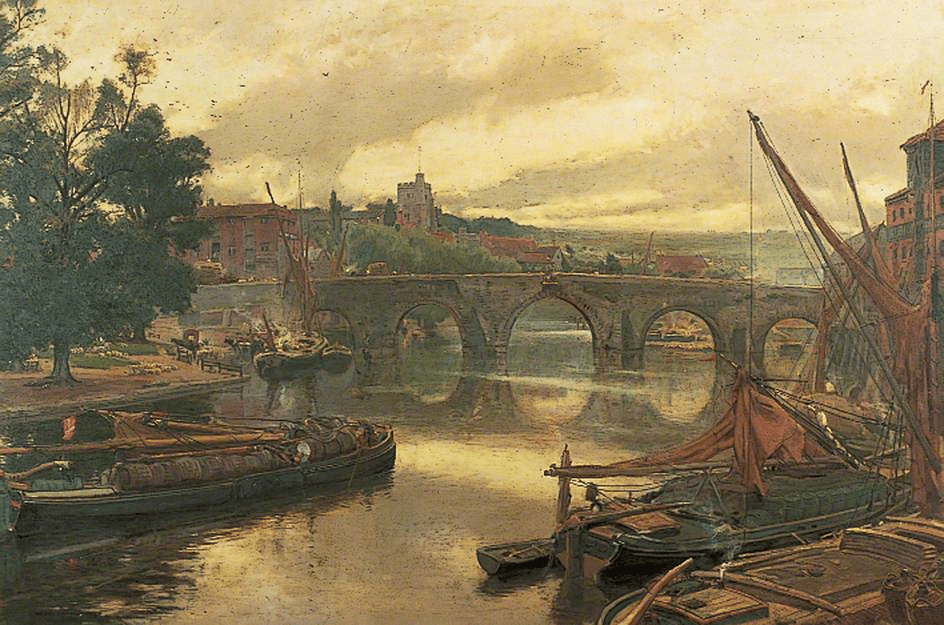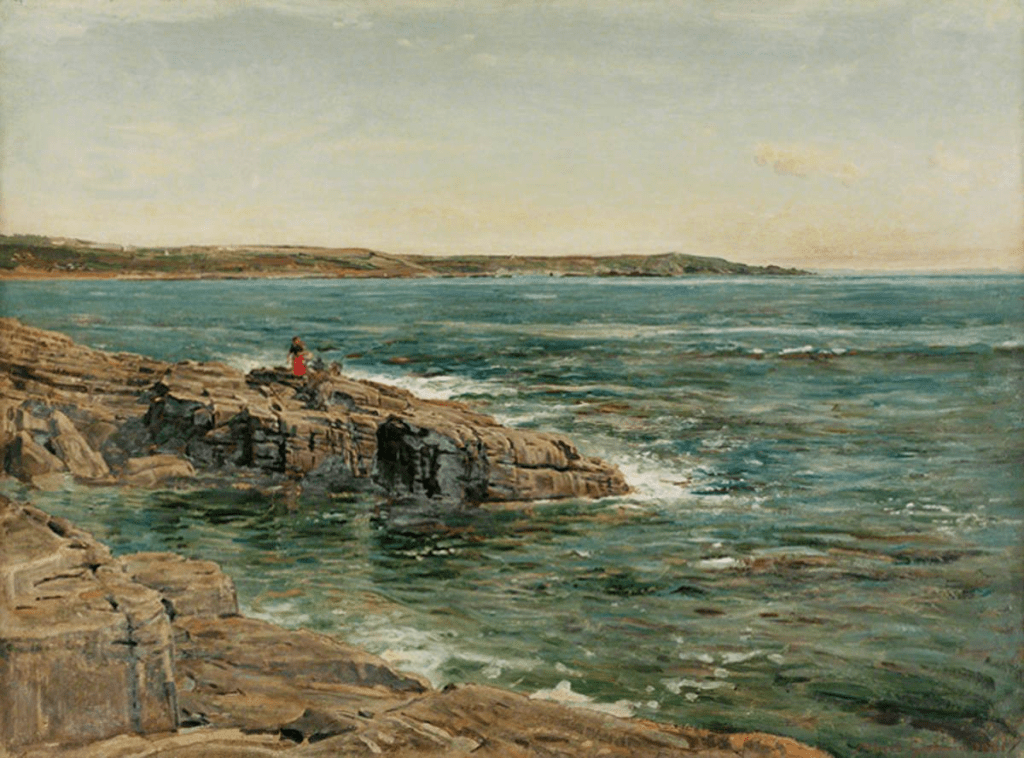Albert Goodwin
The artist I am looking at today is the nineteenth century English painter, Albert Frederick Goodwin, best known for his watercolour landscapes.
The Artist’s Father, Samuel Goodwin by Albert Goodwin (1868)
Albert Goodwin was born at 1 Acton Place, 62 Boxley Road, Maidstone on January 17th 1845. His father was Samuel Goodwin, a builder. His mother was Rosetta (née Smith). Albert was the seventh of eight children, having three older sisters, Emma, Rosetta and Mary Ann and three elder brothers, Charles, William Sidney and Henry (called Harry). He also one younger brother, Frank Alfred. An artistic talent weaved its way through his male siblings. His eldest brother was known for his artistic talent as a young man before he joined the military as a member of the Royal Engineers. Charles became a frame maker and Harry and Frank became professional painters.
Albert was brought up in a devout Baptist household and attended the Bethel Chapel in Maidstone, which his father had built along with its Sunday School in 1934. Albert’s uncle, Thomas Goodwin often preached at the chapel and was its resident organist, which he had also constructed. Albert attended Mr William Henry Wickstead’s School at Rocky Hill House, London Road, Maidstone.
The Old Bridge at Maidstone, Kent, Looking South by Albert Goodwin
Albert became interested in art and at the age of ten when he first exhibited one of his paintings, This was a time at the start of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood and one of its founders, William Holman Hunt had a great influence on young Goodwin. At the age of fourteen Albert Goodwin started an apprenticeship with a local draper but after six months, he realised that the drapery business was not for him as he had set his heart on becoming a professional artist. He just needed a willing teacher. That came by chance, as it is said that whilst painting en plein air in the local woods he was spotted by the Pre-Raphaelite painter, Arthur Hughes who lived in Maidstone with his wife and children. Arthur Hughes was impressed by Albert’s artistic skill and became his first tutor.

