Joseph Mallord William Turner’s painting The Sun Rising Through Vapour was described at the time as masterly, and his early reputation was founded on a series of dramatic seascapes that he regularly showed at the Royal Academy, the British Institution and in his own gallery until about 1810. The sun disperses the clouds and infuses sand and sea with a golden glow. In the foreground against a seascape with the setting sun which casts a golden light over the entire picture, we see a group of fishermen and women unloading their catch and laying it out on the beach for sale. In the distance we see a number of ships at anchor including a man-of-war and a dismasted hulk which was being used as a prison ship, which is a stark reminder that at the time Turner completed the work, France and England were still at war. Turner painted numerous marine subjects early in his career. As here, he sought to make his reputation by matching the Dutch masters of the 17th century. Throughout his life Turner was fascinated with including the sun in his paintings
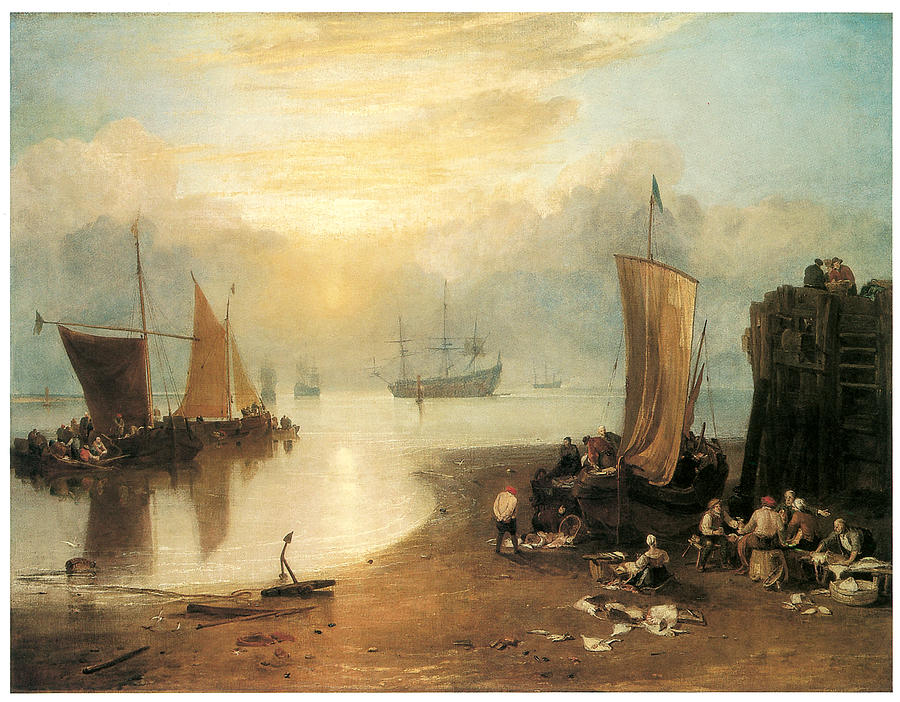
A similar painting can be found in the National Gallery, London entitled The Sun Rising through Vapour. The setting is low tide in the early morning and fishermen unload their catch from a boat beached high and dry on the shore. Some of the people are partaking of a meal whilst others prepare the catch for sale. There is a noticeable contrast between the human activity on the shore with the stillness of the glassy sea which, like a mirror, reflects the hazy sunlight. The sun is just a pale yellow glow and has yet the power to burn off the sea mist which is alluded to with the word ‘vapour’ in the picture’s title.

