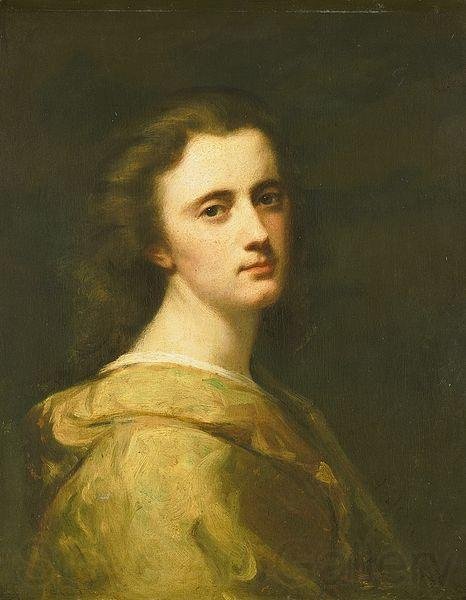
In my previous blog regarding the Dutch painter Thérèse Schwartze I mentioned that one of her early art tutors was Jean-Jacques Henner, the French painter famed for his portraiture. Today I am going to focus on his life and his many artworks.
Jean-Jacques Henner
Henner was born on March 5th 1829 at the Alsatian town of Bernwiller. Henner came from a family of Alsatian farmers who had settled in Bernwiller in the Haut-Rhin. He was the youngest of six siblings of George Guillaume Polycarpe Henner and Madeleine Henner (née Wadel). He had two older sisters, Maria Anne and Madeleine and three older brothers, Séraphin, Grégoire and Ignace. He grew up in this farming community, but despite their modest financial situation, his parents sent him to the College of Altkirch where he studied drawing. His teacher was Charles Goutzwiller who noticed his rapid progress and encouraged him to move to Strasbourg and study at the studio of Gabriel-Christophe Guérin. His artistic studies continued when he enroled at the Ecole des Beaux-Arts in Paris as a pupil of Michel-Martin Drolling, a neoclassic French painter noted especially as a history painter and portraitist. In 1851 he was tutored by another French artist, François-Édouard Picot, famed for his mythological, religious and historical paintings.
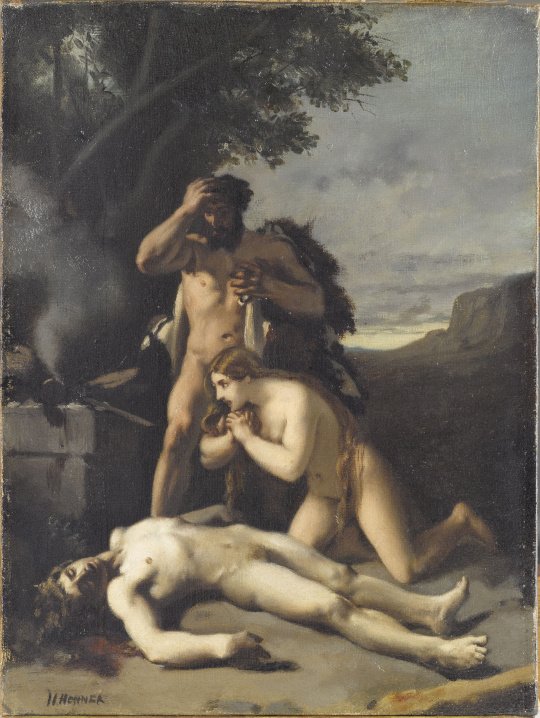

Adam and Eve find the Body of Abel by Jean-Jacques Henner (1858)
In 1848, he entered the École des Beaux Arts in Paris and in 1858 after two failed attempts he won the coveted Grand Prix de Rome award, which was a French scholarship for arts students. His submission was his painting entitled Adam and Eve find the Body of Abel. The prize for the winner was a bursary that allowed them to stay at the Villa Medici in Rome, for three to five years at the expense of the state. The painting can be seen at the Musée d’Orsay.

