Blanche Lazell during her time at the Art Student League, New York
Cornelius Carhart Lazzell, a direct descendent of pioneers who settled in Monongolia County, West Virginnia, after the American Revolutionary War, married Mary Prudence Pope and the couple went on to have ten children, three sons and seven daughters. The ninth child was Nettie Blanche Lazzell who was born on October 10th 1878 and it is she who is the subject of today’s blog.
The Lazzell family, who were devout Methodists, lived on a large farmstead near Maidsville, West Virginia, which lies close to the Pennsylvania border. The town was thought to have been named Maidsville on account of there being a large proportion of “old maids” among the first settlers ! Her education during her early days was at the one-room schoolhouse on the property where students from the first through to eighth grades were taught from October through February.

Amarylis by Blanche Lazzell (1930)
In 1891, when Blanche was just twelve years old, her mother died, aged 48. In her early teens Blanche experienced hearing problems and became partially deaf and it was not until a year later that a Baltimore doctor was able to remedy her illness. In 1893, at the age of fifteen, Blanche enrolled at the West Virginia Conference Seminary, which is now the West Virginia Wesleyan College. From there, in 1899, she transferred to the South Carolina Co-Educational Institute in Edgefield. Once she graduated from the Institute, she became a teacher at the Red Oaks School in Ramsey, South Carolina. In spring of 1900, she returned to her Maidsville home, where she tutored her younger sister, Bessie. In 1901, she studied art at West Virginia University and did well, receiving a degree in art history and the fine arts in 1905. She continued to study at WVU on a part time basis until 1909, allowing her to broaden her knowledge of art and twice substituting as a painting teacher.
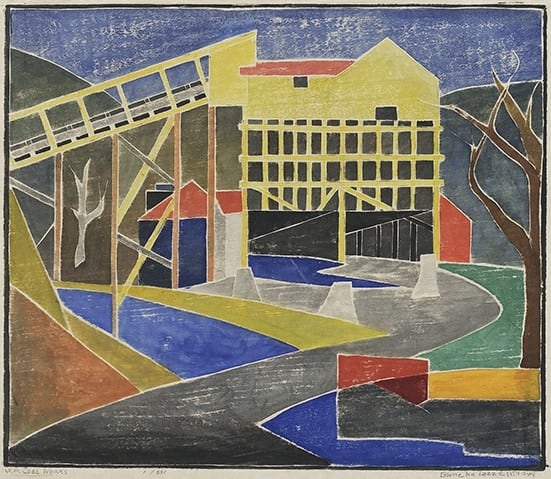

West Virginnia Coal Works by Blanche Lazzell (1949)
In 1908, at the age of thirty, she moved to New York and enrolled at the Art Students League. The League had been formed in 1875 to provide more variety and flexibility in education for artists than it was felt the National Academy of Design provided. This breakaway group of art students included many women, many of whom, in the late 1890s and early 1900s, took on key roles. In Marian Wardle’s book: American Women Modernists: The Legacy of Robert Henri, 1910-1945. She recounts the words of the American artist Edith Dimmock regarding the atmosphere at the Art League:
“…In a room innocent of ventilation, the job was to draw Venus (just the head) and her colleagues. We were not allowed to hitch bodies to the heads——yet. The dead white plaster of Paris was a perfect inducer of eye-strain and was called “The Antique.” One was supposed to work from “The Antique” for two years. The advantage of “The Antique” was that all these gods and athletes were such excellent models: there never was the twitch of an iron-bound muscle. Venus never batted her hard-boiled egg eye, and the Discus-thrower never wearied. They were also cheap models and did not have to be paid union rates…”
During her time at the Art League Blanche studied under Kenyon Cox and William Merritt Chase and one of her fellow students was Georgia O’Keeffe.

SS. Ivernia
On July 3rd 1912, Lazzell set sail on an American Travel Club cruise on the Cunard liner SS Ivernia, crossing the Atlantic and arriving in England. From there Blanche visited the Netherlands, Belgium and Italy. She was fascinated by the architecture of the various churches she visited.

Sailboat by Blanche Lazzell
In August she left the tour party and travelled to Paris. She then stayed in a pension in Montparnasse on the Left Bank. She moved into the Students’ Hostel on Boulevard Saint-Michel, one of the two major streets in the Latin Quarter of Paris, running alongside the Luxembourg Gardens. During her stay in the French capital, she took lessons at the Académie de la Grande Chaumière, Académie Julian, and Académie Delécluse. She eventually established herself at the Académie Moderne where her tutors were the post-impressionist painters Charles Guérin and David Rosen. Of all the art tuition she received in Paris she was the most contented with the ideas and techniques behind the Parisian avant-garde art, a genre which pushed the boundaries of ideas and creativity, which she learnt about at the Académie Moderne.

