
Finnish nationalism as far as language was concerned became prominent in the nineteenth century and was a consequence of the dominance of the Swedish language in Finland’s cultural and political life. With the Russian conquest of Finland in 1809, the Russian government generally supported Finnish linguistic nationalism, as they believed it would alienate the Finns from Sweden and thereby ensure that close ties with or even the integration with Sweden would be halted. This Finnish-language nationalism known as the Fennoman movement soon developed into the most powerful political force in nineteenth century Finland and was summed up by a popular phrase of the time:
“…We are no longer Swedes; we cannot become Russians; we must be Finns…”

Axel Gallén was a fervent nationalist and a follower of the Fennoman movement. It was this passion which was to alter the course of both his personal and artistic life. His interest in Finnish nationalism brought him in contact with Kaarlo Slöör who was a poet, translator, and editor in chief of the Finnish Official Journal and a staunch Finnish nationalist. Through this friendship he first met Slöör’s daughter Mary Helena, a talented concert pianist, and one of Kaarlo’s seven children. Axel Gallén had also attended school with two of her brothers, Karl Rafael, and Fredrik.

Mary had a happy childhood living within a financially secure environment. Tragedy struck the family when Mary was ten years old with the death of her brother Otto in 1878 after suffering from diphtheria and the following year another of her brothers, Karl Artur, died of pneumonia.

Axel and Mary fell in love as can be seen in letters between the couple. In a letter dated May 29th, 1887, a bashful Axel wrote to Mary:
“…Most loved Mary, what you need is when You, as you say, you want to, but you will not be able to be kind to me, to keep me a little bit. In the last some you call yourself ‘ as a friend ‘. Do not know, therefore, that, you my feelings towards you is not friendship, but love. I love you with all my soul and I cannot say it to you… “
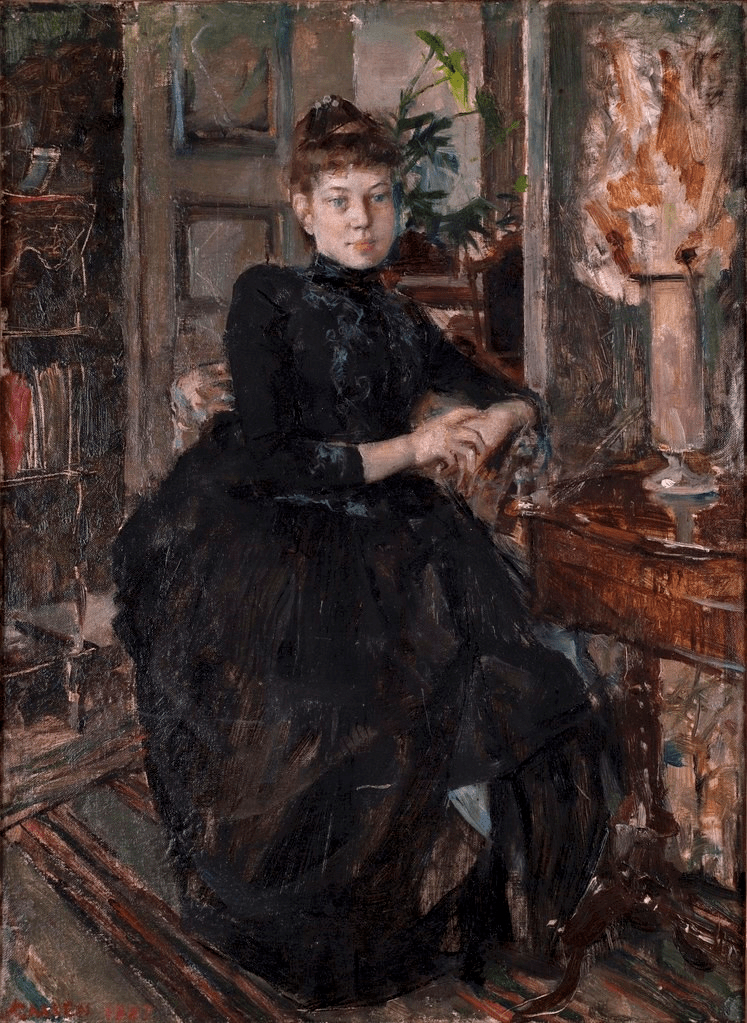
In 1887, Axel painted a portrait of his future wife, Mary, entitled Mary Slöörin muotokuva.
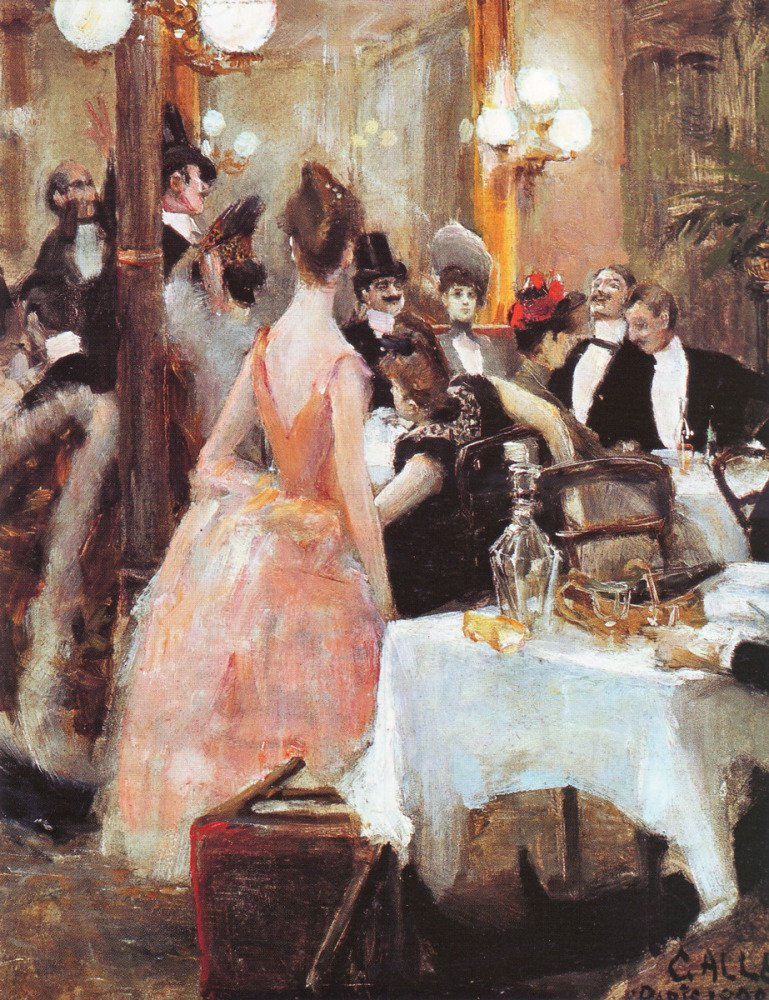
Gallén lived in Paris from the autumn of 1887 to the summer of 1889 during which time he continued at the Académie Julian as well as working at the Atelier Cormon from 1887 to 1888. His Paris paintings, such as Parisian Café and After the Opera Ball, recall the heady days of Paris Society.