Mountains on the Outskirts of Rome by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1861)
During his five-year stay in Rome, he was guided by Jean-Hippolyte Flandrin, a French Neoclassical painter. Like many artists, Henner was captivated by Italy and spent many hours in museums reproducing the works of the painters that he respected. He also had plenty of time during his five-year stay to travel around the country, visiting Florence, Venice and Naples in which time he completed a number of small landscape paintings. His works at that time showed his appreciation of past masters and it was Titian and Correggio who influenced him the most. In 1864 Henner returned to Paris and brought back copies of works by masters and a number of luminous landscapes.

Rome from the terrace of the Villa Medici by Jean-Jacques Henner (1860)
During those five years in Rome Henner painted this work at the Villa Medici where he stayed between 1859 and 1864. This is not simply a view of the Eternal City as observed from the villa. Once he had painted the garden, Henner then populated the terrace with groups of what he believed were “typical” characters, which he had often seen in real life and are simply identifiable by their clothes, monks, peasants, and elegant ladies. All are depicted in front of the classical panorama of the city, in which one can see the silhouette of Saint Peter’s Basilica in the background.

Masure dans la campagne de Rome (Dilapiated House in the Countryside of Rome) by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1863)
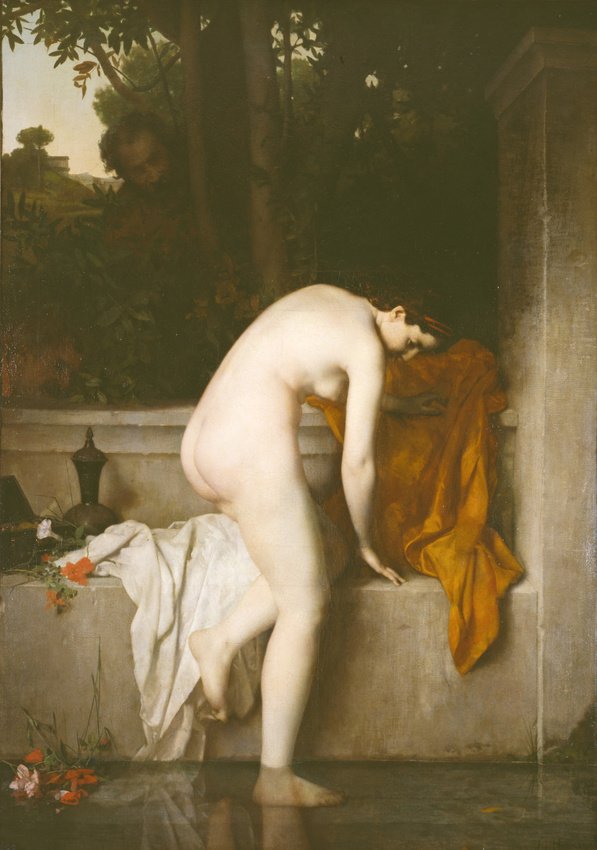

La Chaste Suzanne by Jean-Jacques Henner (1864)
Henner had his painting Bather Asleep exhibited at the Salon in 1863 and at the following year’s Salon his painting La Chaste Suzanne was exhibited. The Biblical episode depicting Suzanne bathing was a popular one for painters and it was above all an opportunity for various artists to paint a beautiful nude. Jean-Jacques Henner sent back his version to the French Academy which he completed whilst in his last year of his residence at the Villa Medici in Rome. For Henner, this was a compulsory exercise, supposed to demonstrate the student’s progress and their skill in execution, and for the Academy to see if their prize winner was advancing artistically.

Sacred Love and Profane Love by Titian (1514)
Henner almost certainly took his inspiration from respected examples left by the great masters’ depiction of nudes which he had seen whilst in the Italian capital. It is thought that Henner was influenced Titian’s 1514 painting entitled Sacred Love and Profane Love which was at the Galleria Borghese in Rome. Henner’s work was not well-received and was harshly criticised for the heaviness and lack of graciousness in the model’s body. It was also criticised for the artificiality of the subject which although being put forward as a history/biblical painting offered little more than a depiction of a bather. However the propensity of ridding any narrative self-justification in painting the nude, and so giving it as a subject in itself, was becoming more common in the work of many contemporary artists, such as Courbet.

Séraphin Henner (brother) by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1881)
Grégoir Henner (brother) by Jean-Jacques Henner (1889)
While a student in Paris Henner was particularly interested in portraiture, and during his frequent visits home to Alsace he would complete many portraits of his family as well as local dignitaries and scenes of Alsatian peasant life.

