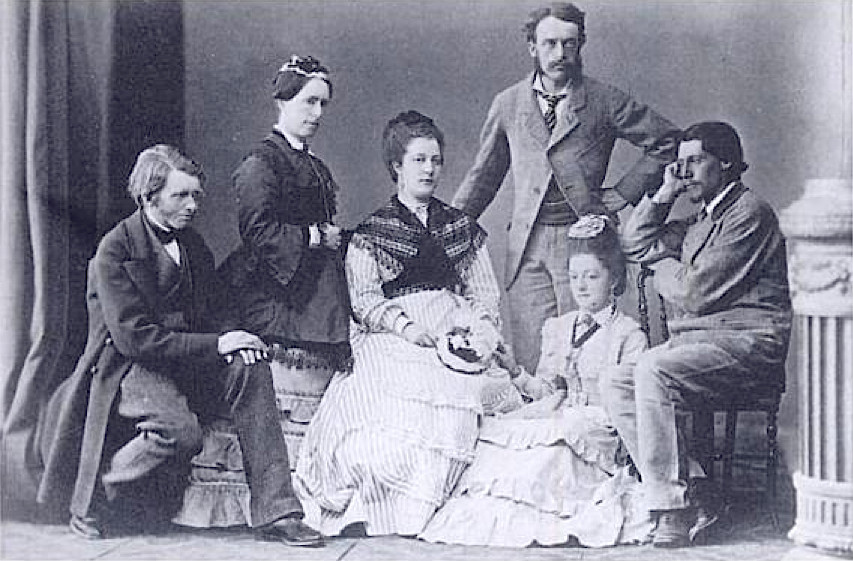
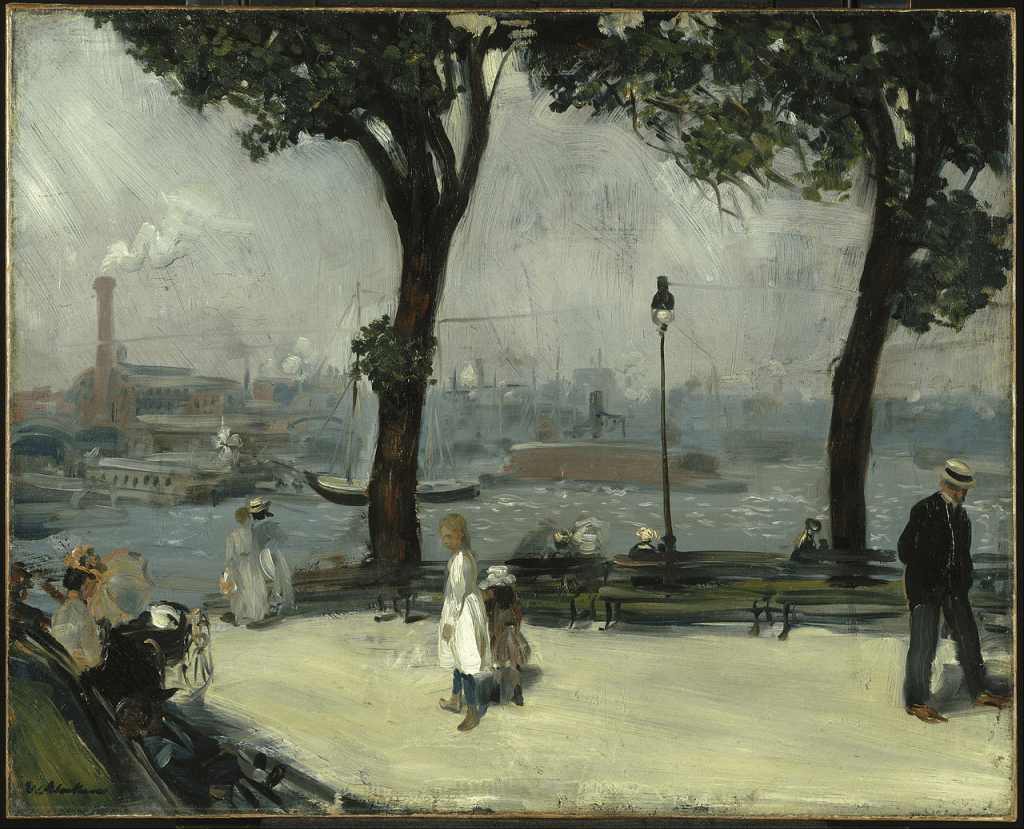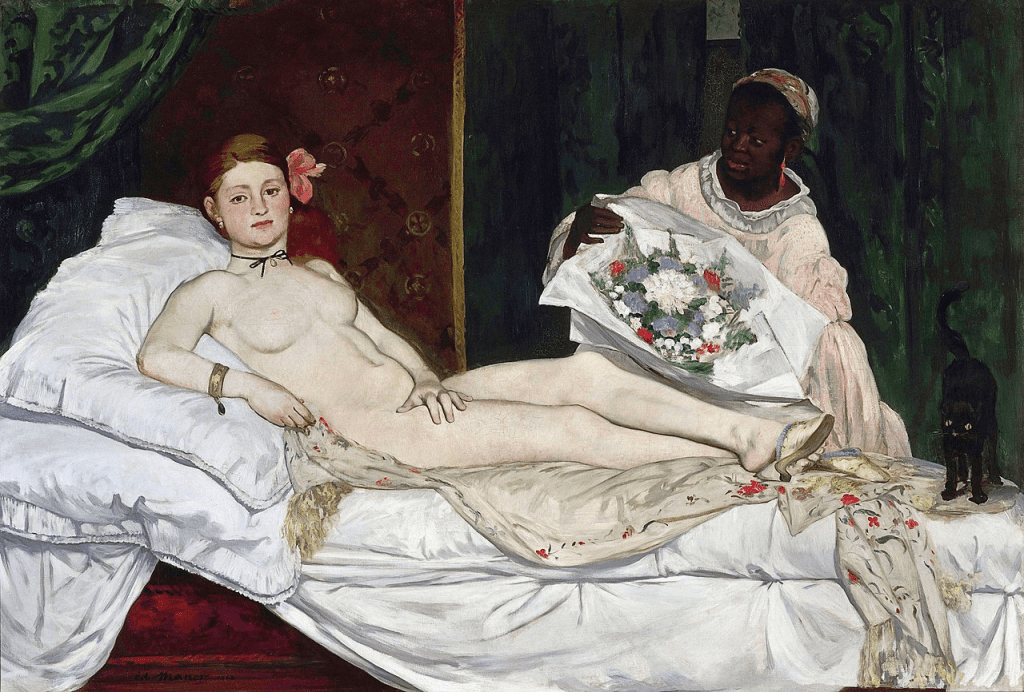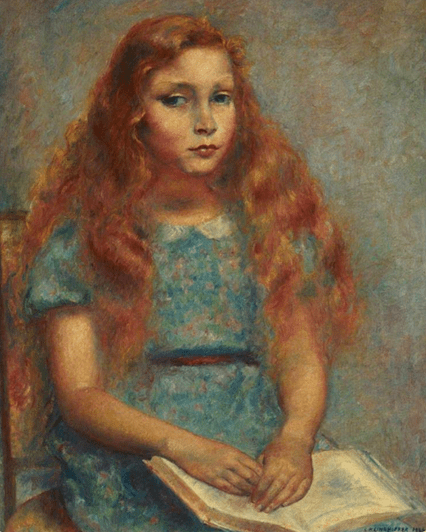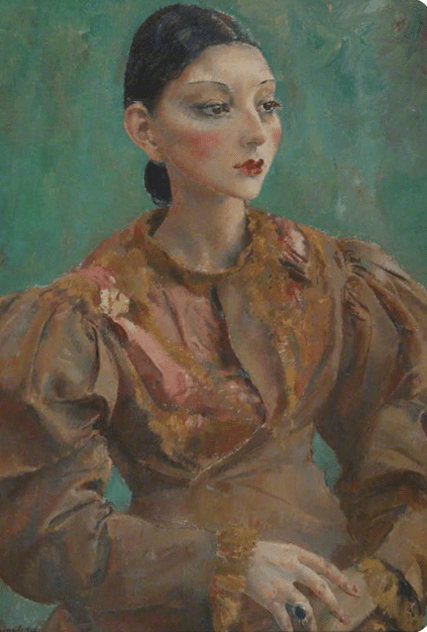My blog today is about a family of artists, the Walton family, a veritable artistic dynasty. The head of the family was Edward Arthur Walton, best known as, simply, E.A.Walton. Walton was born on April 15th, 1860 in Barrhead, a small town in East Renfrewshire, Scotland, thirteen kilometres (8 miles) southwest of Glasgow city centre.