Axel and Mary secretly got engaged in spring 0f 1887 during his visit to Finland and before returning to his artistic studies in Paris. Once Axel’s paintings began to sell and his financial situation had improved, the couple married at the home of Mary’s parents on May 20th 1890. They went on honeymoon to Kuhmo in the south-east of Finland. Axel completed a number of paintings during the honeymoon including Marie Gallén at the Kuhmoniemi-bridge.

There the couple were joined by Swedish artist, Count Louis Sparre, whom Axel had met whilst in Paris. The two men also made a couple of week-long trips to northern Russian Karelia. Axel Gallén was organising himself to paint a new version, commissioned by the government, of his Aino triptych, and whilst in Karelia he hoped to find models and themes for his work. He also planned to enter a new competition, set by the Savo-Karelia Students’ Association to provide illustrations for the Kalevala, an epic poem, consisting of 22,795 verses, divided into fifty songs, compiled by Elias Lonnrot, derived from Karelian and Finnish oral folklore and mythology. It is regarded as the national epic of Karelia and Finland and is one of the most significant works of Finnish literature.

It was during his time studying at the Atelier Cormon in 1888 that Axel started on his famous triptych The Legend of Aïno. For him it was an exciting time. It was the time of the Young Finland, Karelianism and the beginnings of the Kalevala Karelia romanticism.
The tragic tale of Aino was largely created by Elias Lönnrot, collector and writer of the stories behind the Kalevala saga. Myths are a reflection of the society from which they spring, in this case where parents and family decide the marital fate of a girl. The Aino triptych is still very capable of arousing discussions and emotions.
Aino,meaning “the only one”, is a figure in the Finnish national epic Kalevala. It tells of her being the beautiful sister of Joukahainen. Her brother, having lost a singing contest to the storied Väinämöinen, promised Aino’s “hands and feet” in marriage if Väinämöinen would save him from drowning in the swamp into which Joukahainen had been thrown. Aino’s mother was pleased at the idea of marrying her daughter to such a famous and well born person, but Aino did not want to marry such an old man. Rather than submit to this fate, Aino drowned herself (or ended up as a nix – a water being). However, she returned to taunt the grieving Väinämöinen as a salmon.
Gallén painted the story of Aino in three scenes. However, they are not presented chronologically. In the left-hand panel Aino wrenches the string of pearls from around her neck and rejects Väinämöinen’s proposal. In the central panel, Väinämöinen brings up a strange catch when he goes fishing, which he initially recognises as Aino. She mocks Väinämöinen and leaps into the water. In the right-hand panel Aino meets the frolicking water nymphs, the maids of the water goddess Vellamo. In the next stage of the saga, Aino swims to a rock from where she sinks with it into oblivion beneath the waves, but this is not depicted.
Gallén based his work on the Kalevala, and its text didn’t hold back on criticising men, including Väinämöinen. The story of Aino is one of the great tragedies. The girl’s mother bitterly regrets her attempts at marrying off her daughter, against the girl’s wishes. Väinämöinen, on the other hand, “cries evening long, cries morning long, at night he cries still more…”
Aino gets her revenge. She mocks Väinämöinen, who imagined her “wiping his little kitchen, cleaning his floors” and jeers that the “feeble-minded” old man, doesn’t even recognise “Vellamo’s watery maid, the only child of Aho”. This is what Gallén chose as the central discussion point behind his triptych.

After their honeymoon the Axel and Mary moved into rented accommodation in Malmi, a suburb of Helsinki. In the summer of 1891 the couple had their first child, a daughter, Impi Marjatta. Three years later Axel and his family moved to a home he had built in Ruovesi Kalela.

In early 1895 Gallén travelled to Berlin where he took part in a joint exhibition with the Norwegian painter Edvard Munch. Axel completed a portrait of Munch that year.

Axel also worked on a number of drawings for the new Berlin arts and literary magazine, Pan. His stay in Berlin was brought to an abrupt when he received a telegram informing him of the death of his four-year-old daughter Impi Marjatta at their partly-completed home, Kalela, in Ruovesi. She had died of diphtheria.

During 1895 ‘Kalela’ was finally completed. It was built of logs hewn lengthwise on opposite sides, and it became one of the most famous products of national-romantic architecture. Axel and Mary’s second child, a daughter, Kirsti, was born in 1895 and three years later their third child, a son, Kaius Jorma was born. Mary helped Axel in his studio often making and decorating the paintings, and more mundane jobs such as cleaning and washing brushes and palettes. She would also practice wood cutting and gypsum moulding and helped him in the burning of glass stained glass. She often acted as his model.

Axel was now starting to paint using tempera rather than oils and in 1896 he completed a portrait of his mother.

The following year more paintings in tempera illustrating the Kalevala followed including Joukahaisen kosto (‘Joukahainen’s Revenge’)

and Velisurma (‘Fratricide’)

In 1900 Axel Gallén was commissioned to paint frescoes for the Finnish Pavilion at the Paris World Fair. One of the frescoes was Ilmarinen Ploughing the Field of Vipers. Ilmarinen, the Eternal Hammerer, blacksmith and inventor was a character in the epic poem, Kalevala, and is a god and archetypal artificer from Finnish mythology. Axel, a staunch follower of Finnish nationalism, took the opportunity to make the depiction very political as he painted one of the vipers in the fresco as wearing the Romanov crown, and the process of removing the vipers from the field was a clear reference to his wish for an independent Finland.

In 1905 Axel Gallén produced one of his most famous works, Lake Keitele. It is one of the artist’s most eloquent and haunting renditions of the subject and it is still the only painting by him in a public collection in Great Britain. It is housed in the National Gallery in London. Strangely the artist painted four versions of the picture between 1904 and 1906. The year, 1904, had not started well for Axel. He and his wife had been travelling around Europe and during their stay in Granada in southern Spain Axel contracted malaria. He and his wife returned to Finland so that he could recuperate. The couple rented a lodge in Konginkangas on the shores of Lake Keitele which was more practical than returning to his remote studio in Ruovesi. The painting depicts the lake’s scenic shores and crystalline waters which are bathed in brilliant northern light.