Eugénie and Jules Henner by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1865)
Eugénie and Jules were two of the three children of his brother, Séraphin and his wife, Madeleine. Henner was very close to his nephew and niece and he paid for violin lessons for Jules and piano lessons for Eugenie when they were little. Henner had no children of his own, and on his death, he bequeathed them all that he possessed. Here, Eugénie and Jules are depicted together in their childhood.
Paul Henner by Jean-Jacques Henner (before 1867)
A rather sad portrait. Paul Henner was the third child of Séraphin and Madeleine Henner. He was born in 1860, but sadly died seven years later.

Byblis by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1870)
In 1864 Henner returned to France and exhibited with great success at the Paris Salon between 1865 and 1903. During his early days back in France his works were of quasi-mythological subjects, such as his 1867 work entitled Byblis, which was exhibited at the 1867 Salon.
Jean-Jacques Henner in his Paris studio at 11 place Pigalle
Jean-Jacques Henner lived in rue La Bruyère and his studio was at 11 place Pigalle, where he lived from 1867.

L’Alsace. Elle Attend (Alsace, She Waits) by Jean-Jacques Henner (1871)
Jean-Jacques Henner’s birthplace was the region of Alsace and this north-east area of France borders Germany. With the defeat of France in the Franco-Prussian War in 1871, Alsace and northern Lorraine were annexed to the new German Empire. At the conclusion of the First World War, the defeat of Germany, and the Treaty of Versailles, Alsace once again came under French control. In 1940, during the Second World War Alsace–Lorraine was occupied by Germany during the Second World War. Although it was never formally annexed, Alsace–Lorraine was incorporated into the Greater German Reich. With the defeat of Germany in 1945 Alsace returned to French rule. Henner’s 1871 painting entitled L’Alsace. Elle Attend had political overtones. It depicts a young Alsatian woman in mourning and is a political comment on the German annexation of the province after the Franco-Prussian War. The patriotic image was very popular and achieved a wide circulation when it was engraved by Léopold Flameng.
L’Alsace. Elle Attend meaning Alsace, she awaits, was commissioned on the initiative of Eugénie Kestner, a member of the Thann industrial family from Alsace. On completion it was given Léon Gambetta, a French lawyer and republican politician, who was one of the fiercest opponents of the relinquishment of the Alsace-Lorraine region to the new German Empire following the war of 1870. Following the defeat of France by the Prussian armies a sense of fervent and heightened patriotism followed. Henner’s painting quickly became looked upon as a symbol of Alsace’s suffering, a pain shared by the painter who was very attached to the region of his birth. The painting depicts a young Alsatian woman in mourning, unassuming but gracious.

Donna sul divano nero (Woman on Black Divan) by Jean-Jacques Henner (1869)
At that time, Henner had assumed a naturalistic style which can be seen in his painting entitled Woman on a Black Divan, which was exhibited at the Salon of 1869 and now is housed at the Mulhouse, Musée des Beaux-Arts. A smaller version of this painting also included a rosette in the red, white and blue colours of France, pinned onto the traditional black Alsatian bow, gives the painting its patriotic significance without being pompous or anecdotal.
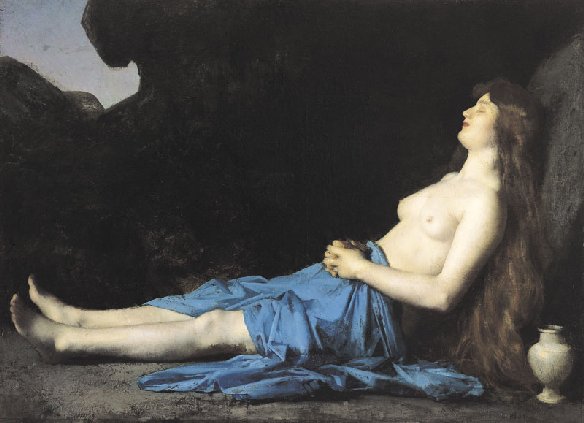

Magdalene in the Desert by Jean-Jacques Henner (1874)
After 1870 Henner’s entire work became a deliberation on the theme of death in various appearances. There were the depictions of Mary Magdalene in what became known as the Magdalene Series, such as Magdalene in the Desert, which was exhibited at the 1874 Salon, and Magdalene Weeping, which he completed in 1885.