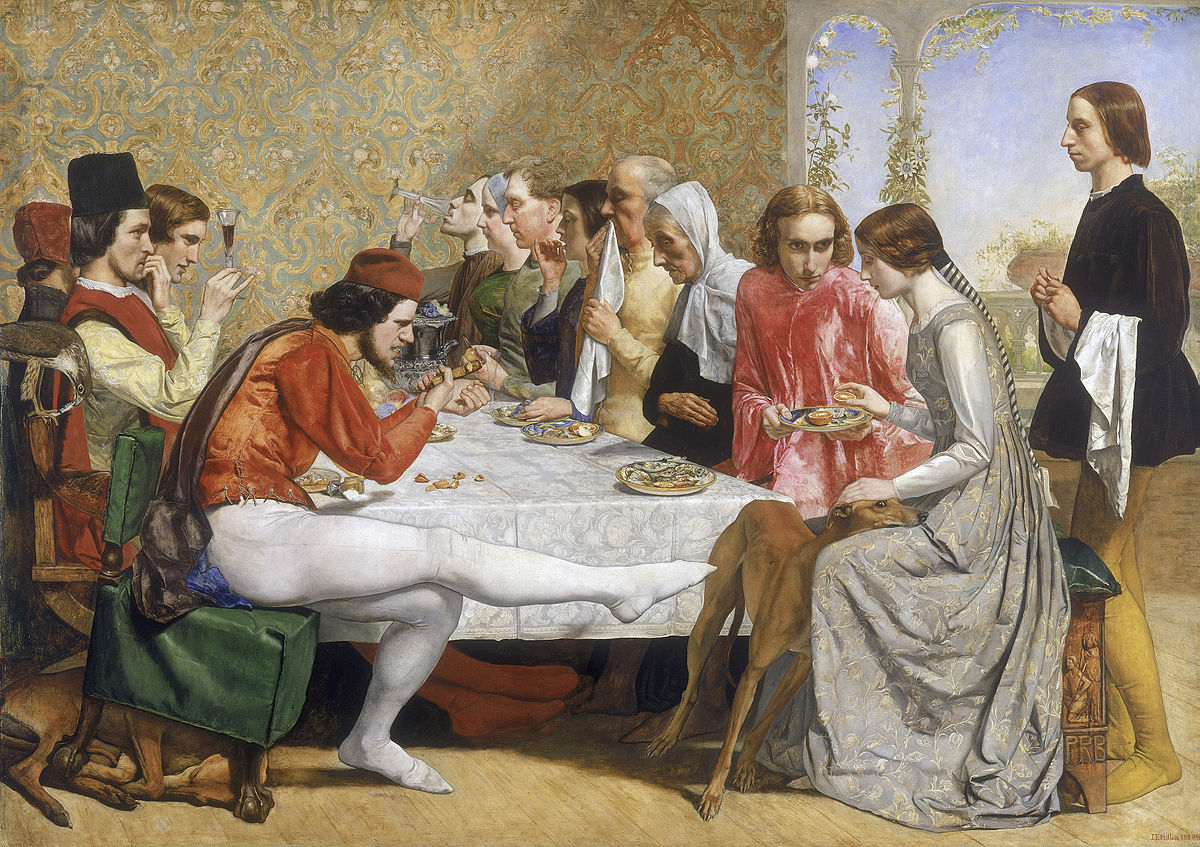
My next offering is by the Italian painter, Jacopo dal Ponte, better known as Jacopo Bassano, named after, Bassano dal Grappa, a village northwest of Venice, where he was born in the first decade of the sixteenth century. He was probably first trained by his father, Francesco, before becoming an apprentice in Bonifazio Veronese’s large Venetian workshop. He was mainly active, throughout his long life, in Bassano, where he painted landscapes and genre scenes. In his painting, Adoration of the Magi sometimes known as the Adoration of the Kings he depicted the Three Kings, or Magi, carrying their gifts, as they approached the infant Christ. It’s a scene that has been caught countless times on canvas. Despite their status and wealth, they bow to Christ who they acclaim as the King of Kings. The setting, is the inside of a ruined classical building and has a symbolic meaning. The decaying building symbolises the decline of the pagan world and the old gods. They will be further ruined as a result of Christ’s divine mission. Look at the various aspects of this picture. Look how Bassano has painted the sumptuously extravagant robes and depicted a splendid collection of animals and servants. Look how the light comes through the decaying architecture and settles on the head of the baby Jesus. This is looked upon as being a light source emanating from God the Father.