Through finnicization, the changing of one’s personal names from other languages (usually Swedish) into Finnish, Axel Waldemar Gallén officially changed his Swedish family name to Akseli Gallén-Kallela in 1907 and from then on always signed his paintings with his Finnish name. However, his wife Mary kept her name as Mary Gallén.

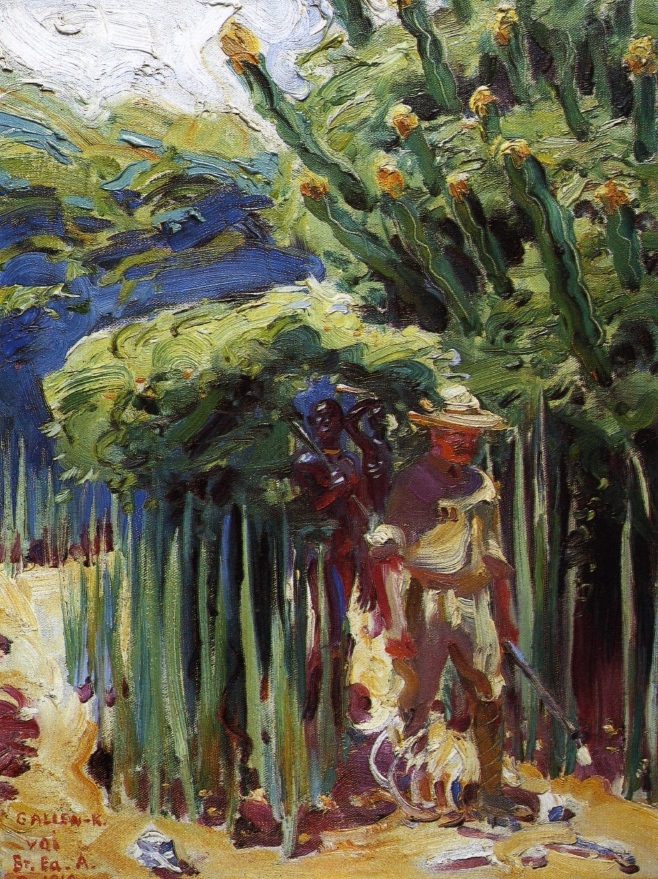
In 1909, Gallen-Kallela moved with his family to the British East African city of Nairobi, and there he painted more than 150 expressionist oil-paintings and collected many East African artefacts. However, the family became homesick and Akseli realised once again that his main artistic inspiration was Finland. The family moved back to Finland in 1911 and between 1911 and 1913 he designed and built a studio and house at Tarvaspää, which lay about 10 km north of the centre of Helsinki.

The collapse of the Russian Empire in 1917 caused a power vacuum in Finland, and civil war erupted between the left-wing labour movement and the conservatives. In 1918, Akseli Gallen-Kallela and his twenty-year-old son Jorma took part in the fighting at the front, in the Finnish Civil War on the side of the conservatives under the regent, General Mannerheim.

In the aftermath of the civil war, the Finns went from being under Russian control to being within the German sphere of influence and the German rulers had a plan to establish a German-led Finnish monarchy. However, this idea was shelved with the defeat of Germany in World War I and finally Finland emerged as an independent, democratic republic. Finally, a nation which had been so divided came together and Finnish society was reunited through social compromises based on a long-term culture of moderate politics and religion and the post-war economic recovery.

From December 1923 to May 1926, Akseli Gallen-Kallela lived in the United States, where an exhibition of his work toured several cities, and where he visited the Taos art-colony in New Mexico to study indigenous American art. In 1925 he began the illustrations for his “Great Kalevala”. This was still unfinished when he died of pneumonia in Stockholm on March 7th 1931, while returning from a lecture in Copenhagen. He was 65 years of age.
Besides Wikipedia, much of the information about the artist was gleaned from a number of websites, including:
Ateneum Art Museum: https://ateneum.fi/nayttelyarkisto/akseli-gallen-kallela-150-years/?lang=en
Kallela Museum: http://www.gallen-kallela.fi/en/akseli-gallen-kallela-and-tarvaspaa/akseli-gallen-kallelas-lifespan-and-timeline/
National Biography of Finland: https://kansallisbiografia.fi/english/person/3194

Fantastic. I love the way you combine history and personal stories with the artwork. Thank you and God bless.