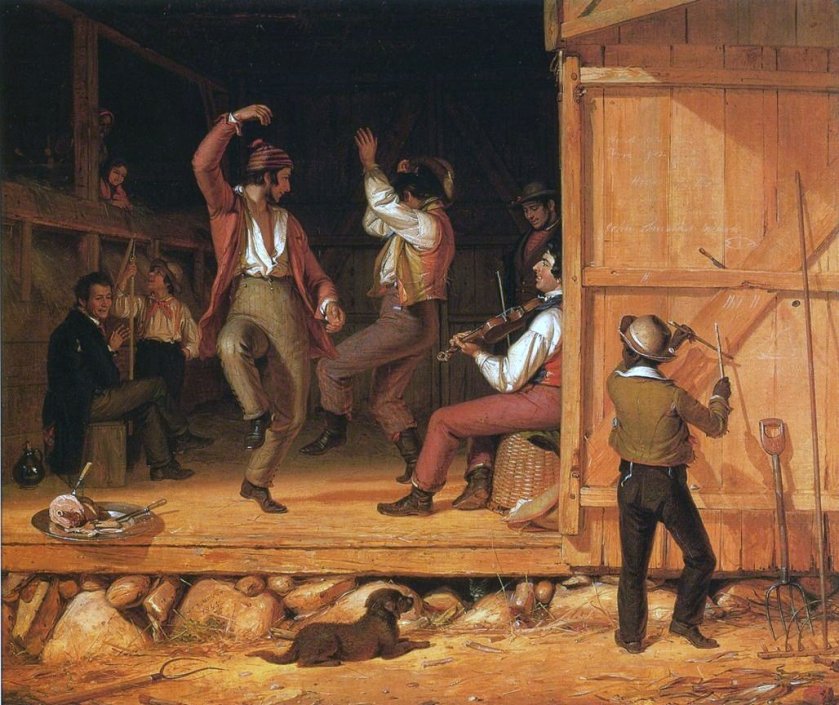
This is Part 3 of my blog featuring the nineteenth century American genre painter and portraitist, William Sidney Mount. In my first blog about this great painter I looked at his genre works which featured his great love of music and musicians. My second blog featured some of his early biblical works and his portraiture and in this last offering I am reverting to his love of genre painting and some of his best known works of art. In the first part of this trilogy I talked about the “heyday” of genre style paintings from the Low Countries in the seventeenth and eighteenth century. They often featured taverns and interiors of homes and were often dark and looked at the life of the peasant classes with a degree of sombreness. Mount’s genre paintings on the other hand, were more light and joyful.
William Mount had entered the National Academy of Design in New York in 1829 and during his time there his studies incorporated the study of European paintings and engravings as well as the study of classical statuary. Whilst he was studying at the Academy he was living with his uncle, Micah Hawkins, who was an amateur poet, and owned a tavern and grocery shop in New York. Micah’s greatest love was the theatre and he would produce plays in which he would combine music and storytelling and the finished opus would have political and national connotations. His nephew William was influenced by this and the American life theme and social comment featured in many of his works of art.
William Mount completed his studies in 1829 and returned home to Long Island where he set about building up a portfolio of paintings which included portraits of relatives and some of the workers on the family farmstead. In 1832 he was elected to the Academy and for the next thirty-three years exhibited there regularly. William Mount was very aware of the class structure in his country. He could see the social gap between the urban citizens and those who worked the land. Towns expanded and became cities and those who worked and lived in these cities became wealthier than their poor relations that remained in the countryside to work the land. With financial wealth came cultural wealth and soon the division between the urban dwellers and the country folk became more obvious.