The Artist’s Mother, Elizabeth Balfour Nicolson, Mrs Jackson Walton by Edward Walton (1885)
Edward Walton was one of twelve children of Jackson Walton and his wife Elizabeth Balfour née Nicholson. Jackson was a Manchester commission agent and a skilled amateur painter and photographer. His brother was George Henry Walton, a noted architect, furniture designer and stained glass designer, who worked with Charles Rennie Mackintosh, a renowned Scottish architect, designer, watercolourist and artist.
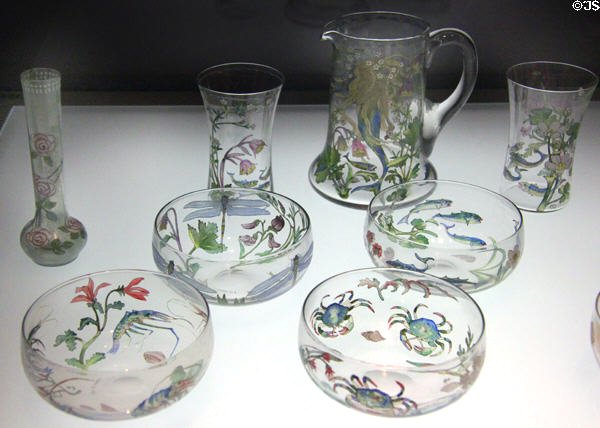