I wrongly associated paintings solely depicting ballerinas with the French painter Edgar Degas but in fact he had another favourite theme for his work – horse racing. Horse racing was a popular pastime in the nineteenth century in France under Louis-Philippe and Napoleon III. Degas became fascinated by the sport while visiting friends in Normandy. During his lifetime, Degas created forty-five oils, twenty pastels, two hundred and fifty drawings, and seventeen sculptures related to horses. One such work featuring horse racing is in the Barber Institute collection, entitled Jockeys Before the Race. It is a painting, made using oil essence, gouache, and pastel, which he completed in 1879. It is an image of three jockeys on horseback readying themselves at the start of a race on a dull winter’s day with its watery sun. This very large work (107 x 73cms) was exhibited at the Fourth Impressionist Exhibition in 1879. There is a definite lack of symmetry about this work as the vertical starting post is placed two-thirds from the left-hand side. The warm red and pink colours of the jockey’s clothes on the left of the painting are balanced by the lighter white/blue colours of the clothes worn by the jockey, who sits astride his horse in the right foreground.

My next choice of painting is both unusual and yet strangely beautiful. It is a 1860 watercolour over pen and pencil, partly heightened with white and gold work by Caspar Nepomuk Scheuren, a German landscape painter and etcher. It is thought to have been commissioned as a prize in a lottery held by Kristiania Kunstforenings, Oslo, the oldest art gallery in Norway, which is why the Norwegian coat of arms is at the top centre of the work. It is an elicitation of a poem by the German nineteenth century poet, Ludwig Uhland which tells of a legendary magical castle, depicted in the centre of the painting, which reaches up towards the moonlit sky and down to the shimmering sea. On one side we see a king and queen and on the other, their musical daughter, who serenades passers-by with a tearful lament, whose premature death forms the focus of the poem’s lament. The castle and characters are surrounded by an architectural framework, in which the separate compartments serve to isolate episodes of the unfolding narrative. The tragic fate of all three characters is depicted at the bottom of the painting. In the centre the king and queen are seen dressed in mourning clothes. To the left we see the tomb of their daughter and to the right we see a depiction of their own tomb. Below is the poem which tells the sad story.
The Castle By The Sea
By Johann Ludwig Uhland
‘Hast thou seen that lordly castle,
That Castle by the Sea?
Golden and red above it
The clouds float gorgeously.
‘And fain it would stoop downward
To the mirrored wave below;
And fain it would soar upward
In the evening’s crimson glow.’
‘Well have I seen that castle,
That Castle by the Sea,
And the moon above it standing,
And the mist rise solemnly.’
‘The winds and the waves of ocean,
Had they a merry chime?
Didst thou hear, from those lofty chambers,
The harp and the minstrel’s rhyme?’
‘The winds and the waves of ocean,
They rested quietly,
But I heard on the gale a sound of wail,
And tears came to mine eye.’
‘And sawest thou on the turrets
The King and his royal bride?
And the wave of their crimson mantles?
And the golden crown of pride?
‘Led they not forth, in rapture,
A beauteous maiden there?
Resplendent as the morning sun,
Beaming with golden hair?’
‘Well saw I the ancient parents,
Without the crown of pride;
They were moving slow, in weeds of woe,
No maiden was by their side!’