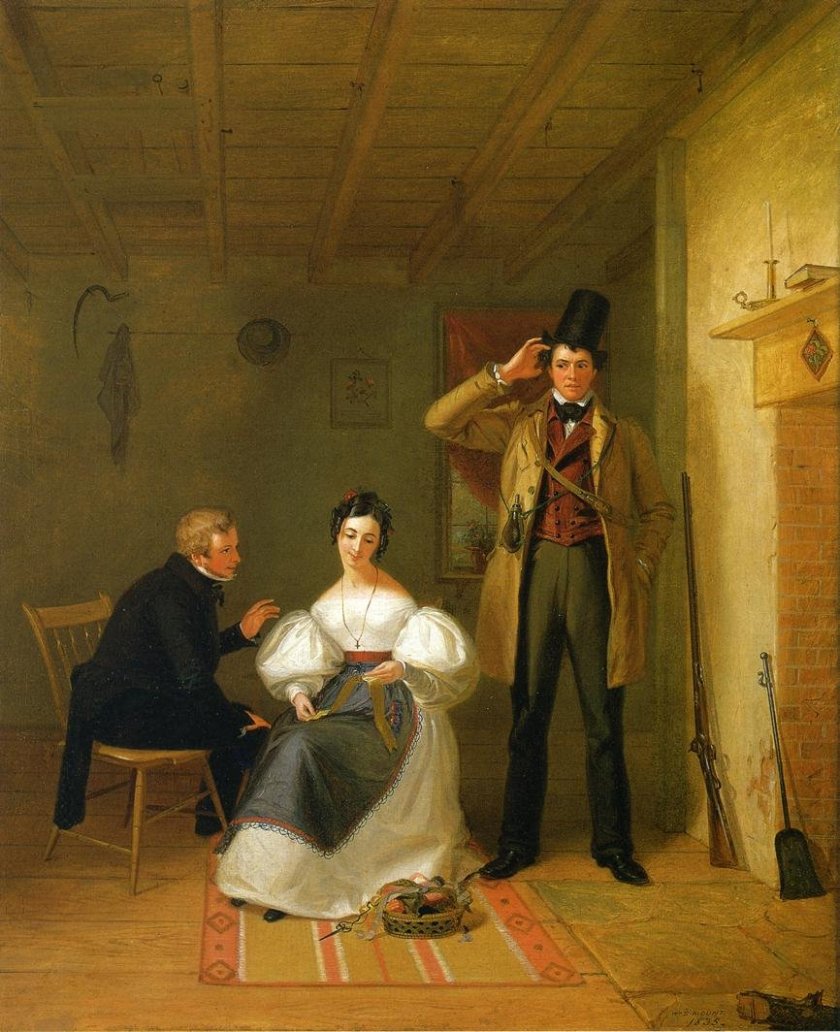

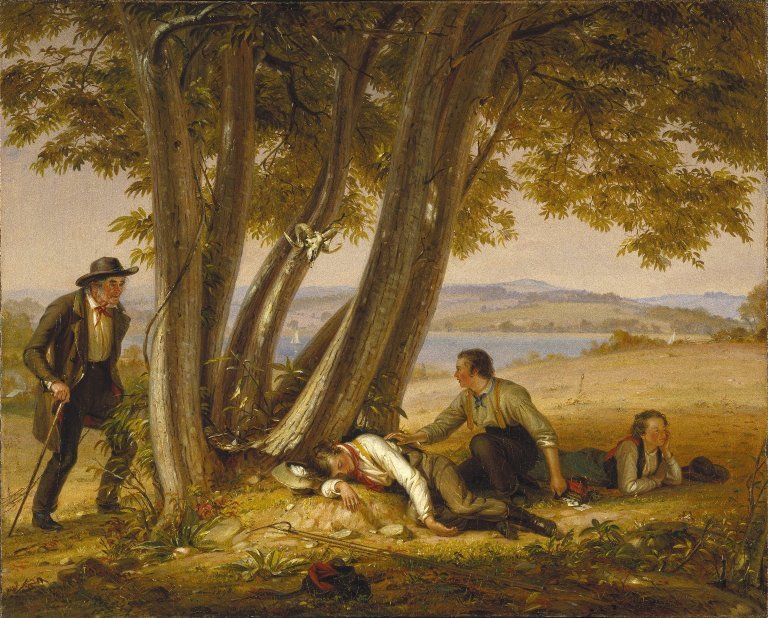
The painting by Mount, which best looks at this cultural difference, was one he completed in 1835, entitled The Sportsman’s Last Visit. In the depiction we see Mount has contrasted the genteel elegance of the city gentleman, dressed immaculately in black, who sits next to the lady and engages her in conversation. She demurely, but coquettishly, looks away from him supposedly concentrating on a piece of fabric which she has been working on. There is a slight smile on her lips indicating that she is enjoying the man’s attention. She completely ignores the man whom we see standing on the right hand side. He is scratching his head, perplexed by what he is witnessing. He is a local country boy. He has none of the airs and graces of the city gentleman but he cannot understand why the lady should favour the city gentleman over him. Mount often painted scenes from rural life with loving depictions but in this one he was hinting at things were about to change. If money was to be made, maybe city life was the way to do it. On an artistic note I love how Mount has cleverly used the ceiling beams to demonstrate a feeling of depth in the painting.