Glassware painted by Helen Walton (1910)
Edward’s sisters, Helen and Constance were also talented artists. Helen Walton was best known for her decorative work in ceramics and glass and as one of the eldest children, Helen became an artistic mentor to her siblings including her brother, Edward Arthur, who was ten years her junior.

Still Life with Roses by Constance Walton
Constance Walton was a much-admired botanical painter. She trained at Glasgow School of Art and became a member of the group known as the Glasgow Girls. This group of women artists and designers pursued different styles and worked in a range of art forms. Many of the women created their own discreet groups while others chose to work alone and although the name of the group was coined by William Buchanan in an essay, he contributed to the catalogue for a Glasgow Boys exhibition held in 1968, many of the women lived and worked outside Glasgow. These female artists became prominent in the late nineteenth century, thanks to the enlightened attitude of Francis Newbery, a painter and art educationist, best known when he was director of the Glasgow School of Art between 1885 and 1917. who set out to enrol men and women equally.

Daydreams by Constance Walton(c.1895)
Day Dreams by Constance Walton is a large watercolour depicting a young girl sitting on steps looking distractedly into the distance. Constance Walton’s figurative paintings are quite rare as after her marriage in 1886 she concentrated on her flower and botanical paintings. This depiction could have been influenced by her brother, Edward’s work of the same name which he completed in 1885.
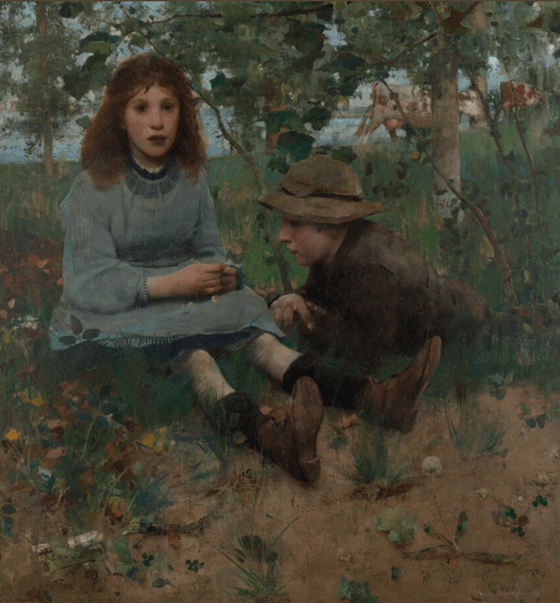
A Daydream by Edward Walton (1885)
Helen and Constance’s brother Edward Arthur Walton was probably the best-known artist of all the siblings

Self portrait by Edward Walton
After completing school and wanting to concentrate on his art he travelled to Germany where he spent two winters at the Dusseldorf Academy of Art before returning to Scotland and enrolling at the Glasgow School of Art in 1878.