The Monongahela River at Morgantown by Blanche Lazzell (1939)
Blanche returned to America on the White Star passenger liner, SS Arabic, at the end of September 1913. On her return to America Blanche went to live with her younger sister Bessie in Morgantown. During her European travels Blanche built up a portfolio of sketches and paintings enough for her to have a solo exhibition in December 1914. To make ends meet, she rented a studio in town and taught art as well as selling her hand-painted chinaware.
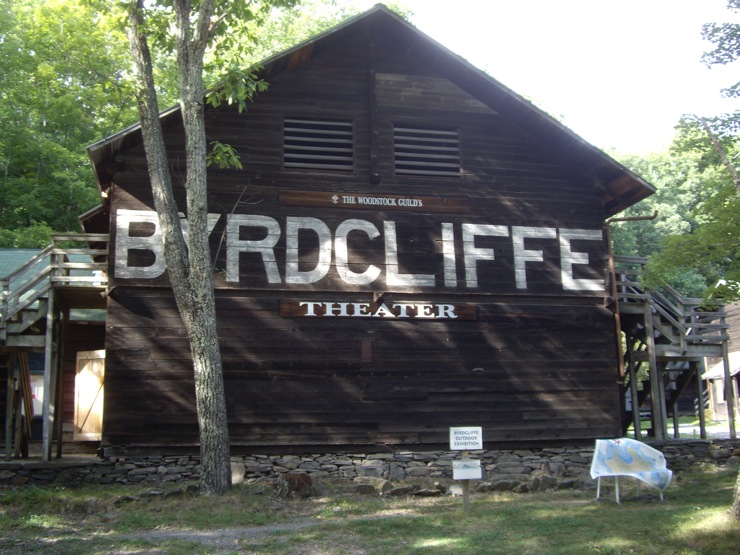

Byrdcliffe Artist Colony

Byrdcliffe Artist Colony
In the summer of 1917, Blanche spent time at the Byrdcliffe Arts Colony, an artists’ colony just outside Woodstock, New York. The Byrdcliffe Art Colony was founded by Jane Byrd McCall and Ralph Radcliffe Whitehead and colleagues, Bolton Brown, an artist and Hervey White, a writer. The name of the colony came from an amalgamation of Jane and Ralph’s middle names. It was founded in 1902 and the complex was formed of a number of Arts and Crafts cottages. It was there that visual artists, poets, and musicians found their muses and spent time creating works of art, music and poetry. In later times famous people, such as Bob Dylan, writer Thomas Mann, and even famous actors, Helen Hayes, and Chevy Chase, spent time at Byrdcliffe. Blanche studied under the Belgian-born artist William Schumaker who whilst in Paris had come into contact with European avant-garde artists. On his return to America he brought with him modernist principles. The term modernism in art was a rejection of history and conservative values such as realistic depiction of subjects; it was an innovation and experimentation with form, that is to say, the shapes, colours and lines that make up the work have a tendency towards abstraction. From 1913 to 1931, Schumaker was artist-in-residence at the artists’ colony at Byrdcliffe.

Still Life by Blanche Lazzell
In 1918 Blanche Lazzell left Morganstown and moved permanently to Provincetown, which is situated on the northern tip of Cape Cod, Massachusetts, a place she had previously visited in 1915. She made the town her summer base while wintering back in Morganstown and Manhatten.
Blanche Lazzell outside her Fish House studio, Princetown
She purchased an old fish house which overlooked the harbour of Provincetown and converted it into her studio. She immersed herself into the local art scene and became a member of the Provincetown Art Association and the Sail Loft Club, Provincetown’s women’s art club. She also became involved with the Provincetown Printers, a group of artists, most of whom were women, who created art using woodblock printing techniques. It was a refuge for artists and a lively hub of experimentation and innovation. It became known as Princetown Print. It was a white-line woodcut print, but it differed from woodcut printing as rather than creating separate woodblocks for each colour, one block was made and painted. Small groves between the elements of the design created the white line. In the main the artists often used soft colours, so that the finished product sometimes had the appearance of watercolour paintings. Recalling her first summer at Provincetown, Blanche Lazzell fondly remembered her time there saying:
“…Hundreds of American artists who had been living in Europe before the first World War flocked to Provincetown. This quaint old seaport town, famous for the first landing place of the Pilgrims, was already an art colony…To be in Provincetown for the first time, in those days, under ordinary conditions was delightful enough, but that summer of 1915, when the whole scene, everything and everybody was new, it was glorious indeed–”
Untitled Abstract work by Blanche Lazzell
Lazzell returned to Paris in 1923 and studied with both Fernand Léger, Andre Lhote and Albert Gleizes, who was said to be one of the founders of cubism. By 1925, Blanche had mastered the static and shuffled planes of Synthetic Cubism, to which she added her own distinctive colour palette and elegant receptivity. Blanche defined Cubism as:
“… the organization of flat planes of colour, with an interplay of space, instead of perspective…”
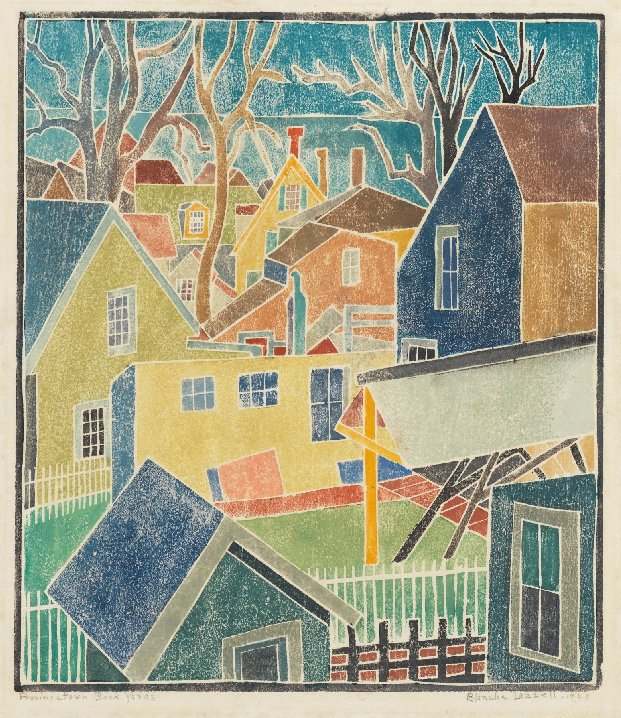