Another of Mount’s painting which recorded changing time, was entitled California News which he completed in 1850., This was in the middle of the chaotic California Gold Rush In the picture we see a local man, with the New York Daily Tribune newspaper in his hands, reading aloud about the gold rush in California. Local people stand around agog with excitement but what is more interesting is the picture above the door which depicts a couple of pigs which is probably a reminder that many who raced across country to make their fortune were simple pig farmers who struggled to eke out a living wage for their family.
In 1834, William Mount met Luman Reed. Luman Reed, who was born in 1784, was a farmer’s son from upstate New York. He made a fortune in the wholesale grocery business in New York City and through his love of paintings, built up one of America’s most important collections of paintings, concentrating on American art of his own time. He became patrons to such American artists as Asher Durand, Thomas Cole and George Flagg, just to name a few. Luman Reed liked the works of William Mount and bought two of his paintings, Bargaining for a Horse and The Truant Gamblers (Undutiful Boys).
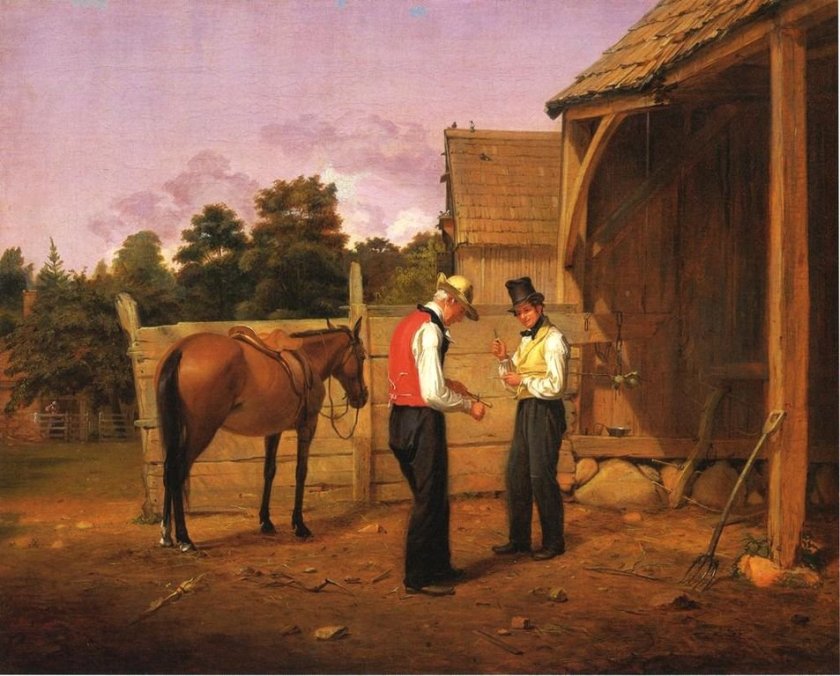

The painting, Bargaining for a Horse, which he completed in 1835, is probably one of the best known and best loved of William Mount’s works of Art. The original title for the painting was Farmers Bargaining but when the painting was published as an engraving five years later the title was changed to Bargaining for a Horse. When Luman Reed received the completed painting he was delighted and commented that this was “a new era of the fine arts of the country”. There was a political connotation to this work by Mount as the phrase “horse trading” referred to a promise of material benefit in return for political support. Mount’s original title for the painting did not so much allude to that colloquialism but the changed title in 1840 made it more apparent to all those who viewed the work.