Joseph Crawhall by Edward Walton (1884)
At the Glasgow School of Art he became good friends with fellow aspiring painters, James Guthrie and Joseph Crawhall whose sister married Edward’s brother. As we have often seen in various blogs, young artists training at State Academies often became disillusioned and disheartened by the academic training which concentrated on historical painting and high levels of finish. It was for this reason that in many countries the young artists rebelled and set about working to their own agenda. In the case of Edmund Walton and his friends they formed a loose group which became known as the Glasgow Boys who decided that their focus should be on realistic depictions, often of rural subjects, depictions that would illustrate real life, the hard-bitten and candid view of living.
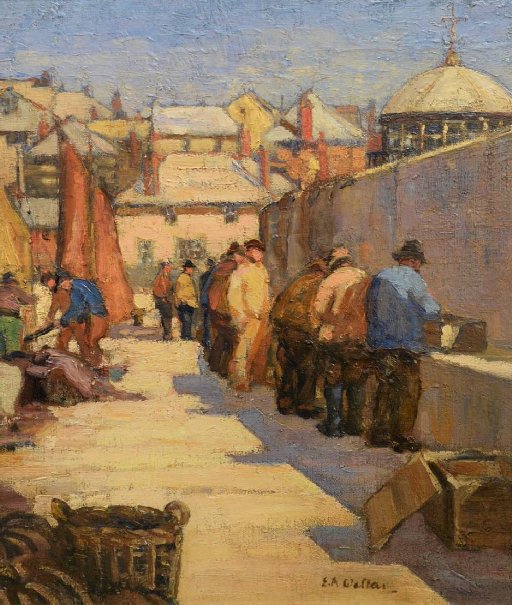

The Harbour Scene, St Ives by Edward Walton
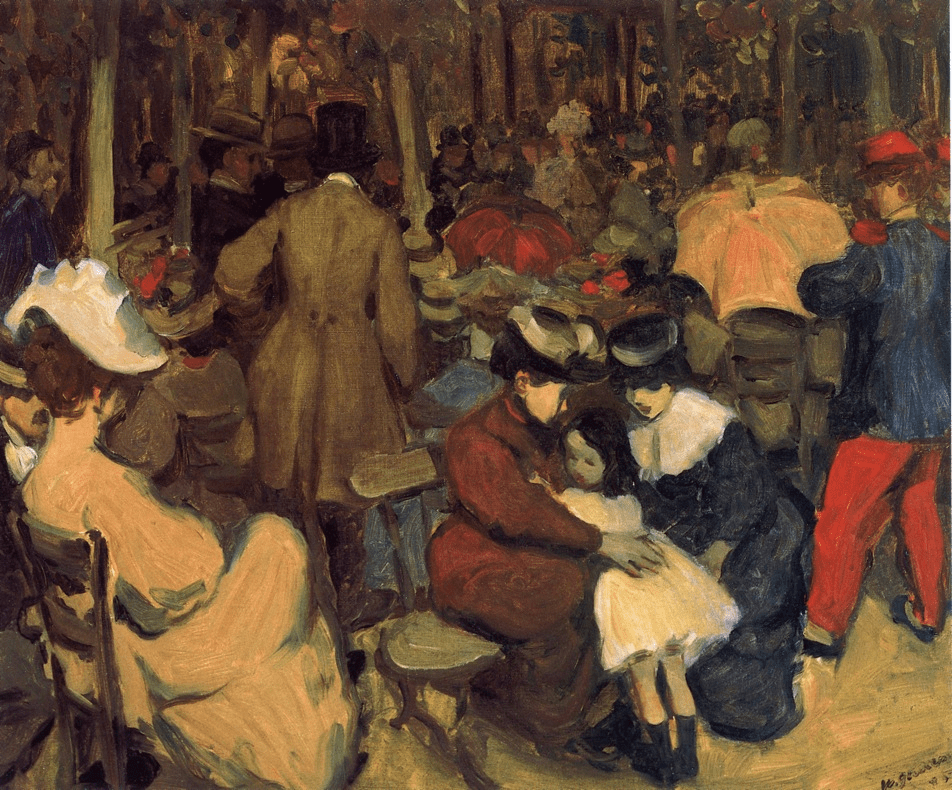
The Glasgow Boys group gained inspiration from the progress in landscape painting in France and sought to take greater notice on the natural effects of light in the open air when setting about painting Scottish rural scenes. The group also took to the French style of en plein air painting when, whilst outdoors, they would paint directly onto the canvas. The painter who had the greatest influence on this group of artists was the French realist painter, Jules Bastien-Lepage whose down-to-earth depictions focused on the real, often, impoverished life that surrounded his village. For all Edmund Walton learnt about art in Dusseldorf and the Glasgow School of Art, nothing compared to the knowledge he gained working alongside his fellow “boys”.