Sunrise over the Sea by Albert Goodwin
In 1859 Goodwin completed his painting entitled Bluebell Hill, Maidstone and in 1860 he exhibited his painting, Under the Hedge. On March 18th 1863, Albert’s mother Rosetta died at the age of fifty-eight. During Albert’s early twenties he was introduced to the well-known artist and art critic John Ruskin and on seeing Albert’s work, Ruskin purchased them all for £50 and Albert put the money to good use, funding his five week painting trip to the south coast resort of Hastings. Around the mid 1860s Albert’s tutor, Arthur Hughes, introduced him to Ford Maddox Brown, a Pre-Raphaelite luminary who took Albert on as his pupil in his London studio. Albert soon became acquainted with the other Pr-Raphaelite Brotherhood, such as Rossetti, William Morris, the Scottish artist William Bell Scott and George Price Boyce, the watercolour painter of landscapes.

The Old Bridge at Maidstone, Kent looking South by Albert Goodwin
Later, according to Albert’s daughter Olive, Albert and his brother Harry, went to work in the studio of William Morris’ company in Red Lion Square in London’s Holborn district. In 1864 Albert set off on his first overseas trip, going to Holland where he visited the cities of Amsterdam and Rotterdam and that summer spent time in Jersey. In the Autumn of 1864, he travelled north visiting Newcastle and Durham as well as the coastal town of Whitby