Look at the two men. There is no eye contact between the seller and the buyer. Both concentrate on the whittling of the wood almost as if the sale is of little importance. Maybe the concentration they have given to the wood carving gives them time to think about their next step in the bargaining process. It is a beautifully composed work which has been skilfully painted. It is a painting which combines humour, warmth, and razor sharp observation.
Luman Reed was delighted with his painting and wrote to William Mount in November 1835:
“…This is a new era of fine arts in this Country, we have native talent and it is coming out as rapidly as is necessary. Your picture of the ‘Bargain’ is the wonder and delight of everyone that sees it…”

A month later Mount wrote to Luman Reed telling him of the other painting he had completed for him. He wrote:
“…You will receive with this letter a picture: ‘Undutiful Boys’. Boys hustling coppers on the barn floor……….My price for the picture ‘Undutiful Boys’ two hundred and twenty dollars. I hope the picture will meet your approbation…”
A week later Luman Reed wrote back to Mount:
“… I yesterday received your much awaited letter of the 4th Instant with your beautiful Picture of the ‘Undutiful Boys’. To say that this picture is satisfactory is not enough, and the least I can say is that it pleases me exceedingly. It is a beautiful specimen of art. The interior is far superior to any thing of the kind I have seen, it is all good and therefore I need not particularize, the price is perfectly satisfactory and the money is ready for you any day you want it. I pride myself on having now two of your Pictures and what I consider your best productions and hope yet to have more but it is no more than fair that others should be gratified too and I must wait until you execute some other commissions…”
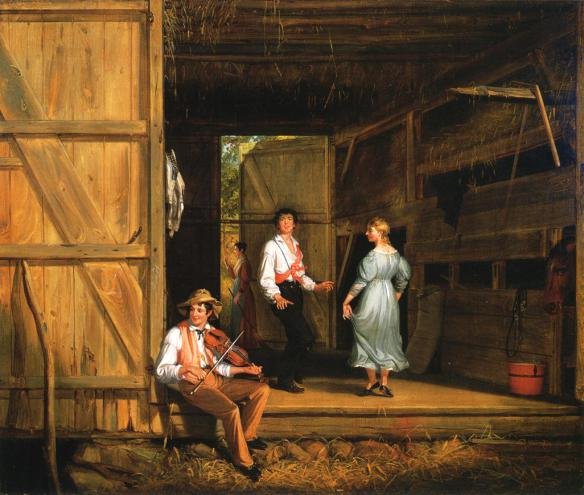
In the painting we see a group of young boys who have decided to abandon their farming chores and, instead, decided to spend some time gambling for pennies. Happy with their decision to forego work, what they do not realise is that the farmer is approaching, pitchfork and switch in his hands and punishment is imminent. This type of genre painting featuring life on the farm was popular in those days as life was changing from an agrarian one to an industrial one and rural life soon became somewhere to relax and enjoy and for people like Luman Reed who was brought up in the Hudson River town of Coxsackie and later moved to the hustle and bustle of New York City, paintings depicting life on the farm may have brought him fond memories of his childhood days. For him this painting was a nostalgic one

In 1837 William Mount left New York City and returned home to Stony Brook and Setauket on Long Island and remained there for the rest of his life with just the odd trips back to New York. He was content to paint rural scenes and the characters who worked on the farmsteads. He maintained his portraiture work as this was a good source of income. Unlike a number of his contemporaries he showed no inclination to travel to Europe to experience artistic life in London, Paris or Rome. Mount fully captivated the rich European artistic legacy that was imported to the United States. It was through engravings, books and copies of European masterpieces, that Mount received a complete schooling in the academic tradition of art and by doing so became America’s first great genre painter. He lived quite a sheltered life and unlike his brothers, he never married.
