embrace all types of art” a suggestion I tend to ignore! I had just sailed up the Thames on the Tate to Tate boat which transports you from the Tate Britain to the Tate Modern as I had been to the Pre-Raphaelite exhibition at Tate Britain in the morning. It was interesting to note the difference in the age group of the people attending the two Tate museums. The Tate Modern certainly had a younger audience and maybe for the young there was an element of rebellion in the art on display there, in comparison with the more staid, more formal art work of the Tate Britain.
Leonor Fini was born in Buenos Aires in August 1907. Her father, Erminio, was an Argentinean of Italian descent and her mother, Malvina Braun Dubich, was a Trieste-born Italian with German and Slavic origins. Her parents’ marriage was anything but happy and their turbulent partnership ended in divorce when Leonor was just one year old. Her mother left her abusive husband and took Leonor back to Trieste to live with her grandparents. Leonor’s father made a number of attempts to abduct his daughter and have her back with him in Argentina. His wife, who received no protection from the local authorities and was so afraid that Leonor would be taken from her, decided to take the matter into her own hands and so for the next six years she dressed her daughter up as a boy whenever they ventured out the house. Eventually Leonor’s father gave up his attempts to snatch her and went back home to Argentina and was never seen again. Despite this traumatic early part of her life in Trieste, Fini grew up in a very cultivated, well-ordered household. Having had to suffer the threat of being kidnapped during her early life, Leonor was to suffer another trauma during her early teens when she contracted an eye disease, which forced her to wear bandages on both of her eyes. She was now locked into a prison of darkness in which she had no alternative but to develop an inner vision and during these long periods of darkness, she would visualise fantastic images, which in some ways would be later mirrored in her art. It was with these strange images that she had conjured up in her mind during those days of enforced darkness that once her sight was restored she decided that she wanted to become an artist.

Leonor was a very determined and headstrong teenager and was expelled from several schools on account of her rebellious behaviour and her unwillingness to abide to school regulations. Like many teenagers she was very precocious and in a way this manifested in the creation of a persona of incredibly strong will and intense sensitivity. She became an avid reader and it is said that by the end of her teenage years she had read all the works of Freud. In a way she educated herself and this thirst for knowledge made her popular within the local artistic and literary circles. Her interest in art was furthered by her visits to her uncle, a lawyer, where she spent many hours in his library rummaging through and reading his extensive collection of art books about the lives of artists and was especially enthralled by those of the artists of the pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, Aubrey Beardsley and Gustav Klimt. She also travelled widely in Italy and Europe visiting all the museums. Once her decision had been made to become an artist and having no formal training, she taught herself anatomy by studying corpses in the Trieste mortuaries. When she was seventeen years of age she had some of her artistic works shown at an art exhibition in Trieste and this led to her receiving portrait commissions from some leading dignitaries in Milan. In 1929, aged just twenty-two years of age, she managed to stage a show of her work at the Galerie Barbaroux in Milan. Seven years later she left Italy and went to live in Paris, a city Leonor would often referred to as “my real city”.
In 1936, in Paris, she staged her first one-woman exhibition of her work at the Galerie Bonjean, whose director was Christian Dior and the success of this brought her into contact with a number of Surrealist painters such as René Magritte, Paul Eluard, Salvador Dali, Max Ernst, Viktor Brauner and their de facto leader, André Breton. It was around this time that she started to paint Surrealist images and began to be drawn close to this artistic movement. However her youthful rebellious nature once again surfaced and she would not kowtow to the dictates of André Breton’s and intensely disliked his authoritarian leadership. She sided with Dali’s view of Breton and his Surrealist theories. Dali described Breton as having a typical petit bourgeois mentality. However, despite this, she did exhibit with the Surrealist group. The eminent American feminist writer and curator Whitney Chadwick wrote about Leonor’s early days in Paris:
“…In Paris she became a legend almost overnight. When one of the Surrealists saw a painting of hers in a Paris gallery in 1936 and sought out its creator, she arranged a rendezvous in a local cafe and arrived dressed in a cardinal’s scarlet robes, which she had purchased in a clothing store specializing in clerical vestments. ‘I liked the sacrilegious nature of dressing as a priest, and the experience of being a woman and wearing the clothes of a man who would never know a woman’s body…”
Leonor’s dislike of Breton’s despite his redoubtable charisma was mirrored by his dislike of what he viewed as her often scandalous behaviour and pension for the company of homosexuals. Breton was known to be fiercely homophobic. Although she strongly denied she was a Surrealist she did align herself with the group and they welcomed her. She made her first trip to New York in 1936, showing at the Julian Levy Gallery and in December of that year she participated in the famous “Fantastic Art, Dada and Surrealism” exhibition at New York’s Museum of Modern Art
With the onset of the World War II looming, Leonor fled Paris with her close friend André Pieyre de Mandiargues, a French writer and an associate of the Surrealist set. The two of them spent part of the summer of 1939 as guests of Max Ernst and Leonora Carrington in Ardèche, before they moved on to Arcachon, where Salvador and Gali Dali had their wartime refuge, the Villa Salesse. From there the pair went to Monte Carlo.