Victoria Road Helensburg by Edward Walton
In 1883, Edward Walton joined James Guthrie, at Cockburnspath, Berwickshire where he honed his talent as a painter in both oil and watercolour in the open air. He also spent time in Helensburgh, an affluent coastal town on the north side of the Firth of Clyde where he completed a series of watercolours depicting the well-dressed affluent residents of this prosperous suburb.

Helensburgh by Edward Walton
His skill as a watercolourist resulted in him being accepted as a member of the Royal Scottish Society of Painters in Water Colours in 1885 and shortly after he became a member of the New English Art Club. In 1894, when he was thirty-four, he moved to London living in Kensington and later Chelsea, where his neighbour and good friend James Whistler lived. Other artistic neighbours were the Irish-born painter John Lavery and Philip Wilson Steer, a British painter of landscapes, seascapes plus portraits and figure studies. Steer was also an influential art teacher and a leading figure in the Impressionist movement in Britain.

Edward Arthur Walton Artist, with his Fiancée Helen Law or Henderson as Hokusai and the Butterfly by Sir John Lavery (1889)
Around 1889 Edward Walton met Helen Law. Love followed and the pair got engaged. To celebrate their engagement the couple attended the Grand Costume Ball, organised by the Glasgow Art Club November 29th 1889. Edward dressed as the Japanese printmaker Hokusai, (an exhibition of his work was on show in Glasgow at the time) while his fiancée’s costume represents the painter Whistler’s signature in the shape of a butterfly. Photographer James Craig Annan took a photograph of the couple. Artist and the couple’s friend, the artist, John Lavery, sketched this portrait of Edward and Helen on the night and presented it to them as a gift for their engagement, which they had announced earlier that evening.

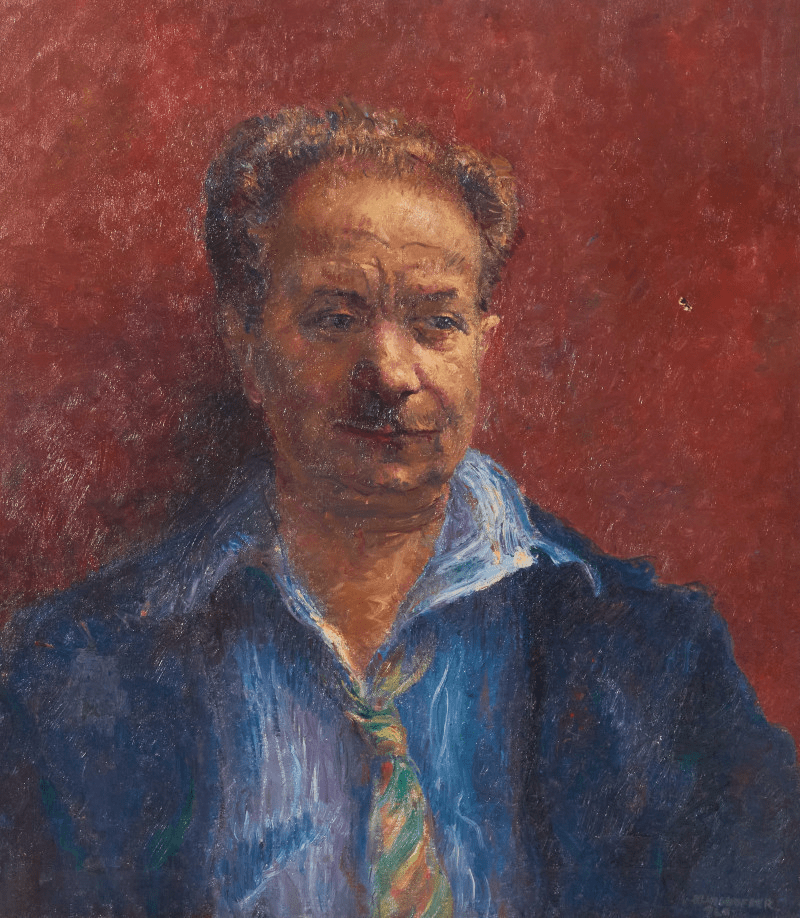
Eric Robertson
Edward and Helen married and went on to have four children, the eldest of whom was their daughter Cecile who was born on March 29th 1891. In 1894, Edward Walton, his wife and two-year-old Cecile moved from Scotland to London. In the summer the Walton family travelled to Suffolk where they rented the Old Vicarage at Wenhaston, which was a few miles from Walberswick, a village on the Suffolk coast, where Frank and Jessie Newbery lived and the two families painted together in the summer. Cecile Walton and Newbery’s daughter Mary became close friends and later both developed strong links with Galloway area of Scotland. The Walton family returned to Scotland in 1904 and took up residence in Edinburgh where Cecile enrolled at the Edinburgh College of Art.