When we look at his works of art we are struck by the amount of detail in them. Mount loved detail and worked painstakingly slow to ensure no detail was omitted from the finished work and this resulted in a small number of completed works, believed to be no more than two hundred completed in the thirty years that he painted.

My last featured painting is one of my favourites. It is entitled The Raffle (Raffling the Goose) which William Mount completed in 1837 and is now housed in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. In this work, like a number of his other paintings Mount liked to highlight the social and political issues of the time. Before us we see six men gathered around a table eagerly awaiting the result of an impromptu lottery to see who had won the plump goose which lies in front of them. If you look carefully at the table you will see signs of blood which indicate the bird had recently been killed and plucked. Such lotteries were common in the rural communities of Long Island around this time. The year 1837 was a year of hardship for Americans. The Panic of 1837, as it was known, was the financial crisis in the United States that touched off a major recession that lasted until the mid-1840’s. Profits, prices and wages went down while unemployment went up. Mount alluded to food shortages during this hard time in this painting and what people had to do to survive and put food on the family table. Mount worked on the painting through the winter of 1836 and completed it early in 1837. Mount exhibited the painting that year at the National Academy of Design Spring Exhibition.
In the first part of this William S Mount trilogy I talked about his inventive nature and how he had invented a violin/fiddle which produced a larger volume of noise. In about 1860 Mount designed a portable studio and home on wheels which was drawn by horses. It afforded him the opportunity to drive himself around the area and paint en plein air. He spent much time during his last years in this unique conveyance, but sadly, due to ill health, his painting days were almost over.

William Sidney Mount died on November 19th 1868, at Setauket and is buried in the Presbyterian Church Cemetery.
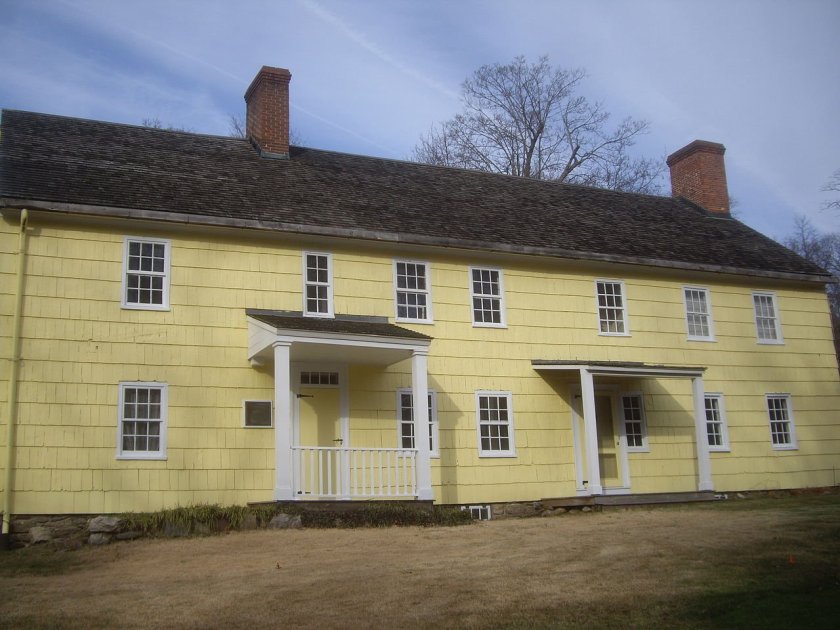

His home and studio, now known as The William Sidney Mount House is one of America’s National Treasures. One of the local elementary schools in The Three Village Central School District, a district in Long Island so named from the older, original “Three Villages” of Setauket, Stony Brook and Old Field, is named after the artist.
There were so many paintings I could have included but these are just a few of my favourites. Besides the usual internet sources I gleaned a lot of my information from an old book I just bought entitled William Sidney Mount by Alfred Frankenstein. The William Sidney Mount House at Stony Brook, Long Island houses numerous works of art by William Sidney Mount and I would be interested to hear from anybody who has visited the museum.