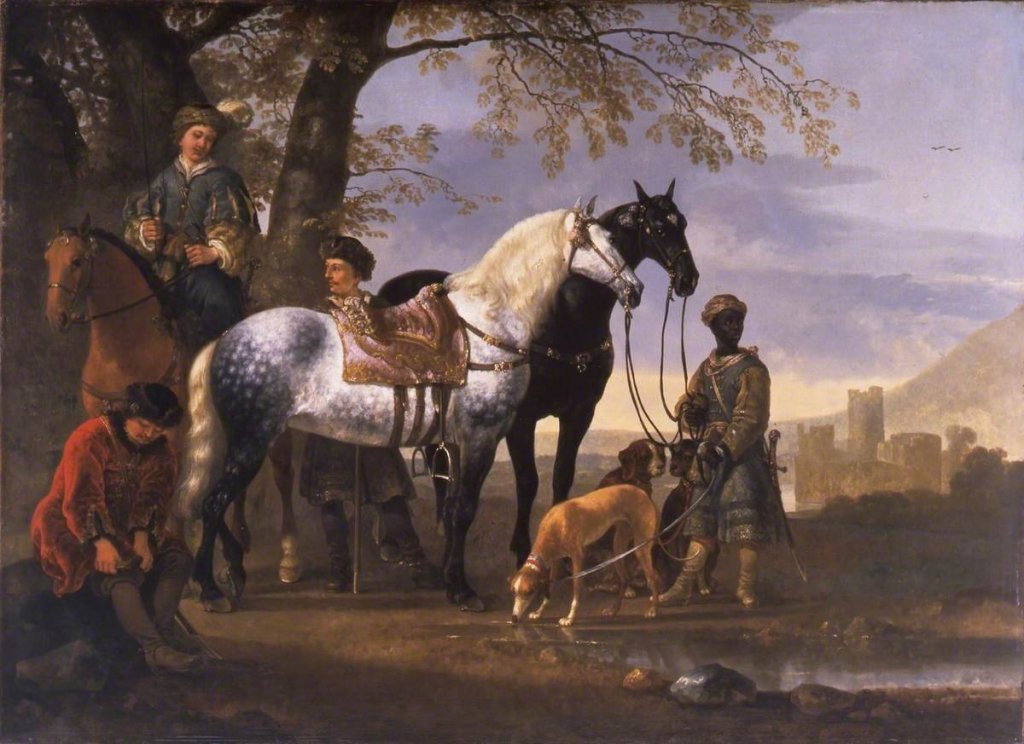

One of my favourite Dutch painters and one who is regarded as one of the finest artists of the so-called “Golden Age” of Dutch painting, a period during and after the later part of the Eighty Years’ War (1568–1648) for Dutch independence is Aelbert Cuyp. Cuyp was born and raised in the town of Dordrecht where he completed paintings for his patrons. His notoriety as a great painter only came the late eighteenth century when British aristocratic collectors began to collect his pictures. His works were admired for the way he combined his figures with his beautiful landscapes and the British aristocracy particularly liked his many depictions of equestrian and hunting themes. Although Cuyp did not visit Italy himself, but he studied those Dutch artists who had been there and who had adopted the poetic light of the paintings by the French artist, Claude Lorrain. In fact, Cuyp was dubbed the Dutch Claude.
In this work we see a party of hunters at rest under the shade of a large tree. The huntsmen we see depicted are the three sons of Cornelis van Beveren, Cuyp’s wealthiest patron. De Beveren was the most powerful man in mid-seventeenth century Dordrecht. On five occasions he had been appointed burgomaster of the town, representative to the Staaten-General and ambassador to England, as well as to France. The van Beverens were not classed as aristocrats but undoubtedly prosperous members of the so-called “striving classes” – the nouveau riche.
The three riders wear fashionable Hungarian hunting costume and are accompanied by an exotically dressed black servant, another sign of their wealth. Why Hungarian costumes? The reason was probably because Hungarians were admired by the Dutch not only for their famed equestrian skills but also for their staunch support of the Protestant cause, which also reflected a newfound sense of Dutch national pride and independence from the Catholic Spanish rule. The depiction shows the hunting party has come to rest in a landscape bathed in a warm golden light more associated with southern Europe than Holland. The right to hunt had once been jealously guarded by royalty and aristocracy, and thus those who hunted were afforded a traditional mark of the very highest status. However, in the region of Zuid Holland, which governed Dordrecht, regulations had been altered in 1623 expanding hunting privileges to owners of country estates and to citizens with an annual income of more than 100 guilders.