Die Magadalena by Jean-Jacques Henner (Exhibited at the 1878 Salon)

La Magdaleine by Jean-Jacques Henner
Henner complted many more Magdalene paintings.

The Dead Christ by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1884)

Jesus at the Tomb by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1879)
There was also a number of works in Henner’s Dead Christ series with paintings such as Jesus at the Tomb, which was exhibited at the 1879 Salon and is now part of the Musée d’Orsay collection and the painting entitled Dead Christ which was exhibited at the 1884 Salon and now hangs at the Musée Beaux-Arts in Lille.

Portrait of Madame Laura Leroux by Jean-Jacques Henner
Jean-Jacques Henner will best be remembered for his portraiture which would provide him with financial stability. During his lifetime he completed many portraits of his family and famous people like his Portrait of Madame Laura Leroux. Laura Leroux-Revault was a French artist and painter. Her first teacher was her father, the painter Louis Hector Leroux and she later trained at the Académie Julian art school in Paris. She also trained under Jules Lefebvre and in Jean-Jacques Henner’s studio. The two artists were friends of her father.

Portrait of Jean-Gaspard-Félix Laché Ravaisson-Mollien by Jean-Jacques Henner (1889)
Another famous person to be immortalised by Henner was Jean-Gaspard-Félix Laché Ravaisson-Mollien, a French philosopher, said to be France’s most influential philosopher in the second half of the nineteenth century.

The Reader by Jean-Jacques Henner

La comtesse Kessler by Jean-Jacques Henner (c.1886)
Henner’s love of portraying nudes in historical or mythological settings was not his only love. He had a passion for the colour red and of portraying women with red hair !

Woman in Red by Jean-Jacques Henner

Les Naïades by Jean-Jacques Henner (1861). Painted for the Soyers’ dining room, 43 rue de Fauborg Saint-Honoré. Paris.
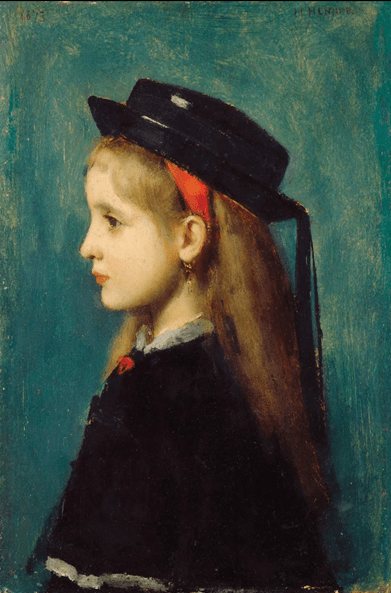
Alsatian Girl by Jean-Jacques Henner
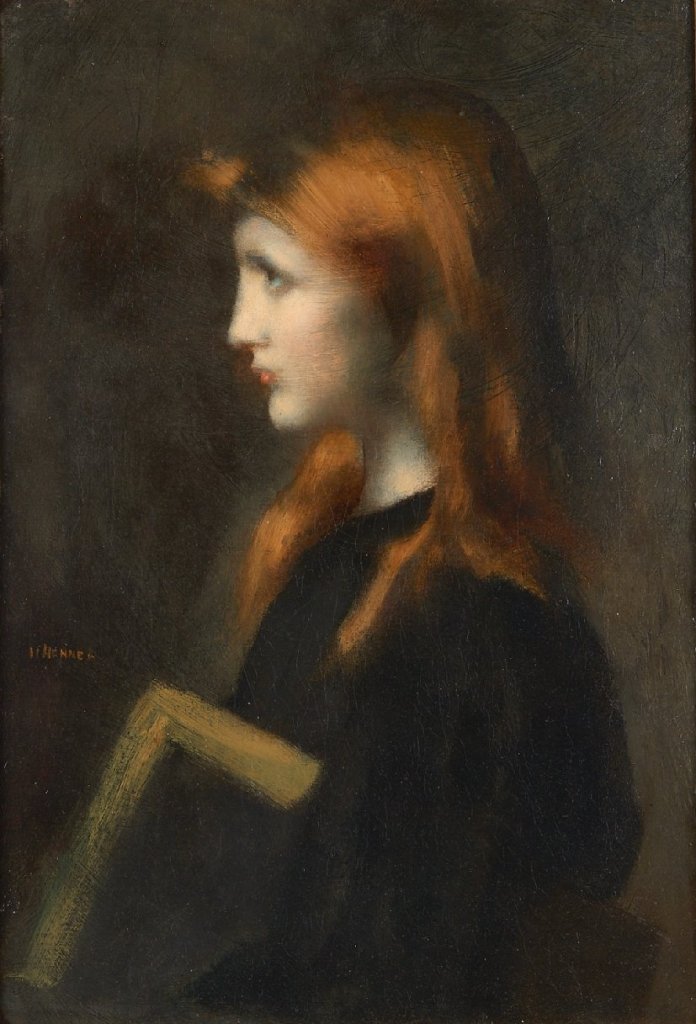