Princetown Backyards by Blanche Lazzell
This was a style which was excellently suited to her woodcuts and often mirrored the angular patterns of the Provincetown houses, rooftops, and wharves which are depicted in many of her woodcut prints. It is also interesting to note that Lazzell was a passionate gardener, and images of flowers often featured in her work but even these images, although based on direct observation, were changed into recurrent interactions of abstracted shapes.

The Flaming Bush by Blanche Lazzell (1933) At auction it realized $87,500.
Blanche’s younger sister Bessie gave birth to a son, in August 1924 and Blanche decided to return to Morganstown to help her. Lazzell also became a mentor and role model for her niece, Frances Reed, the daughter of her sister Myrtle. Blanche eventually returned to Princeton in 1926 and one of her first tasks was to pull down her previous studio, the Fish House, as it was getting too cold in the winter months due to the numerous drafts.

The Violet Jug by Blanche Lazzell
Trees by Blanche Lazzell (c.1930)
In 1928 she was invited to be on the board of directors of the international art group, Société Anonyme. Lazzell later joined the New York Society of Women Artists and the Society of Independent Artists. In the 1930s, Blanche took part in an exhibition called Fifty Prints of the Year where she exhibited her compositions The Violet Jug and Trees.
Ecuyère (Horsewoman) by Albert Gleizes (c.1923)
Around the same time she produced a number of pure abstract compositions which shows the influence of Albert Gleizes.
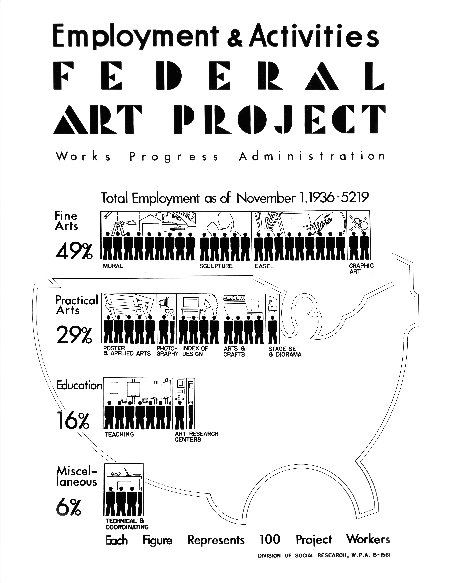
In 1934, America was in the midst of the Great Depression and Blanche Lazzell was one of two West Virginian artists who received Federal Art Project grants through the Works Progress Administration. This was due to the American government which hired hundreds of artists who collectively created more than 100,000 paintings and murals and over 18,000 sculptures to be found in municipal buildings, schools, and hospitals in all of the 48 states. President Franklin Roosevelt sought to put as many unemployed Americans as possible back to work and to buoy the morale of the citizens. Some of the 20th century’s greatest visual artists were employed by the FAP, along with many nascent Abstract Expressionists.

Blanche Lazzell on her porch of her Provincetown studio, 1942

Blanche Lazzell outside Little Church around the Corner, New York
In May 1956, Blanche Lazzell’s health began to fail and she was taken to a hospital with a suspected stroke. Lazzell died on June 1st 1956 and she is buried next to her father in Bethel Cemetery in Maidsville. She was aged 77.