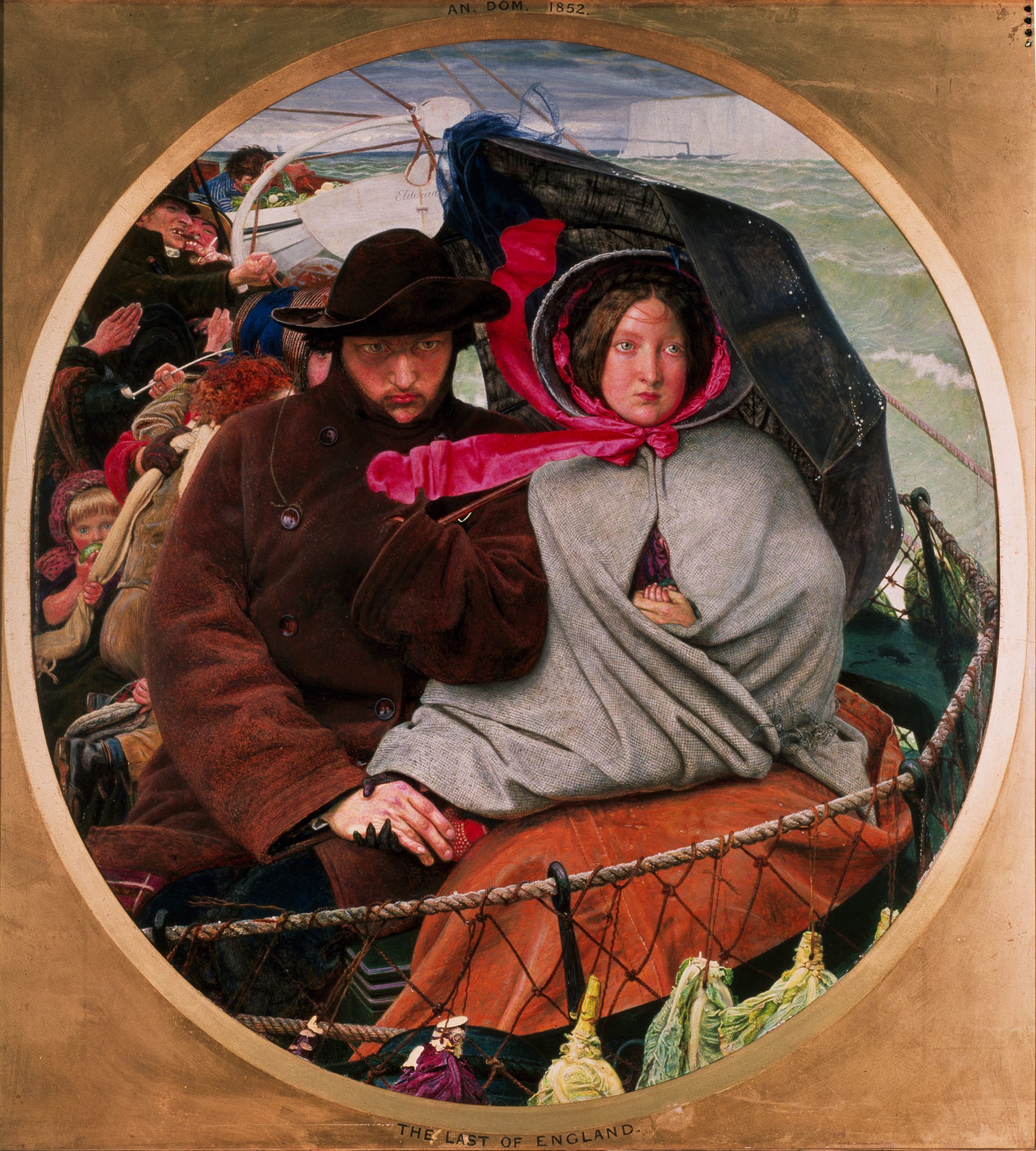

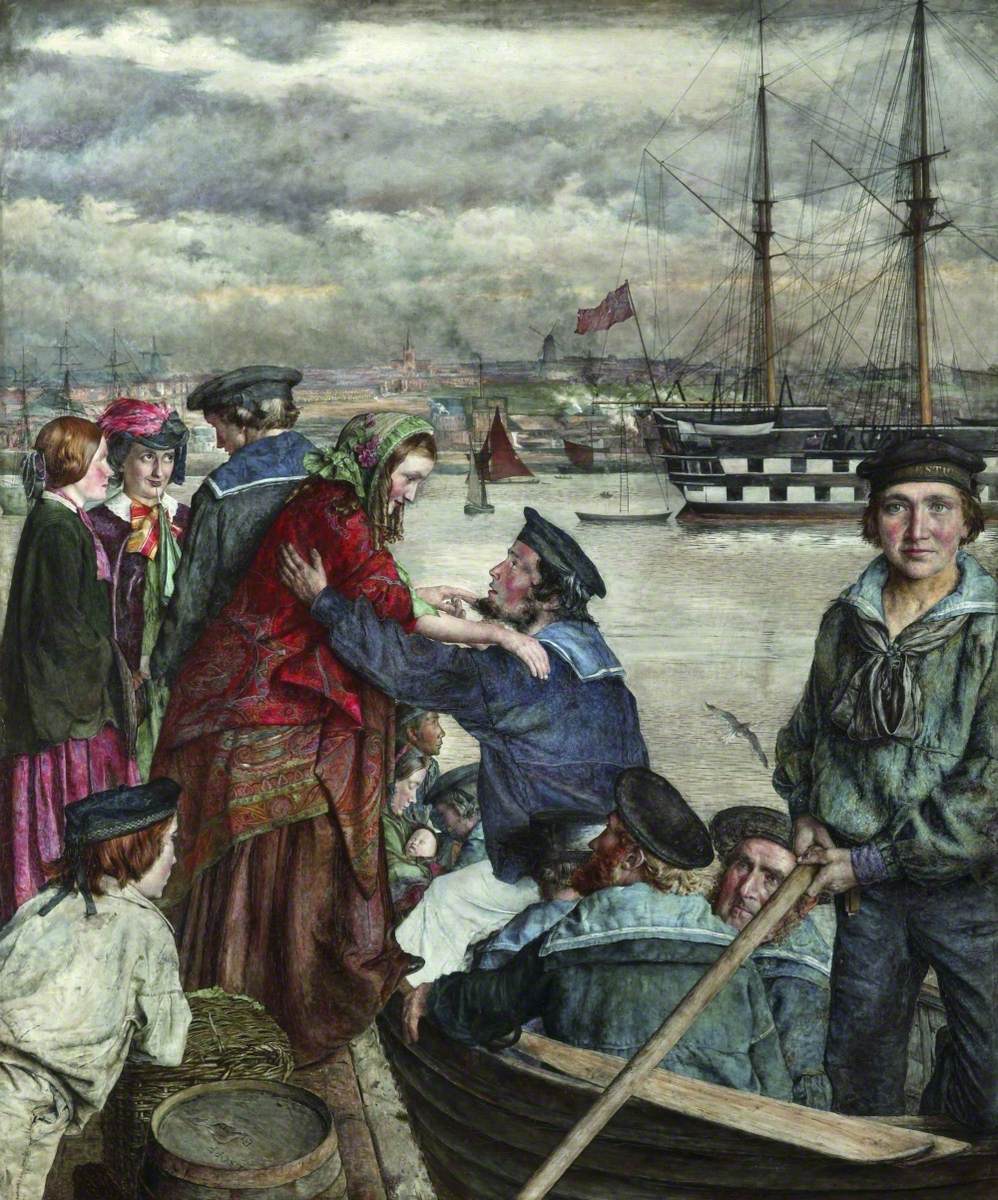
For my last offering I want to look at a painting which is part of the collection usually on display at Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery, but as I said at the start of Part One of this blog, the main Birmingham Museum is closed for renovations and this painting was then loaned out to the Barber Institute. The Last of England was completed in 1855 by the leading Pre-Raphaelite artist Ford Madox Brown and is recognised as a masterpiece of Victorian painting. In the depiction we see a young family huddling together on an open boat as they say farewell to the shores of England and head off to find a better life and a fresh start in Australia. This oval shape of the work which is almost circular, makes us concentrate our focus on the faces of the young couple, who have literally turned their backs on their homeland. In the picture we see a father, mother and two children wrapped up well against the cold sea breezes as the ship leaves the familiar shores of their English homeland. The picture, in some way, was inspired by the emigration to Australia of Maddox Brown’s friend, the sculptor Thomas Woolner in 1852. It is ironic that although Maddox Brown started the painting the year Woolner departed from England, he had returned to England the following year, disillusioned by the false promises of wealth to be had from the gold rush. This was some two years before Ford Madox Brown had completed the work. Thousands of working-class and lower middle-class people, who were totally disillusioned with their life of poverty and slum-like dwellings of England, just packed up the few possessions they had and made this long and momentous journey to the other side of the world. There were about fifty thousand free immigrants arriving each year in Australia. The immigrants were following their dream and although they believed