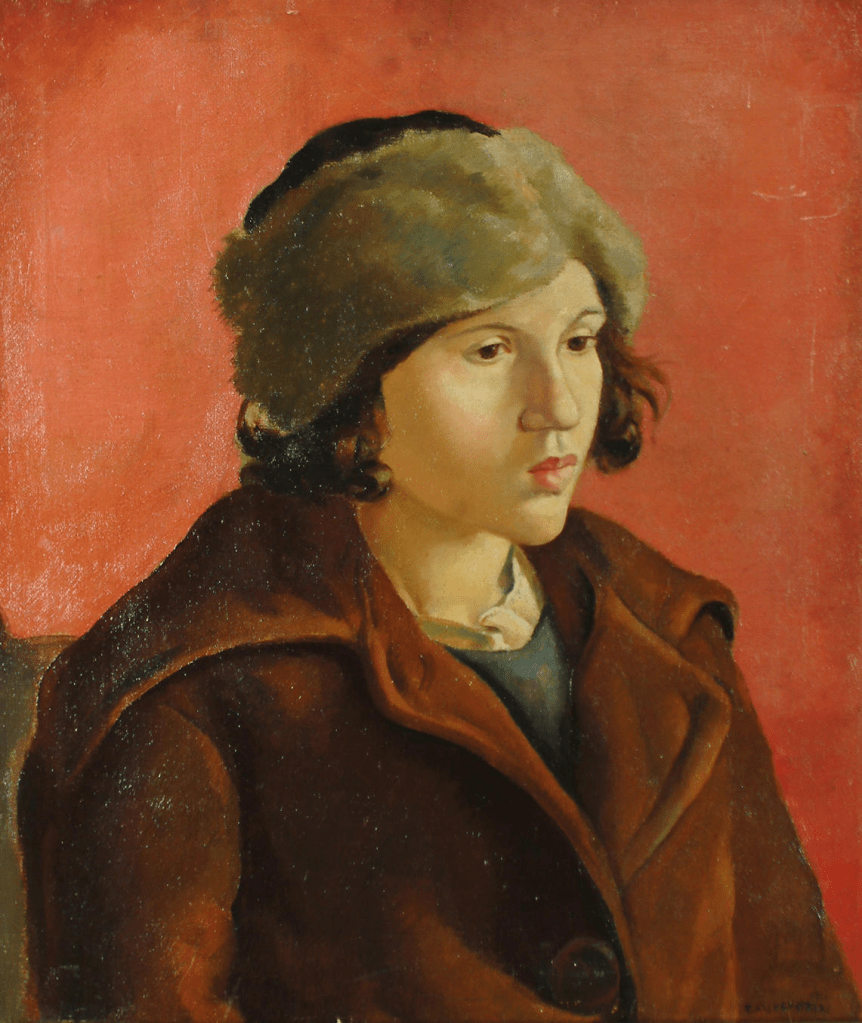
Cecile Walton by Eric Robertson (1922)
She also had private tuition from the Symbolist painter, John Duncan who taught her to appreciate Florentine art of the Renaissance and it was whilst at John Duncan’s house that she met another painter, Eric Robertson. Cecile’s parents were not enamoured with her friendship with Robertson as he had a reputation of being a heavy drinker and a philanderer but despite her parents’ views Cecile and Eric Robertson married in 1914 and their first child, Gavril, was born in February 1915.