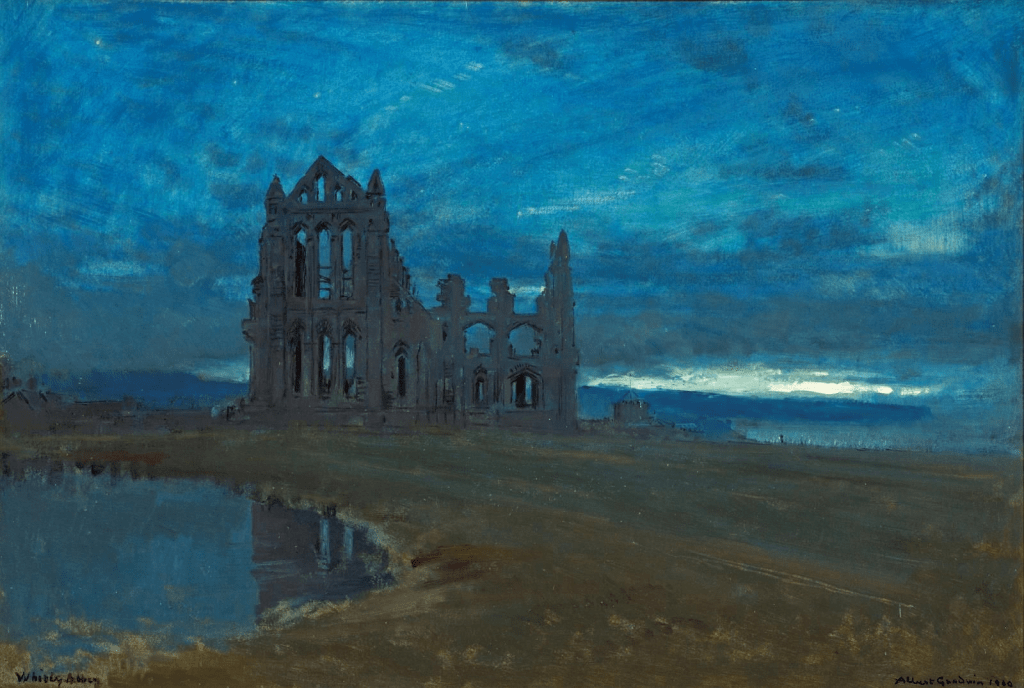
Whitby Abbey a watercolour by Albert Goodwin
Albert Goodwin completed a colourful watercolour of Whitby Abbey as seen from the east. The abbey which had been founded in 657 by St Hilda was later destroyed by marauding Danes in 867. This view is of Whitby Abbey from the east. The ruin depicted in this watercolour is as it is now after one of the towers collapsed in 1830. Goodwin painted another version of the Abbey in 1910 but this was completed using oils and is now housed in the Victoria Gallery, Bath. Albert Goodwin’s diary entry of July 22nd 1909 declares his love for Whitby. He wrote:
“…Whitby once again…I am again inclined to repeat myself in the belief that one or two things in it (for colour) are as good as anything can be…”
Whitby Abbey by Albert Goodwin (1910)
Goodwin always loved to depict dramatic, poetic landscapes. In the 1910 version of Whitby Abbey the thoroughly radiant deep blue of the sky in this work is so typical of his work. Albert liked Whitby Abbey as a subject for painting because of its ruinous manifestation, but also because he was a deeply religious man, and had an interest in spiritual subjects. Goodwin had painted many scenes featuring the abbey over the previous fourteen years.
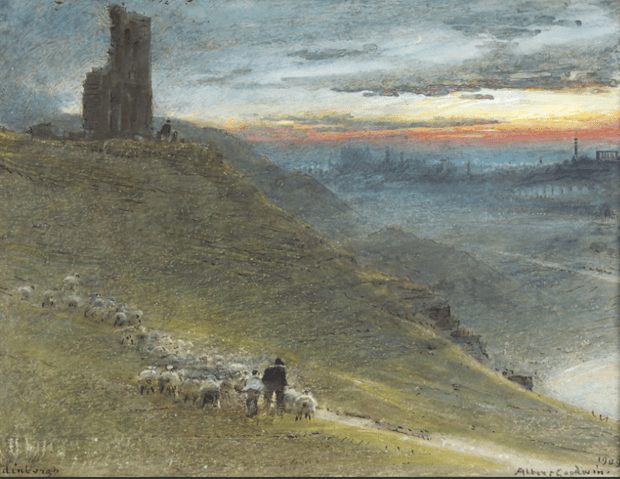
A Prospect of Edinburgh from the East by Albert Goodwin (1909)
Albert Goodwin carried on painting in the 1860s and exhibited his work at many exhibitions including the Dudley Gallery in London. On February 16th 1867 Albert married Mary Ann Lucas, who was the eldest daughter of George Lucas, a fruiterer from Brighton and a year later his brother Harry married Henrietta Lucas, the sister of Albert’s new wife. Sadly, on December 13th 1869 Albert’s wife Mary Ann died, aged twenty-nine of peritonitis. Albert and Mary Ann had no children. Around this time Albert went to live with Arthur Hughes and his family in West Brompton, London and he was employed as Hughes’ studio assistant.