the “grass would be greener” for them in Australia, they would a little as to whether they had made the right decision. Such worry and doubt was etched on the faces of the couple in the painting and in some ways we can empathise with them even though we know they had a free choice in the matter.
In the background we can make out the white cliffs of England as they fade away in the distance. This rock structure of white chalk is often depicted in paintings which highlight the coast of England. In contrast to the white rock formation, we see a black steamship, with billowing black smoke coming from its funnel, heading for port. The ship that the family is sailing on is surrounded by choppy green seas topped with white crests and this may in some way allude to the testing and difficult times ahead for our emigrants. It is interesting to see in the foreground netting around the lifeboat deck, hanging on which are some of the ship’s fresh vegetable supplies. We can see some cabbages and wonder how long they will remain fresh during this long, probably six-to-eight-week journey. If we look behind “our family” we can see a small child wearing a pink bonnet, her right hand grasping the scarf warn by her mother, whilst she eats an apple held in her other hand. Somebody, slightly hidden from view, can be seen smoking a long clay pipe but the characters that amuse me the most, and who are just visible in the background in this painting, are a pair of angry men arguing. The man wearing the top hat has turned away and as he looks back at the departing coastline, waves his fist at it. To this man, his departure from England is a thing of joy and for some reason he seems to be cursing the country he has just left behind.
