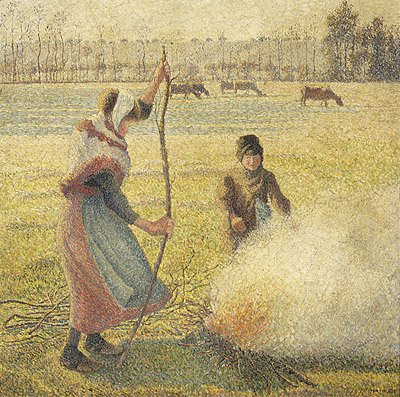
My Daily Art Display’s featured painting today is entitled Peasant Girl Lighting a Fire. Frost, which was painted by Camille Pissarro in 1888 and can now be found in the Musée d’Orsay in Paris. At this time Pissarro was still a leading light of the Impressionist movement, a movement he had helped to form. However it was two years prior to this work that Pissarro began to become interested in the experimental work of young artists, who had adopted the fragmented brushstroke technique which Georges Seurat and Paul Signac were trying out, known as pointillism , a technique Pissarro used in parts of this painting. For a more in depth look at pointillism see My Daily Art Display October 21st 2011 for a painting by Georges Seurat and November 29th 2011 for a painting by Paul Signac. Pissarro had been introduced to Seurat and Signac in 1885 and in the following years he began to work in the pointillist style which had then been adopted by the Neo-Impressionists. By the time Pissarro was in his sixties he found that this pointillism technique too restricting and in the last ten years of his life he returned to a purer Impressionist style.
Camille Pissarro was fifty-eight years of age when he completed today’s featured work of art. Ten years earlier his style of painting was such that he would portray nature in his landscapes by a myriad of smaller comma-like brushstrokes built up on the surface of the canvas such as his 1877 work, The Red Roofs (see My Daily Art Display of November 30th 2010). Pissarro was concerned that these works lacked clarity and so he decided to change the way he worked. He spent time working in collaboration with Degas, who was, of all the Impressionists, a great believer and advocate of figure painting and the primacy of the human figure at the expense of landscape background. It was maybe the views of Degas that led to Pissarro to complete some works in which the human being(s) took pride of place in the painting, as is the case with today’s featured work.
The painting depicts two peasant girls working in a field in a cold and frosty winter morning and we see one of them tending a fire. Pissarro often painted peasant women at work. Two fine examples of this are his 1881 work entitled Girl with a Stick and the 1893 painting entitled Woman with a Green Shawl. His portrayal of peasants received some criticism for copying the ideas of Jean-François Millet but Pissarro firmly contested such a notion. However in general art critics looked upon his works as true representations of peasant life. Look at the beautiful way in which Pissarro has depicted the landscape. At the time of this painting Pissarro was extremely interested in the pointillism technique of Seurat and Signac and he used this method to present us with a sumptuous backdrop to the two girls. The painting has a light and airy feel to it and there is a subtle delicate nature to the work. The work was painted in Eragny just north-west of Paris where Pissarro and his family lived for a time.
In the far distance we can see the low hills topped by irregular spaced bushy trees. In the middle ground, we observe grazing cows in the meadow, a line of poplar trees at the foot of the hills and possibly a hidden stream running horizontally across the mid ground. Notwithstanding the backdrop, the focus of the painting is on the two girls in the foreground, who almost appear to stand next to us. The scene is lit up by the sun, somewhere out of sight, to the left, which throws off long blue shadows across the field. It is a wintry sun and still low in the sky, hence the long shadow of the girl in the foreground, which disappears off the painting to the right. Although it emits light, the sun gives off little warmth and so our two young workers are wrapped up well. The temperature is even colder due to the wind chill factor. Look how the girls skirt and the smoke from her small fire are blown horizontally by the wind which comes from the left of the painting. One can imagine how cold it is with the driving wind on a wintry day. We almost shiver as we look at this work of art.
The girls are both well wrapped up against the morning’s wintry chill. The girl on the right, who seems no more than a child, is warming her hands by the fire. She wears a blue dress and a thick dark brown coat. She has a dark woolen hat on her head which is pulled down to protect her ears from the icy wind. The older girl, who is closest to us and because of her height, is the main focus of our attention. She has taken a branch from the pile behind her, and is about to break it up and add it to the fire. She wears a pink skirt with a blue apron. She too has protected her head, wearing a white scarf tied beneath her chin. Her final layer of protection is a pink and white shawl from which emerge long black sleeves of her dress.
The colour combinations Pissarro uses to achieve the colour we see is fascinating. The girls pink dress is made up of a combination of yellow, blue and pink. The green grass of the meadow is achieved by using a combination green, blue, yellow, pink and white. The only orange Pissarro used was for the flames of the fire.
Pissarro fled the traumas of the Franco-Prussian War in 1871 and, like Monet, went to live in London. It was whilst in London that he saw a number of paintings by Turner. Pissarro later commented on Turner’s works and was amazed by the way Turner succeeded in conveying the snow’s whiteness, not just by the use of white alone but by combining a host of multi-coloured strokes, dabbed in, one against the other, which when looked at from a distance, created the desired effect. It is in this painting that Pissarro has, without the actual presence of snow, managed to give us a crystalline frost of a cold winter’s morning encapsulated in an aura of diamond blue.






