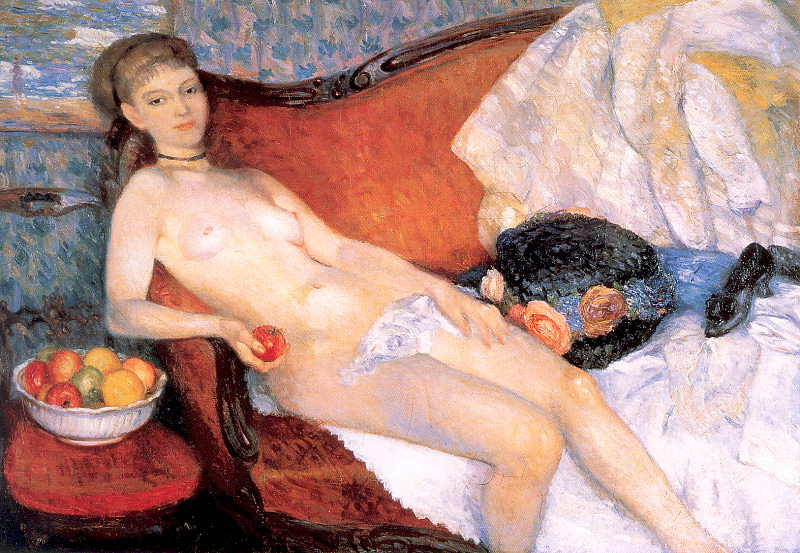
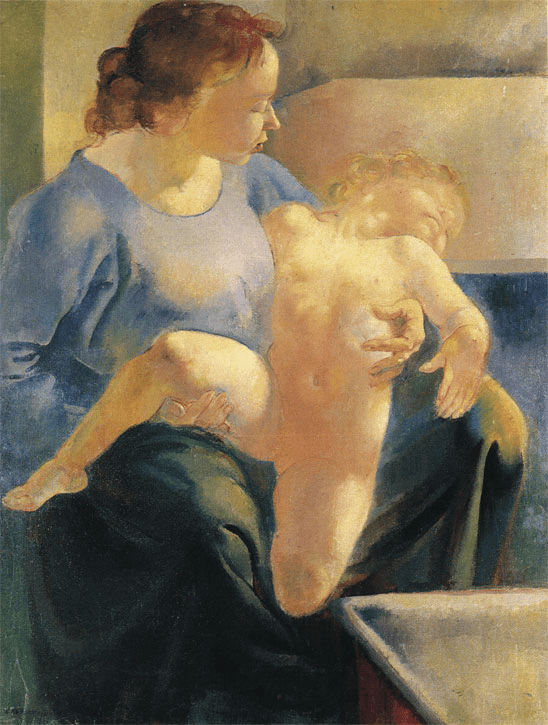
Romance by Cecile Walton (1920)
Cecile and Eric’s second child, another son, Edward, was born in December 1919 and it was shortly after his birth that Cecile started what was to be one of her most famous paintings, Romance. Cecile Walton depicts herself holding up her new-born son, Edward, for intense scrutiny, whilst her elder boy, Gavril, clutches his gollywog doll. Although nowadays the toy is recognised as a racist caricature, they were commonplace in British childhoods until the 1960s. The depiction of mother and baby is usually associated with the Madonna and Child but in Cecile’s painting, the depiction knowingly echoes a well-known impressionist image of a sex worker; Olympia as portrayed by Edouard Manet, and this implies a more troubled attitude to motherhood. The inclusion of carefully placed details such as petals on the floor, and the apple, add to the sense of unease. In the painting we see Cecile, depicted lying half naked in bed holding her new baby son. At the foot of the bed, we see her first-born child Gavril looking on. In an article in the Woman’s Art Journal, Frances Fowle, art historian and curator comments on the painting:
“…The title Romance seems inappropriate and the picture itself has a disconnected feel: the figures seem strangely dislocated, the scene has an almost surreal clarity, and the eye is arrested by the disagreeable greenish hue of the wall. The picture poses questions; even the objects on the table and the discarded rose on the floor invite interpretation. The artist lies stretched out on the bed, naked except for a curious yellow hat and towel wrapped around her hips…”
The thorns on the stem of the rose symbolise the suffering of the virgin and this may, in this case, allude to the suffering of the woman during childbirth. The crushed rose seen on the floor next to the bed is thought to symbolise Cecile’s failing marriage brought on by her husband’s unacceptable habits and his surrender to the demon alcohol. Cecile was not in a good place at this time having to endure her husband’s drunkenness and infidelity. Marriage and subsequent children had also deprived Cecile of her personal freedom and curbed her artistic output, similar to what happened to her mother once she married Edward Walton. The painting was exhibited at the second Edinburgh Group Exhibition in 1920.
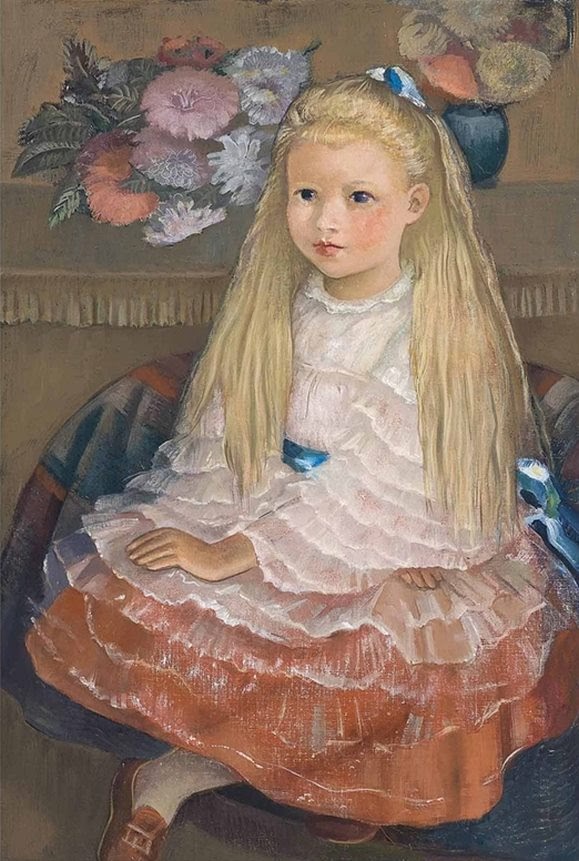