designed by Leonor Fini
In the 1940’s, after World War II her career branched out and she began to design theatre sets and costumes for the theater, opera and ballet. She also worked for Elsa Schiaparelli, the Italian fashion designer, and designed the bottle for the perfume Shocking, which was to become the top selling perfume for the House of Schiaparelli. The bottle was in the shape of a woman’s torso, which was said to be inspired by Mae West’s tailor’s dummy and Dalí paintings of flower-sellers. The packaging was also designed by Fini and was in shocking pink, which was one of Schiaparelli’s signature colours.
Leonor Fini had a number of lovers but was married only once. Her husband was Federico Veneziani but the marriage was short lived and following her liaison with the Italian Count, Stanislao Lepri, she and her husband divorced in 1941. Lepri, who was the Italian consul in Monaco where Leonor was living, abandoned his career shortly after meeting Fini and the two lived together. With her encouragement, Lepri became a painter, and the couple moved to Rome shortly before the Allies liberated the city in 1943. Several years later, they returned together to what had once been her home in the rue Payenne, Paris. In 1952 she met the Polish writer Konstanty Jelenski, known as Kot Jelenski, in Paris soon after the war. Kot joined Leonor and Lepri in their Paris apartment in 1952 and the three remained inseparable until their deaths. In a way she managed to put into practice one of her more famous quotes:
“…Marriage never appealed to me, I have never lived with one person. Since I was 18, I’ve always preferred to live in a sort of community – A big house with my atelier and cats and friends, one with a man who was rather a lover and another who was rather a friend. And it has always worked…”
In the summer of 1954, Leonor, during her travels, discovered a haven of tranquility in Corsica. It was a ruined monastery near Nonza. It was set in a wild landscape and she immediately felt at peace in this place and from then on she would return to it every summer to paint. Leonor was, from an early age, a great lover of literature and reading and she illustrated more than 50 works by writers such as Charles Baudelaire, who was one of her favourite authors. In her later life, she continued to design sets and costumes for the theatre, opera, and film. In early 1960, Leonor Fini moved to an apartment in Paris’ rue de La Vrillière, between the Palais Royal and the Place des Victoires. She was rarely alone, always in the company of her friends and surrounded by her numerous Persian cats, (at one point she had 23 cats) which along with the sphinx, often featured in her paintings. Fini adored cats, which were Egyptian symbols of dignity and power, and she identified herself with the sphinx, the mythological hybrid of lion and woman. She divided her time between the apartment and her home in Saint-Dyé-sur-Loire, in Touraine, up until her death in January 1996. Leonor Fini died at the age of 88 but one of her obituaries commented that it was impossible to imagine her being old. It went on to say that she would always be, for those who admired her, the wild, raven-haired, ill-proportioned beauty who haunted her pictures. The lethal yet irresistible sphinx, the vampire we would most like to visit us. Her obituary in The Times paid homage to her beauty, the erotic quality of her art and mentioned her legion of lovers whose names “read like a roll call of the literary and artistic talents of that brilliant age.”
She continued to be friends with some of the best known writers, artists, and thinkers of her time while simultaneously being a bona fide cat lady. Throughout her artwork, Leonor always venerated the female form. She would often show females as the dominant ones of a partnership, who were protecting their male lovers or in some instances, women loving other women. She depicted women exploring their own identity at a time when female identity, both physically and mentally, was being defined by men.
My Daily Art Display featured work today is the painting entitled Petit Sphinx Ermite, (Little Hermit Sphinx), which Leonor Fini completed in 1948. Fini adored cats, and she used the image of the Sphinx, the mythological hybrid of a lion and woman, partly as a self-portrait. She looked upon the Sphinx as a symbolic intermediary between the human and animal realms, and between the conscious and the uncharted areas of the mind and spirit. The sphinx in this work is child-like domesticated creature, which we see sitting in front of its ramshackle home. At its feet we see a skull of a bird and more bizarrely above the sphinx’s head we see a creatures body hanging from the door lintel, which in a way adds a sense of violence to the scene.
Maybe having seen the painting you will understand why I kept coming back to it, trying to fathom what it was all about !!! Her works of art are fascinating and I urge you to take a look at more of her paintings.





