Ely Cathedral by Albert Goodwin
In 1871 Albert went on another European trip visiting Bruges. That year he was elected Associate of the Society of Painters in Watercolours and at the time his address was given as Maltravers Street, Arundel, Sussex where he lived with his brother Harry and his wife Henrietta. Sadly, Henrietta died that year, less than two years after her sister had passed.
The Medway at Maidstone by Albert Goodwin (1871)
Almost ten years had passed since Albert had first met John Ruskin and in Spring 1971, Ruskin offered Albert a job as his assistant and asked that he came to work with him at his home in Abingdon, Oxfordshire. At the Royal Academy annual exhibition in 1871 Albert Goodwin exhibited his painting entitled The Medway at Maidstone.
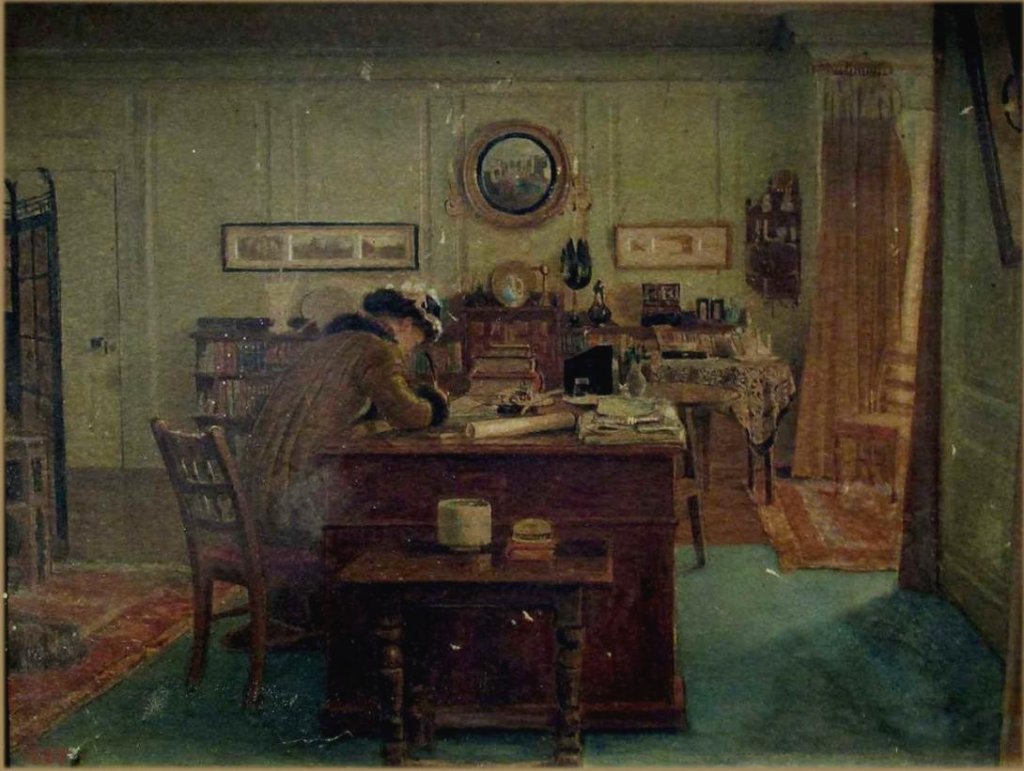

The Drawing Room at Dixton Manor (Drawing Room at Dixton Manor with K.M.G. writing) by Harry Goodwin (1883)
In 1872 Albert’s brother Harry married for the second time following his first wife’s death. His new wife was fellow painter, Kate Malleson. Harry depicted his wife writing at a desk in Dixton Manor.
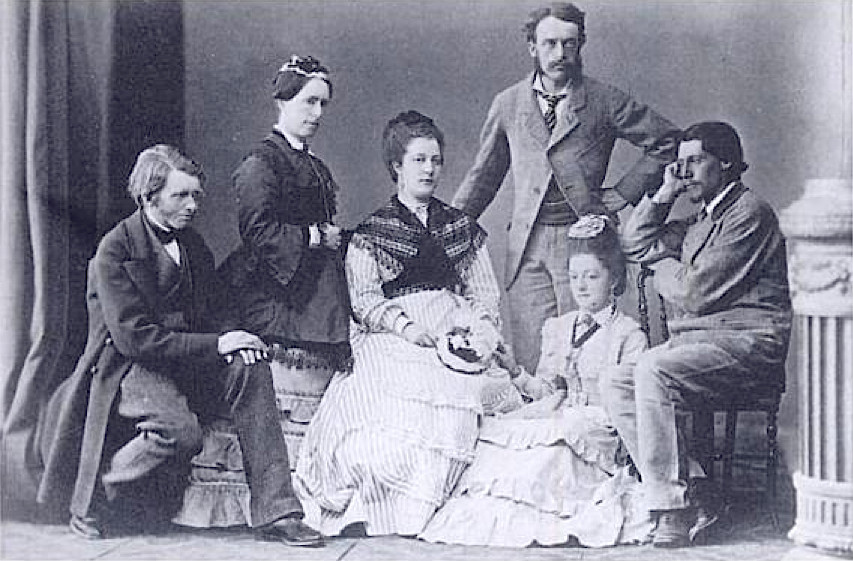