L’Ecoliere by Jean-Jacques Henner
Over the years Henner tutored many aspiring painters. Between 1874 and 1889 he taught at what was termed “the studio of the ladies”, which he organized with Carolus-Duran, during the time when women were not allowed entry to the École des Beaux-Arts. Some of these students also served as his models such as Dorothy Tennant, Suzanne Valadon and Laura Leroux-Revault, daughter of his close friend Hector Leroux; Henner’s full-length portrait of Laura Leroux (shown earlier) is now at the Musée d’Orsay having been shown at the Paris Salon of 1898 and purchased by the French State.
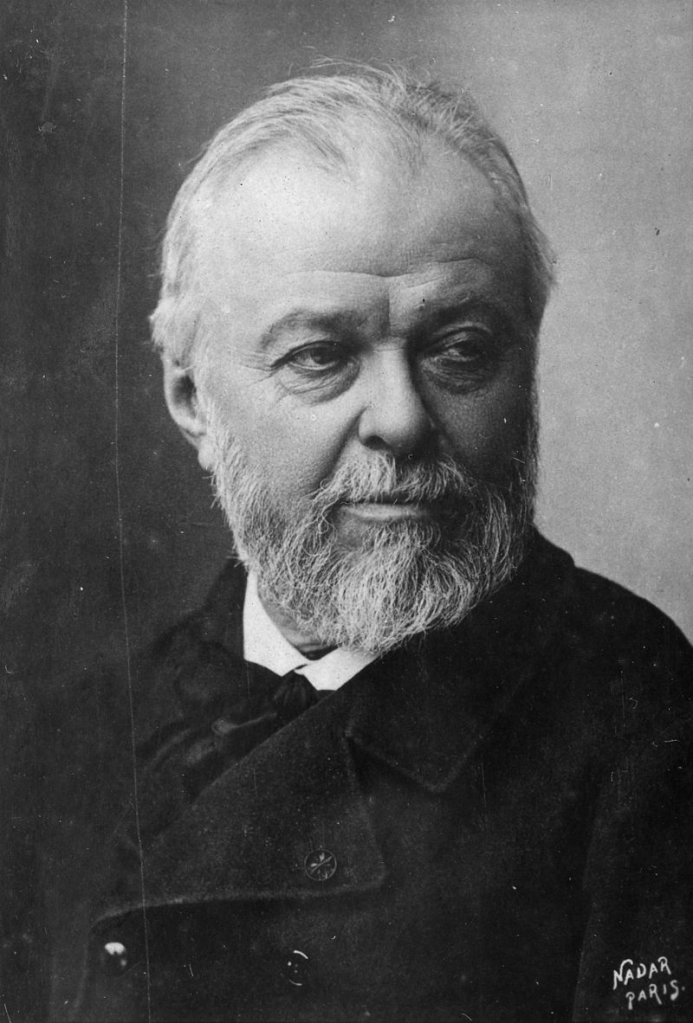
Jean-Jacques Henner (Photograph by Nadar c.1900)
Jean-Jacques Henner died in Paris on July 23rd 1905 aged 76.