The main characters in this painting are the father and mother and these are portraits of the artist himself and his second wife and beloved model Emma Hill. The small fair-haired girl in the background eating the apple is their daughter Katty and the baby hidden from view is their son, Oliver. The father is tightly wrapped up in his warm brown woollen coat. His hat is being buffeted by the strong winds but see how there is a “safety string” from the hat attached to and wrapped around a button of his coat. The sight of the father with his grim determined face says it all for me. This is a journey into the unknown and probably he is still racked with doubt with regards his decision to remove his family from the safe environment of their home and whisking them off to a foreign land. It still troubles him but he knows that he and his family cannot go back now and so his resolute look tells us that he is determined to see the venture through to its conclusion. The look on the face of his wife is indicative that she too has concerns about their venture. Her small, slim black leather gloved-hand tightly grasps her husband’s bare workman-like hand, the force of which wrinkles his skin. It is, in a way, a sign that she supports him and it lets him know that fact. Her other hand is holding the tiny fingers of the baby she cradles in her arm and which is hidden from view inside her warm woollen cape. She is wearing a pink bonnet which is partly covered by the grey hood of her cape but we see the pink ribbons of her bonnet flying horizontally in the gale-force wind. It is a touching picture of a family on the move.
This tense and challenging time for our emigrants was mirrored by the testing times felt by the artist himself. Commenting on his frame of mind at the time of the painting, Maddox Brown said:
“…I am intensely miserable, very hard up and not a little mad…”
And it was at these times that he, himself, thought about emigrating to Australia.
That is my final blog about the works held in the Barber Institute of Fine Arts’ collection and if you ever visit Birmingham, England, I hope you will visit this excellent institution.