From left to right: John Ruskin, Mrs JC Hilliard, Mrs Joan Severn, Arthur Severn, Constance Hilliard, Albert Goodwin.
Albert Goodwin’s friendship with John Ruskin continued and, along with Ruskin’s cousin Joan Severn and her husband Arthur Severn, visited Matlock Bath and the following year Albert Goodwin and Ruskin travelled to Italy and Switzerland.
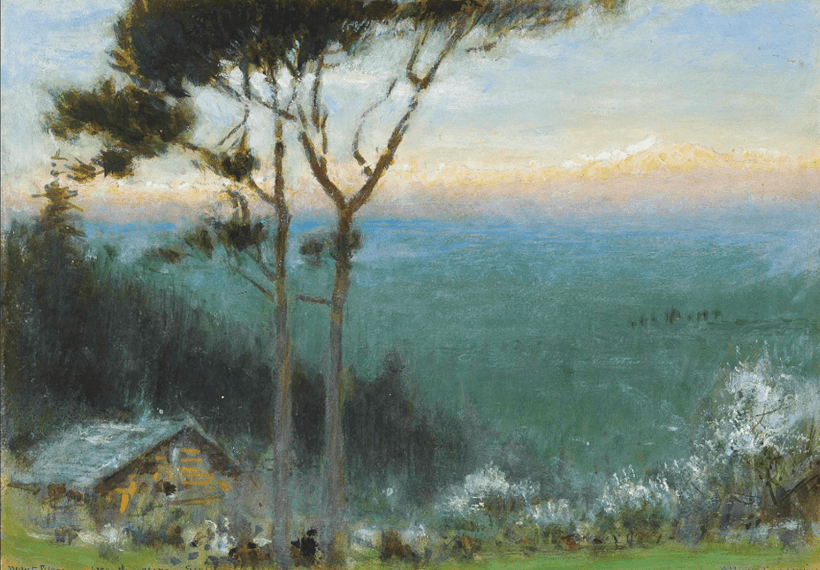
Mont Blanc from the Sèleve, near Geneva
In 1873, Albert Goodwin stayed for three months in the Swiss village of Simplon which lies close to the Italian border.
An Arabian Night, Cairo by Albert Goodwin (1876)
In 1873, like his brother the year before, Albert Goodwin a widower for four years, married his second wife, Alice Desborough at Holy Trinity Church in the West Devon village of Gidleigh. The couple went on to have seven children, two sons and five daughters. In 1876, Albert and Alice travelled to Marseille before boarding a ship for Egypt. They also called at Gibraltar, Naples and Crete.
Blue Water in Mounts Bay, Cornwall by Albert Goodwin (1881)
Albert Goodwin had first met the naturalist, Charles Darwin when he was introduced to him by John Ruskin. He visited Darwin at his Kent home, Down House.
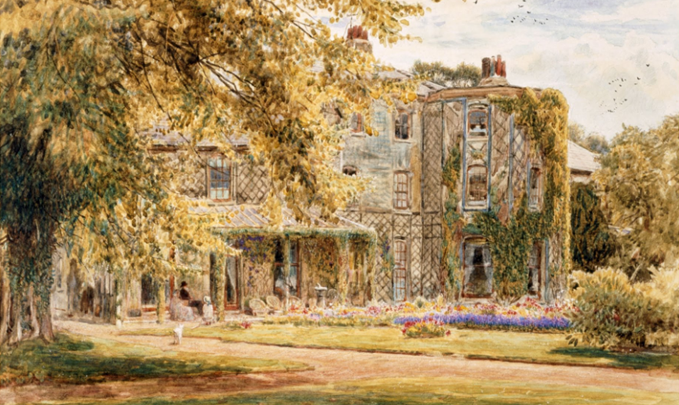