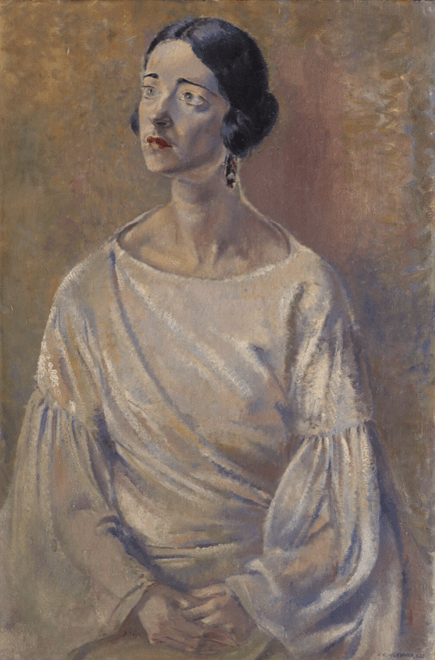
The Favourite Dress by Cecile Walton
Cecile’s marriage to Eric Robertson ended in 1923 due to his unacceptable behaviour and Cecile, along with her two sons, moved out of the family home and went to live with her friend Dorothy Johnstone. Her divorce was finalised in 1927. In 1924 Dorothy and Cecile staged a joint exhibition of their work. However since the ending of her marriage and subsequent divorce Cecile’s artistic output decreased and her artistic career began to fail.

Deserted Ferry by Cecile Walton (1949)
Eric Robertson’s artistic career also broke down after his separation from Cecile, and he eventually capitulated to alcohol. In 1923, following the failure of his marriage he moved to Liverpool and by the early 1930s, he was largely forgotten as a painter. Cecile Walton remarried in November 1936. Her second husband was to Gordon Gildard, a BBC producer, and she moved to Glasgow to be with him. Unfortunately, their marriage was short-lived and the couple divorced in 1945. Cecile went to live the rest of her life in the vibrant fishing port and artists’ town of Kirkcudbright, within Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland.

Cecile Walton died in Edinburgh on April 23rd 1956, aged 65.