Down House from the Garden by Albert Goodwin (1880)

Down House by Albert Goodwin (1880)
Whilst there he made sketches of the house and gardens and later completed two watercolour paintings of Darwin’s residence, which had been built in the early 18th century, and remained Darwin’ and his wife, Emma’s home for forty years until his death in 1882. It was here that Darwin developed his theory of evolution by natural selection and wrote his ground-breaking work On the Origin of Species in 1859.
Ilfracombe by Albert Goodwin (1884)
Albert and his wife and children left London and moved to Montpelier Terrace Ilfracombe in 1877. He continued on his painting trips around Britain and further afield to France, Switzerland and the Italian Lakes often accompanied by John Ruskin and Arthur Severn, sometimes accompanied by his brother Harry. During these trips Goodwin made a large number of annotated sketches and watercolour studies direct from nature, a method he used, alongside working from memory, throughout his career. Ruskin was fascinated by the large number of sketches, which he termed “flying sketches”, which Goodwin produced on a daily basis. Goodwin was happy with his system and in his 1917 dairy entry, he wrote:
“…To me this method of work is one of the happy things of the art that I practise, for I get the realisation of a place twice over, and often the memory makes the scene a better one than the first experience…”
Meanwhile his wife Alice was at home in Ilfracombe with their seven children, Ivy, Olive, Edytha, Albert, Christabel, Alice and Harold and their two servants, one a cook and the other a nurse. A few doors down from them were Alice’s mother and sister Mary.

Florence, Evening by Albert Goodwin (1896)
In 1881 Goodwin was elected a member of the Royal Society of Painters in Watercolours. Albert Goodwin was continually influenced by John Ruskin who was constantly advising him with regards artistic techniques. Goodwin was a master of depicting topographical and landscape views. For him, it was all about colour, and tonal values. Ruskin was pleased and proud of his protégé and was constantly talking about the art of Turner and proudly showing off his own collection of Turner’s work. Albert Goodwin wrote about the influence Turner had upon him in a diary entry in 1911. He wrote:
“…I sometimes wonder if the spirit of old Turner takes over my personality. I often find (or think I find) myself doing the very same things that he seemed to do…”
Art critics of the time often likened his work to that of Turner. In The Standard of October 1893, the art critic wrote:
“…In water-colour drawing Mr. Albert Goodwin is the legitimate successor of Turner…”

The Source of the Sacred River by Albert Goodwin (1900)
Albert Goodwin travelled to India in 1895 and one of the works from this trip was The Source of the Sacred River which he completed in 1900 and was exhibited at the Royal Academy that year. The source in the title refers to the source of the River Ganges, which is regarded by the Hindu population of India as sacred, is at Lapthal, is in the Himalayas on the frontier between India and China. Of the painting, the art critic of The Athenaeum, a British literary magazine, in 1900 wrote:
“…Allegorical landscape, and still more allegorized landscape painting, is a difficult and particularly uncertain sort of art in which Mr Goodwin, its most accomplished practitioner amongst us, is one of the few who contrive even to approach success. The Source of the Sacred River is almost as suggestive, quite as well painted, and much more understandable. In general, it does not differ from a score of similar works by Mr Goodwin, who is not content with painting nature so admirably that few rival him and leaving to her sympathetic lovers the task of recognizing the pathos and poetry which, so to say, harmonizes itself with the spectator’s mood. There is nothing to tell us that the stream Mr Goodwin depicted so rarely is sacred in any exceptional sense, but there is much we can be grateful for in its abundant and sumptuous harmonies of colour, form, and light, and the dignity of its masses…”

Rye – The Winter’s Tale by Albert Goodwin (1920)
Albert Goodwin carried on with his painting trips around Britain and across the world, visiting South Africa, West Indies, Australia and New Zealand. His works were shown at a multitude of exhibitions and were always appreciated by critics and visitors alike. Goodwin died at his home, Ellerslie, in Bexhill-on-Sea on April 10th, 1932 aged 87.
Much of the information regarding the life and times of Albert Goodwin came from the Chris Beetles Gallery catalogue, Albert Goodwin RWS (1845-1932). The John & Mary Goodyear Collection, which I found in a charity shop in London.
and the website